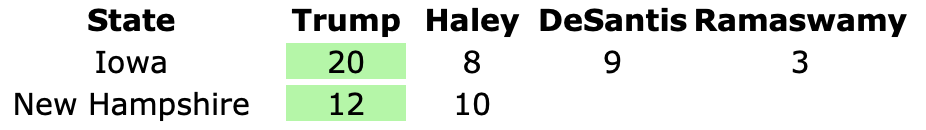
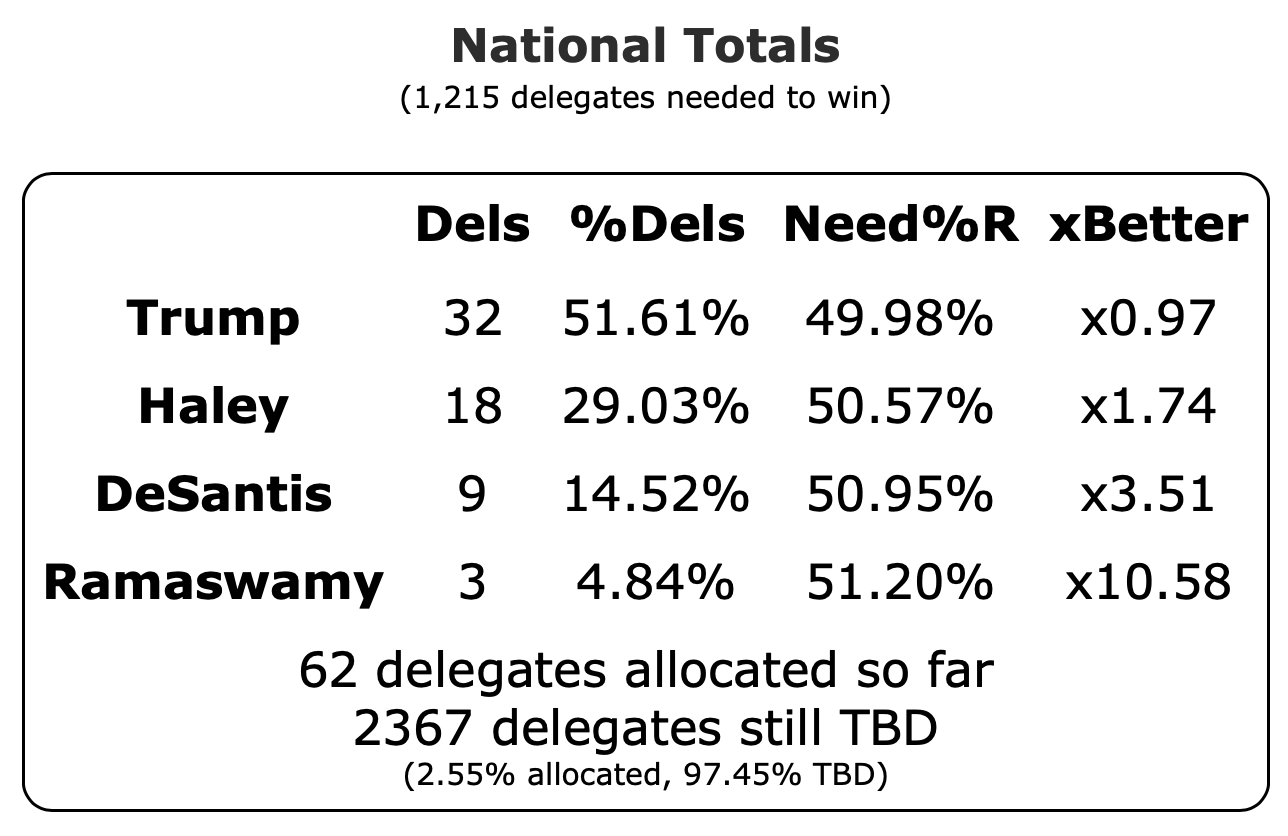
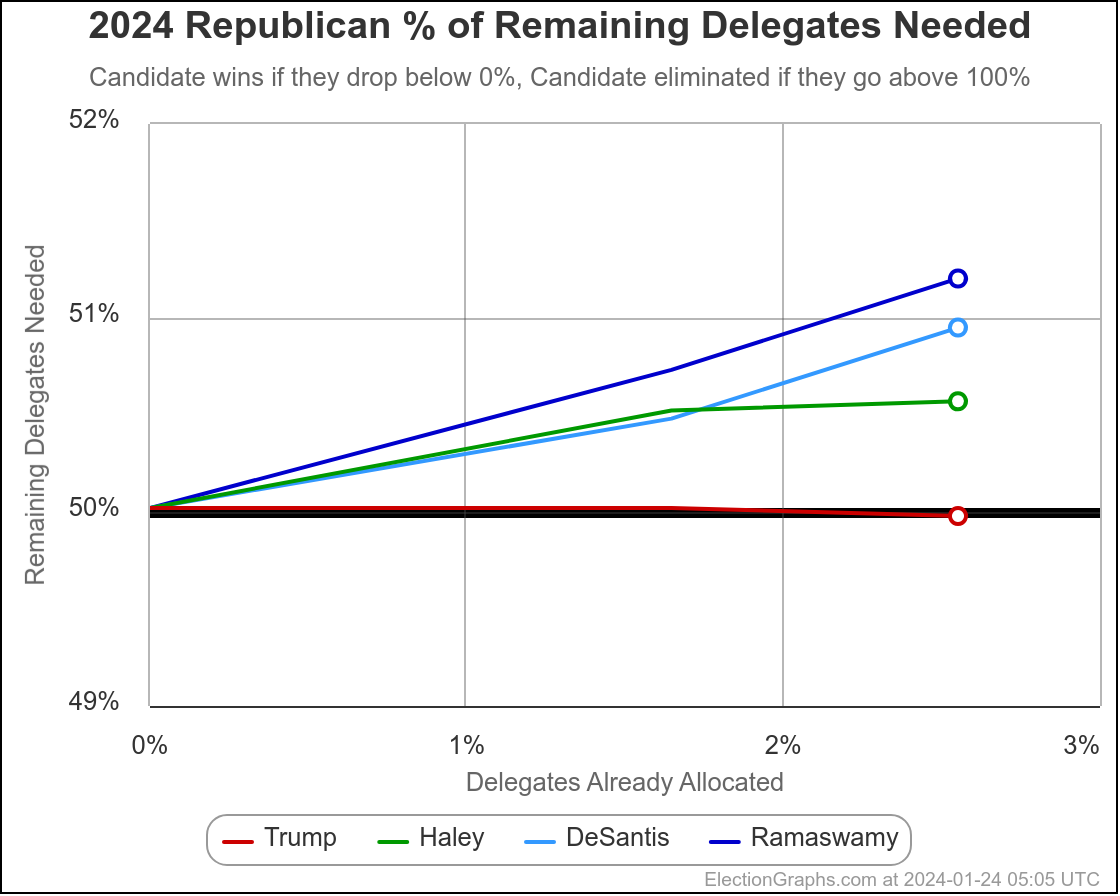
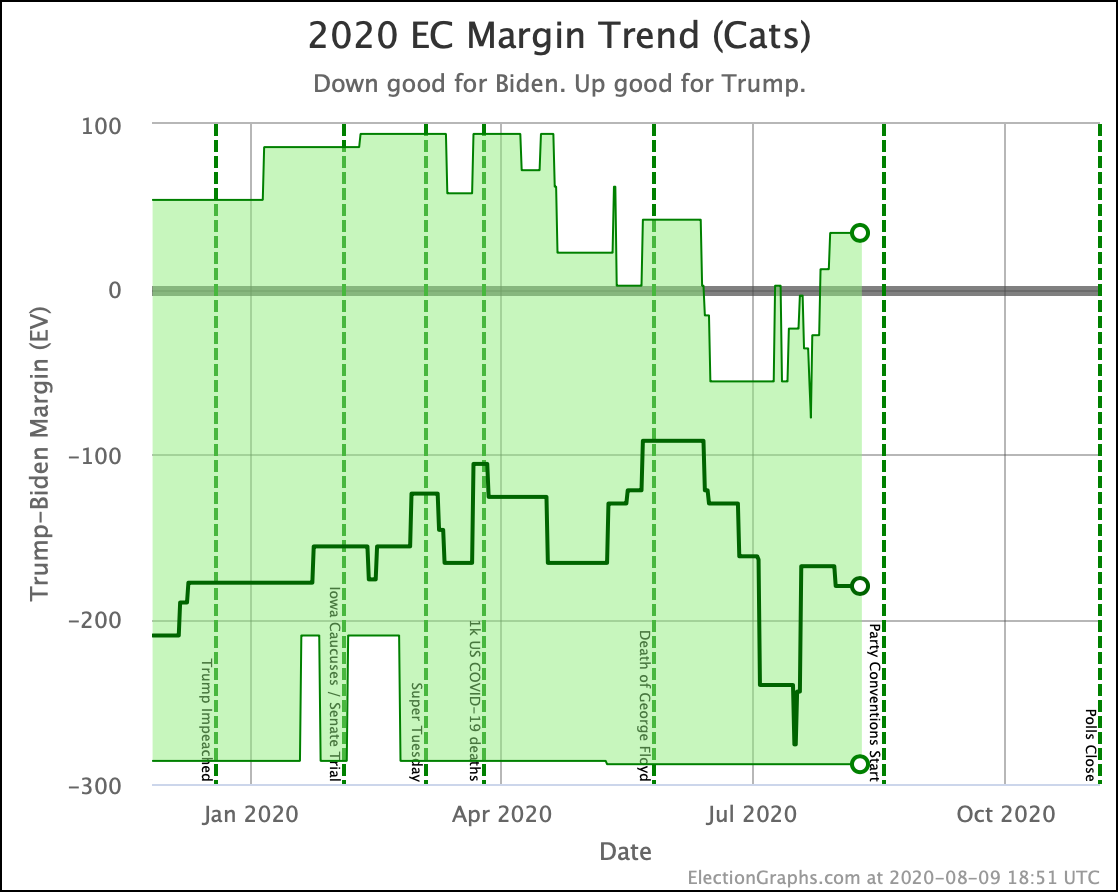
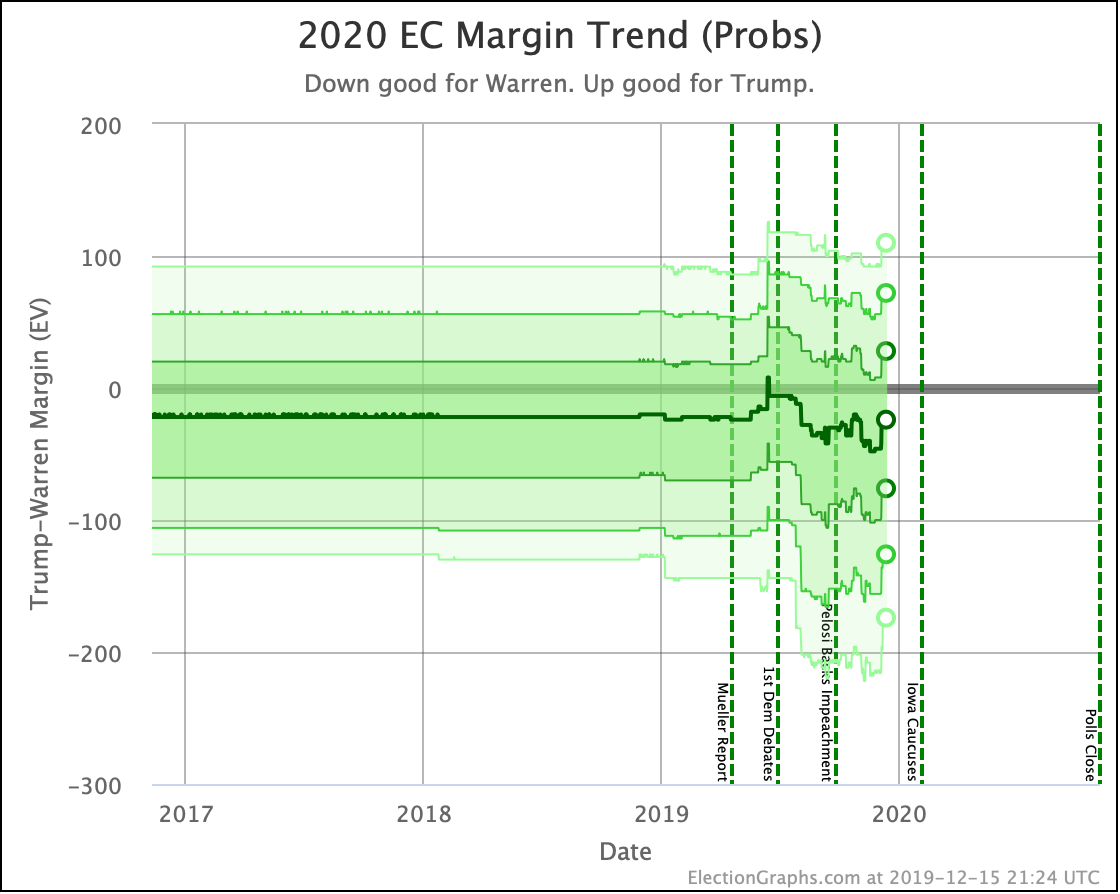
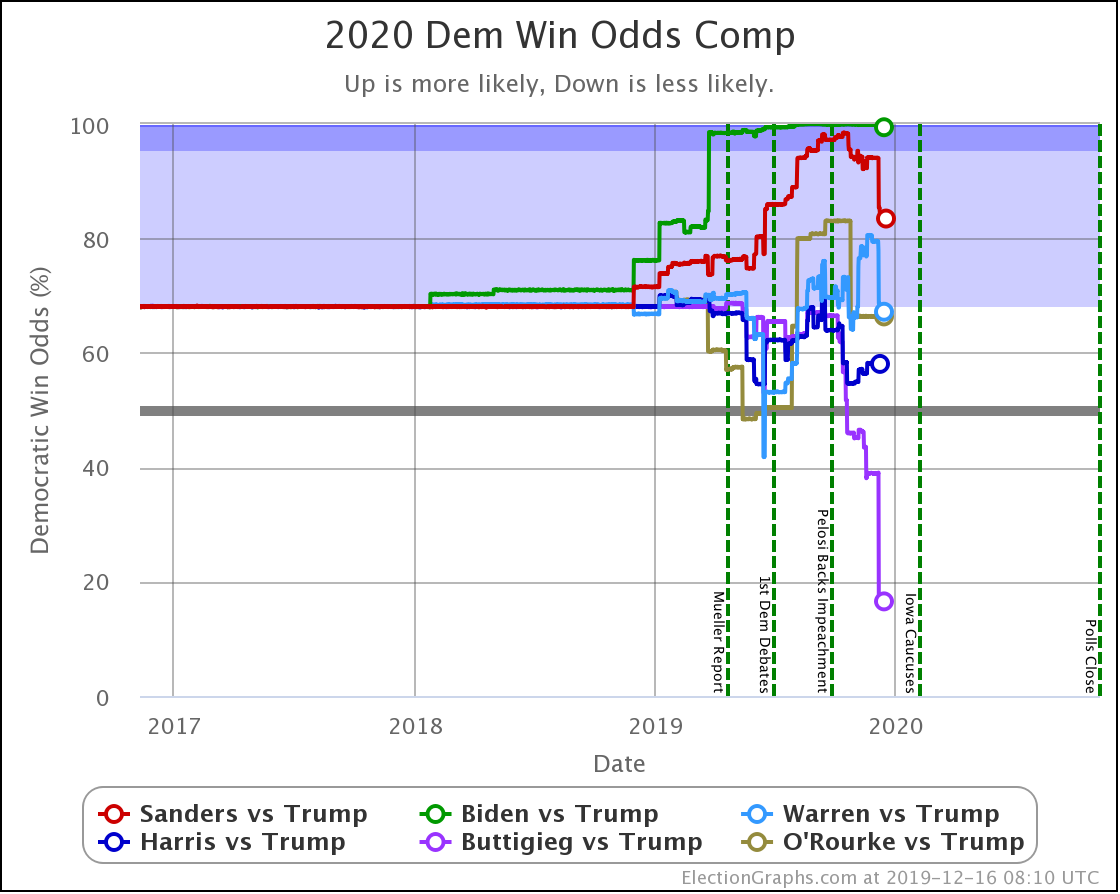
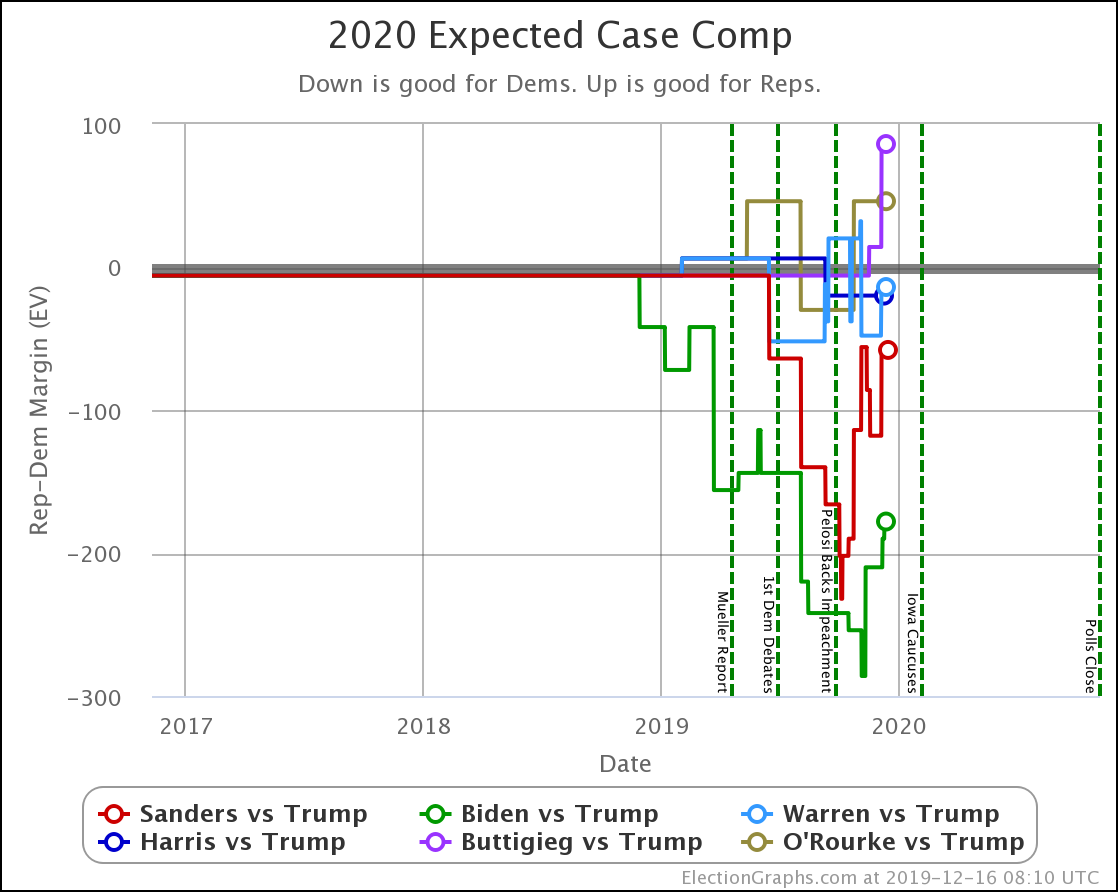
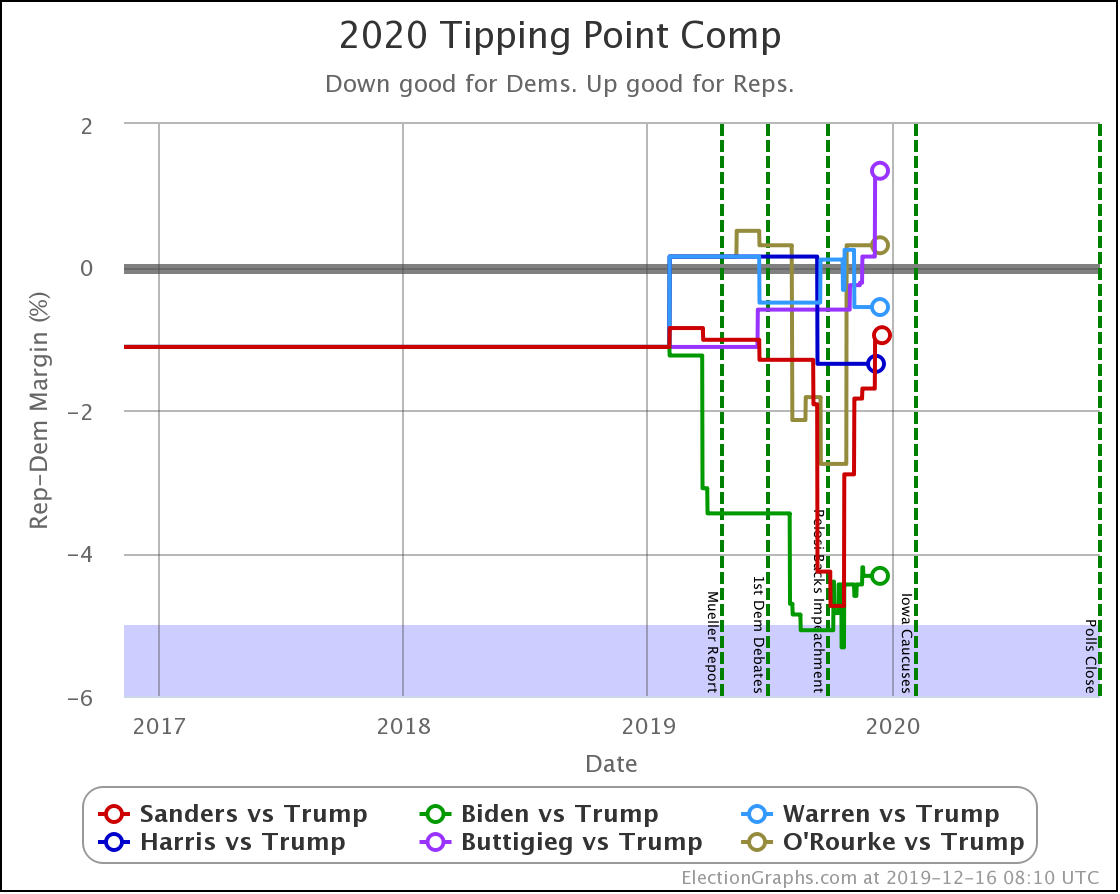
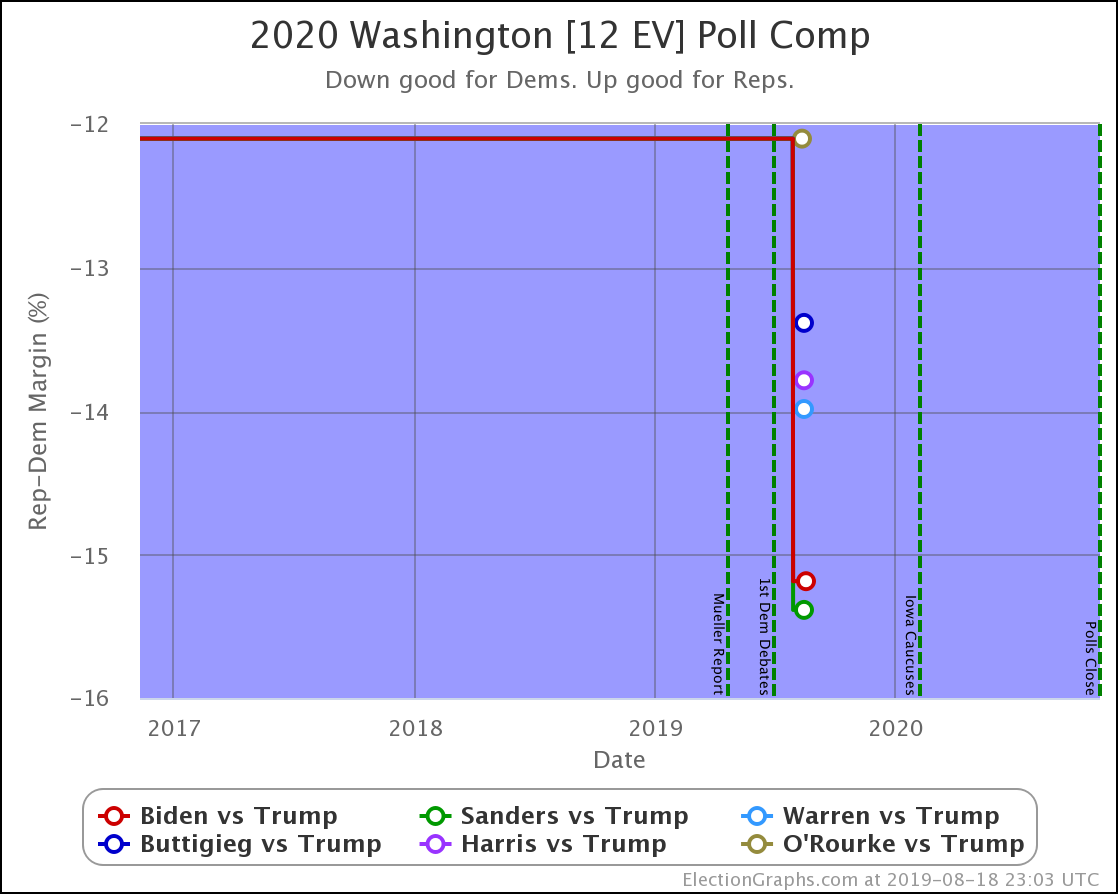
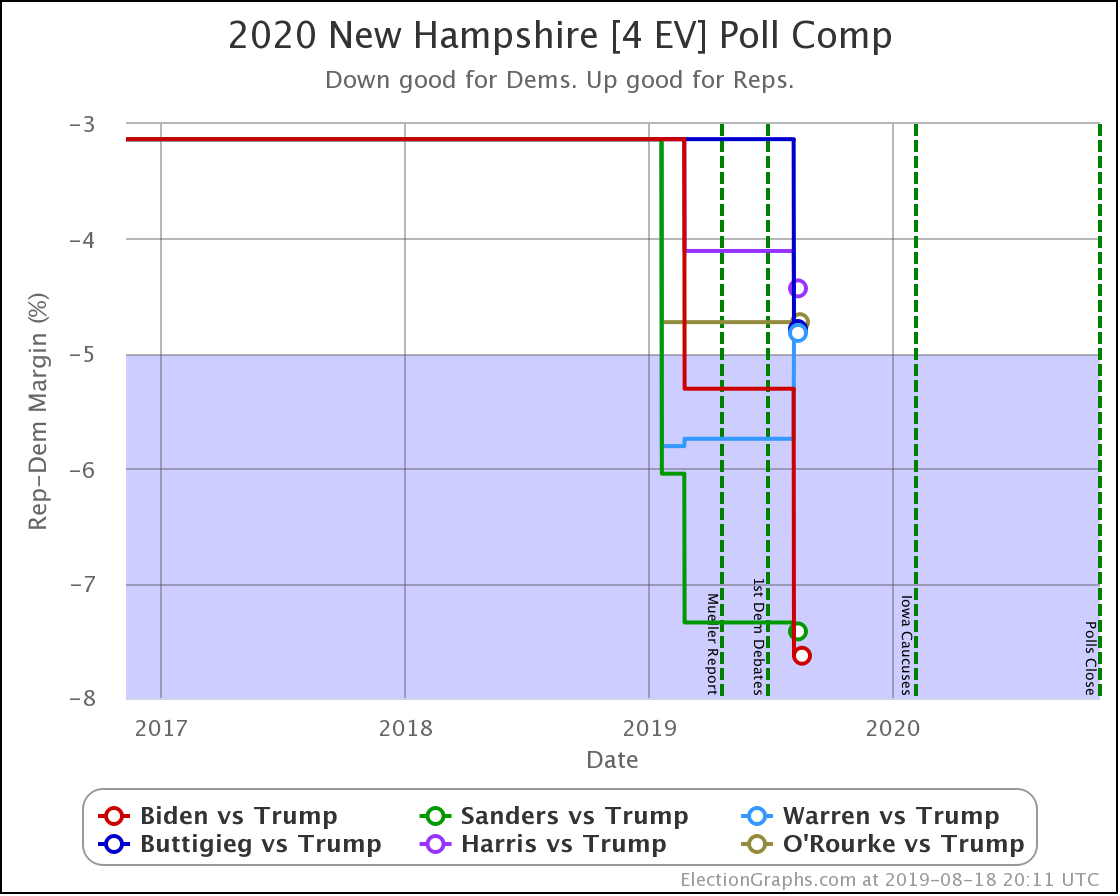
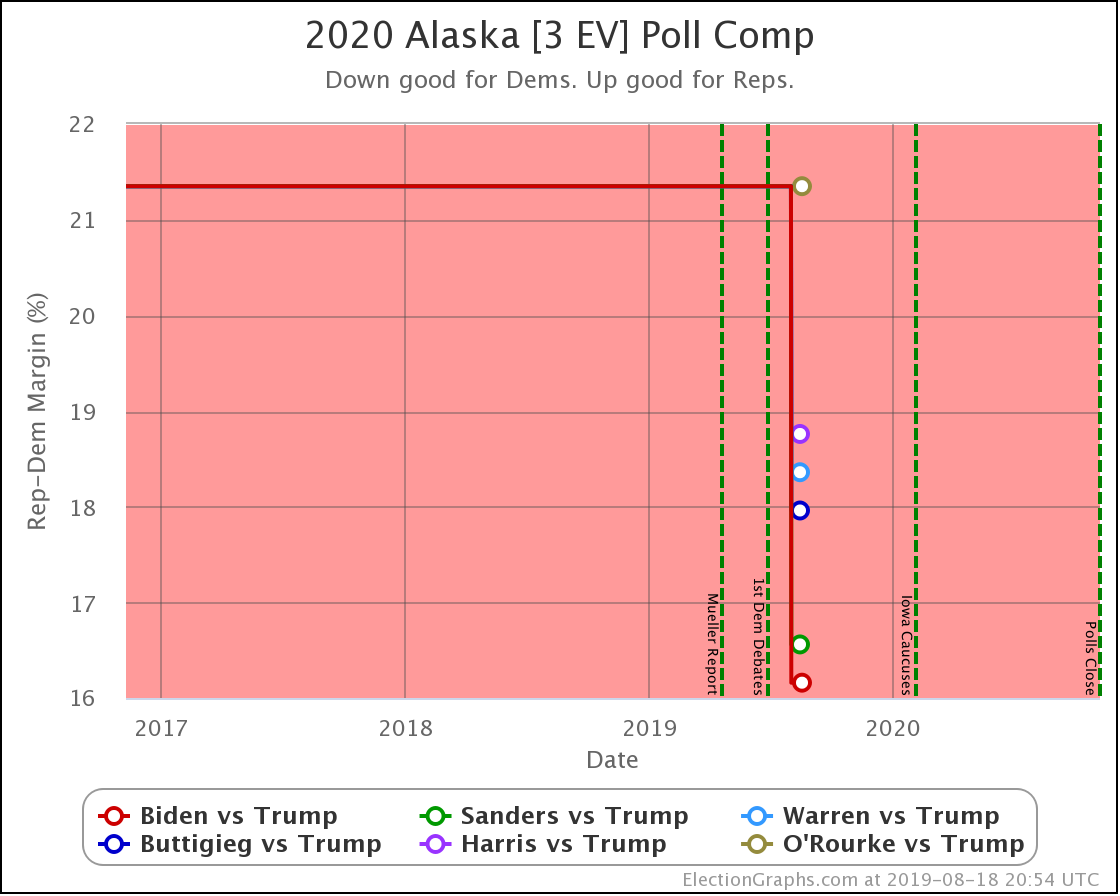
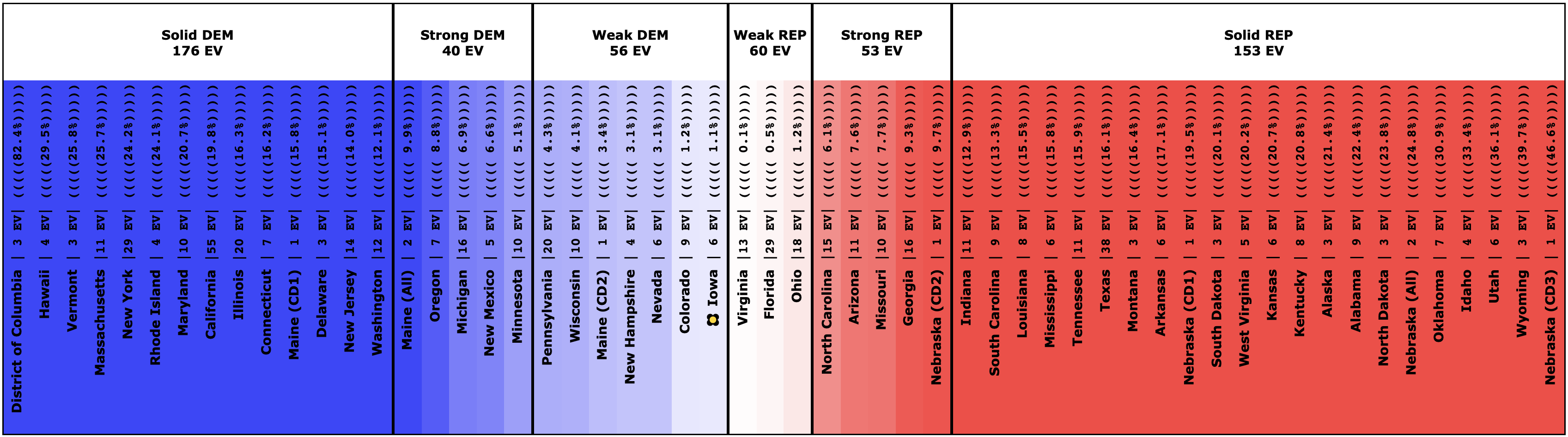
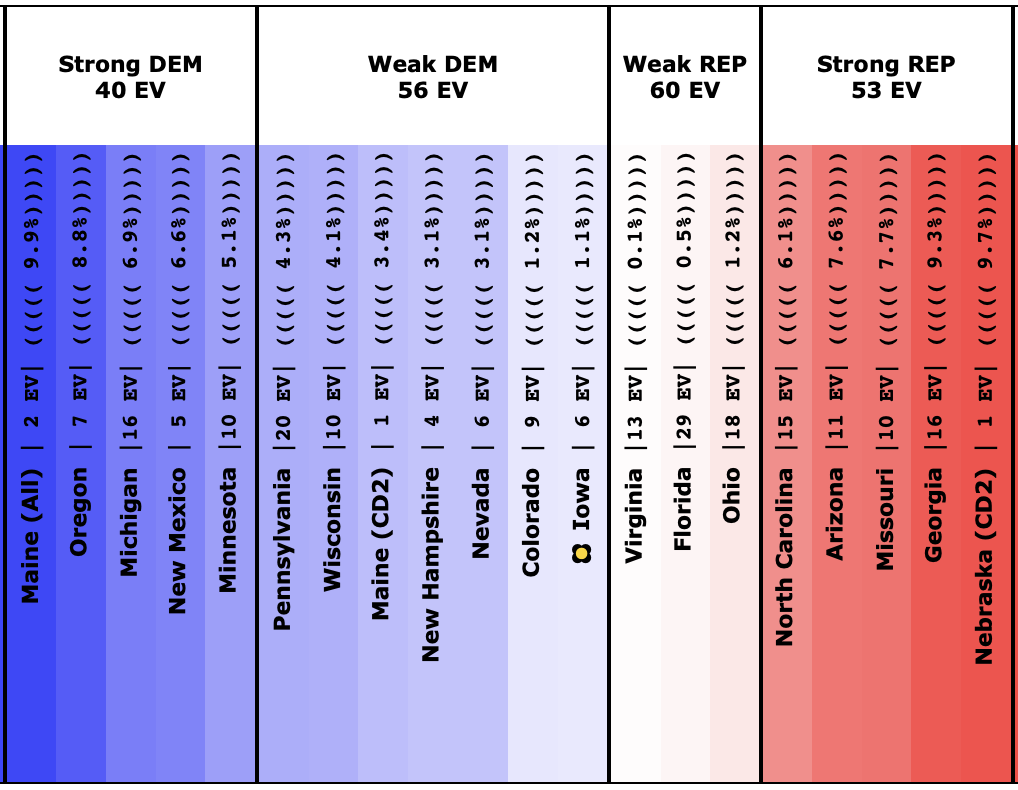
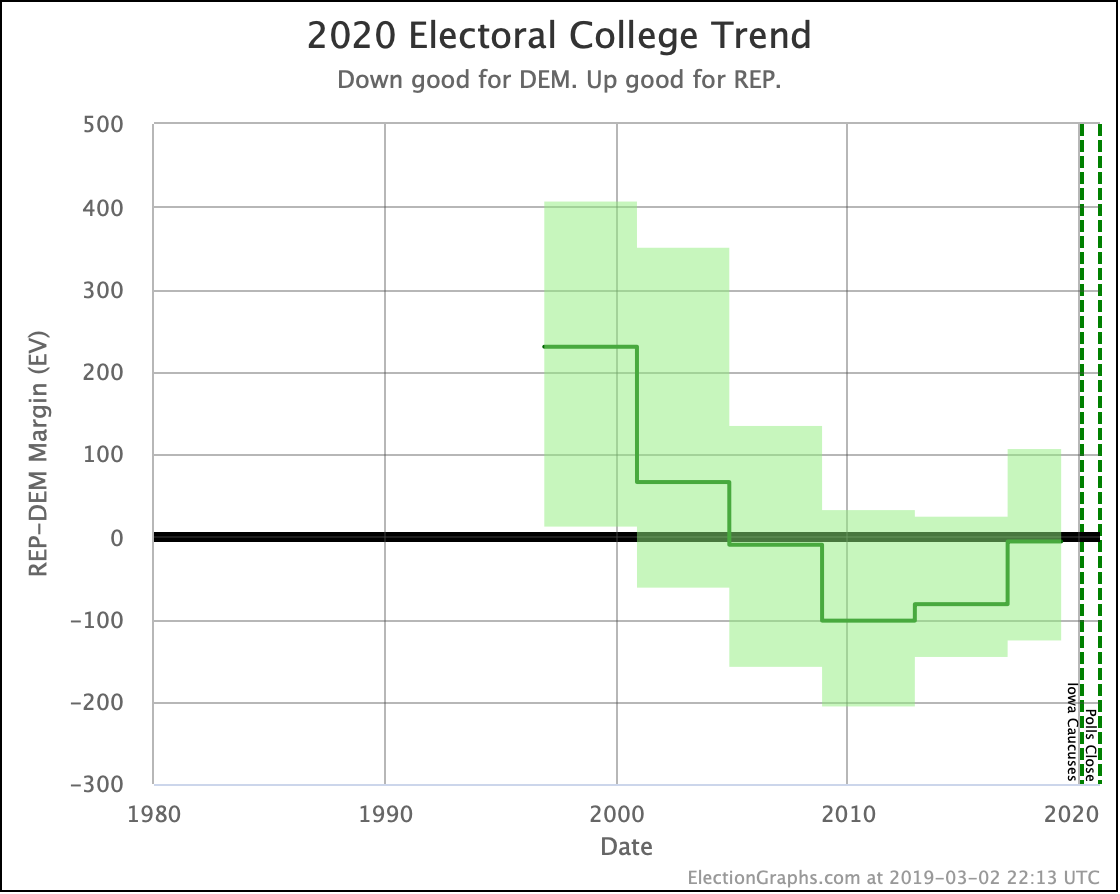
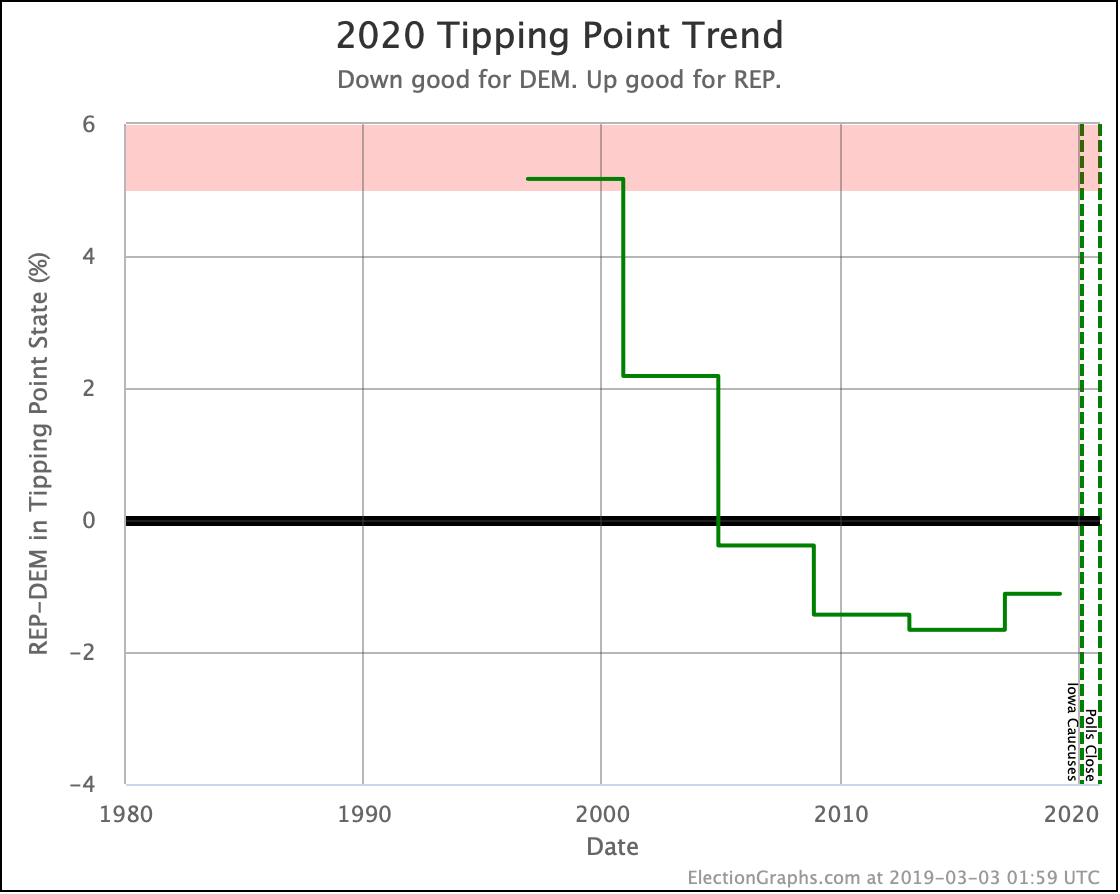
It has once again been longer than I like, but it is time for another post.
Since the last update, there have been new polls in Michigan (x3), Nevada (x2), Texas (x2), Arizona (x2), Pennsylvania (x3), Florida (x2), North Carolina (x3), Wisconsin (x2), Iowa, Georgia (x4), and New Hampshire.
That is a lot. Sorry about that. Oops.
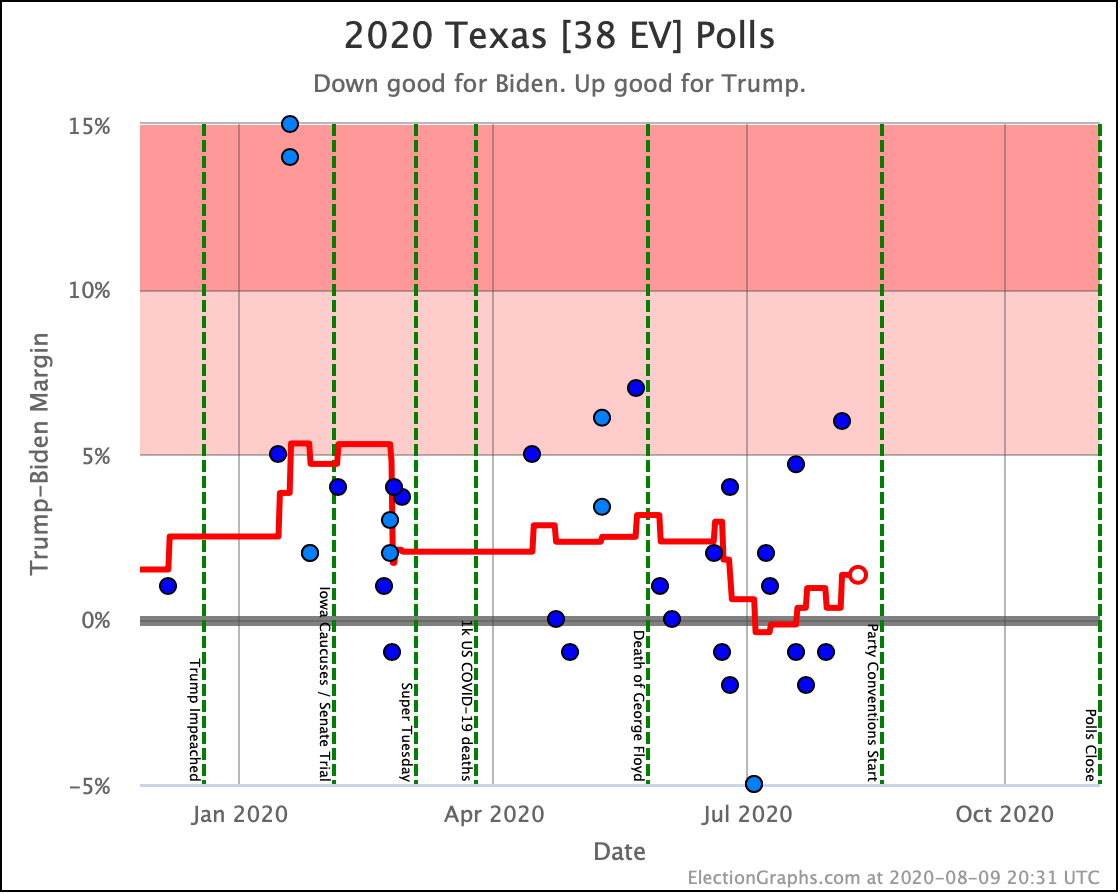
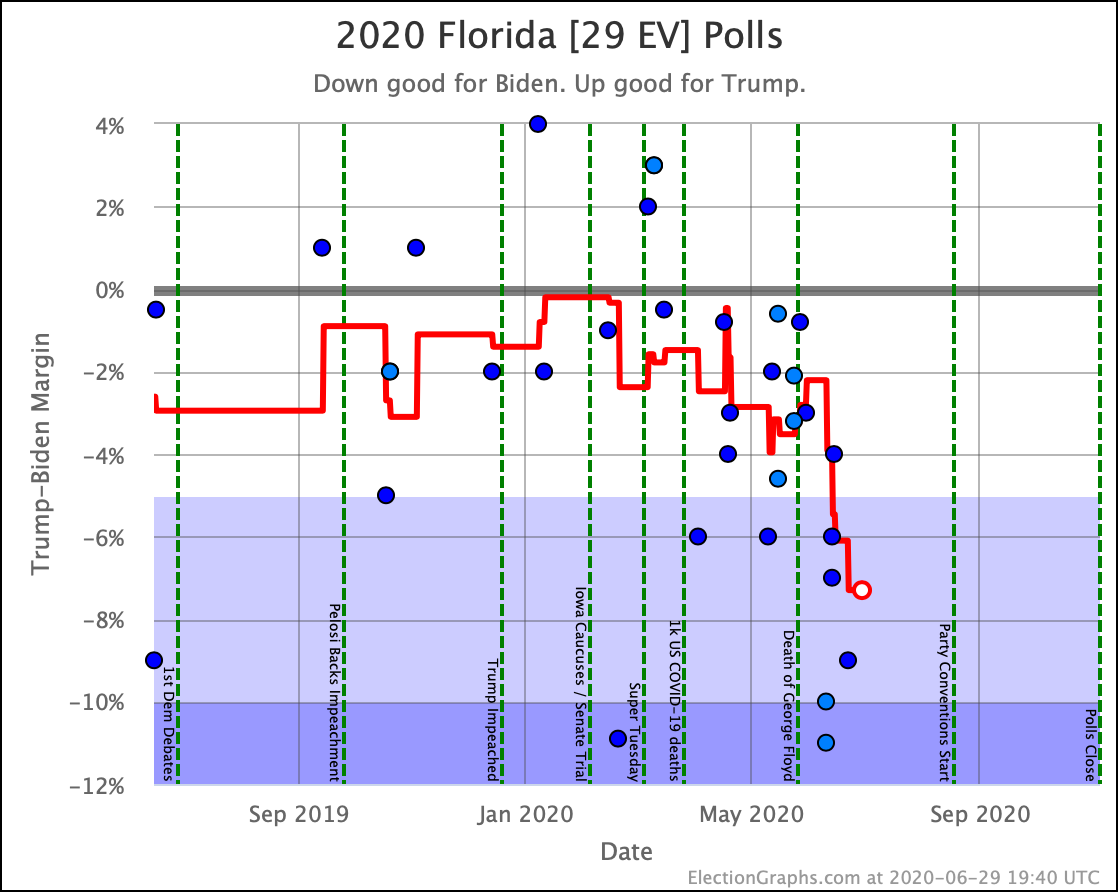
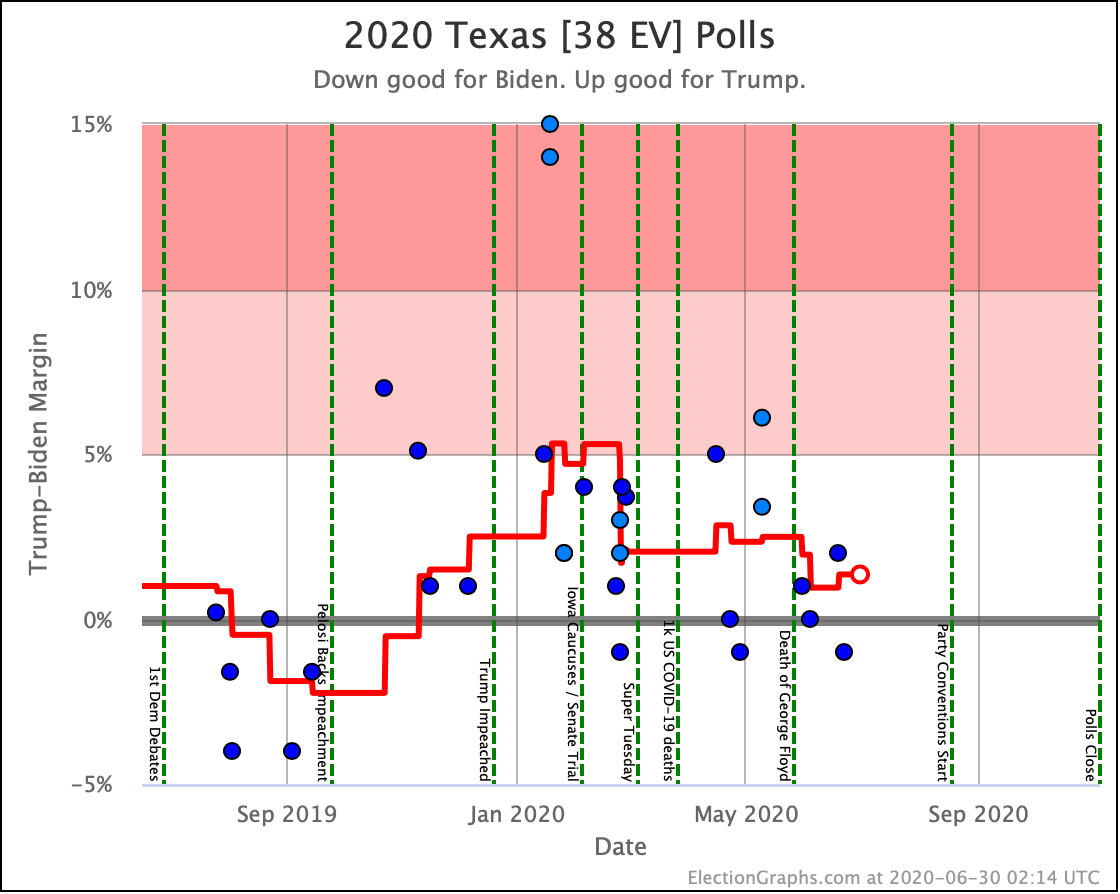
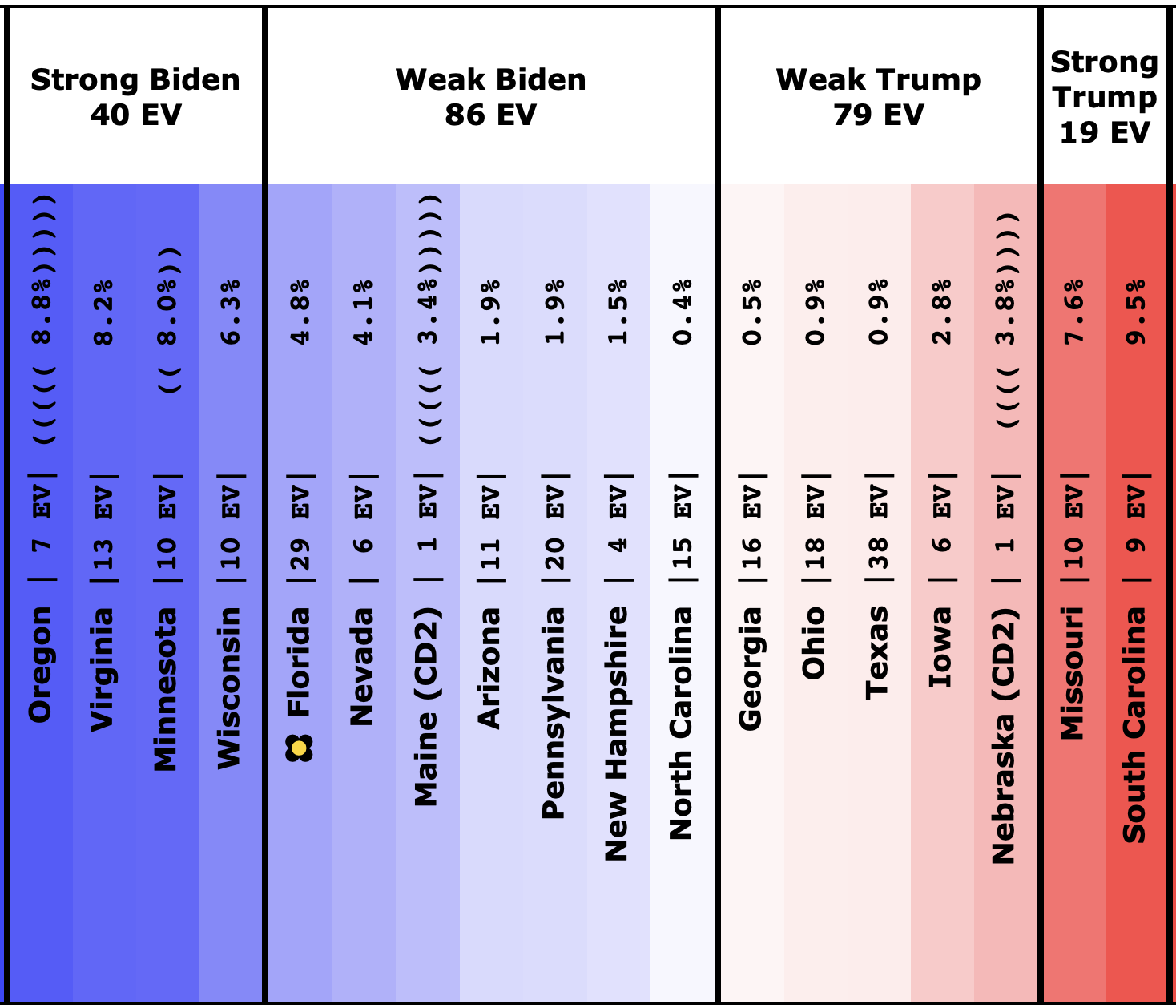
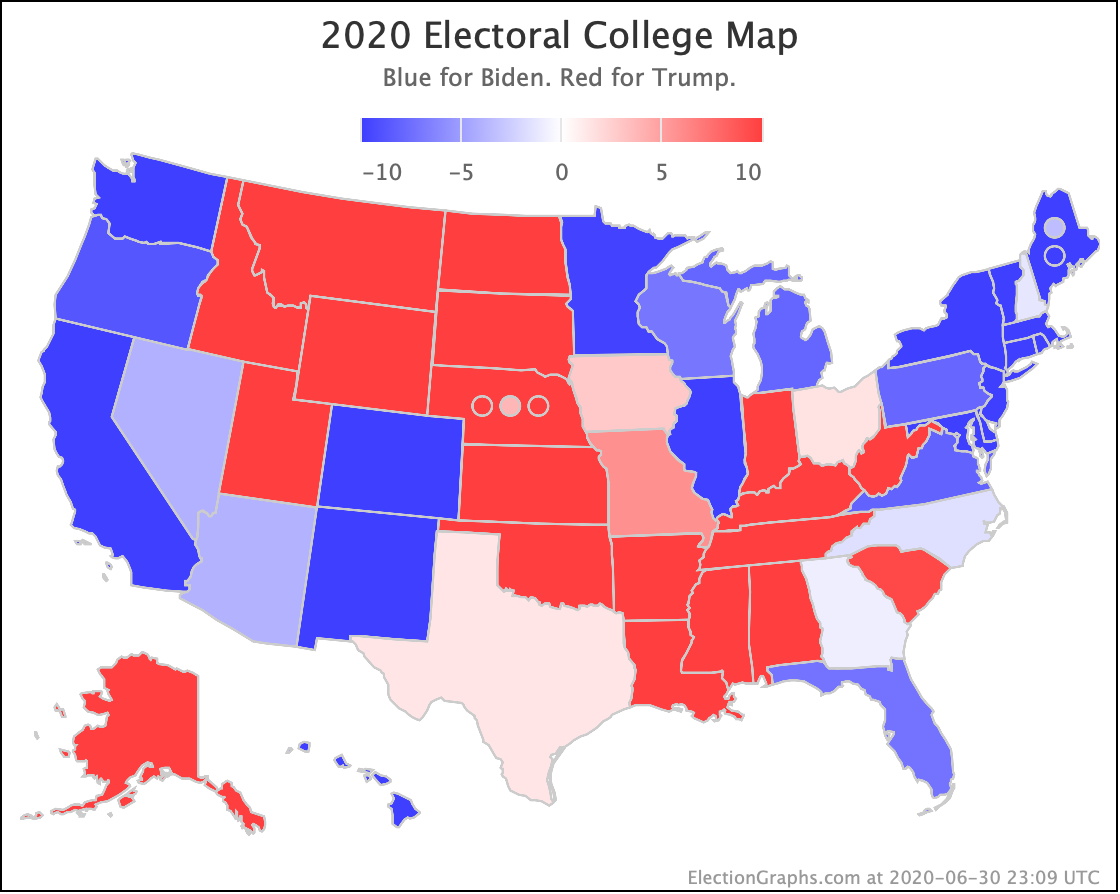
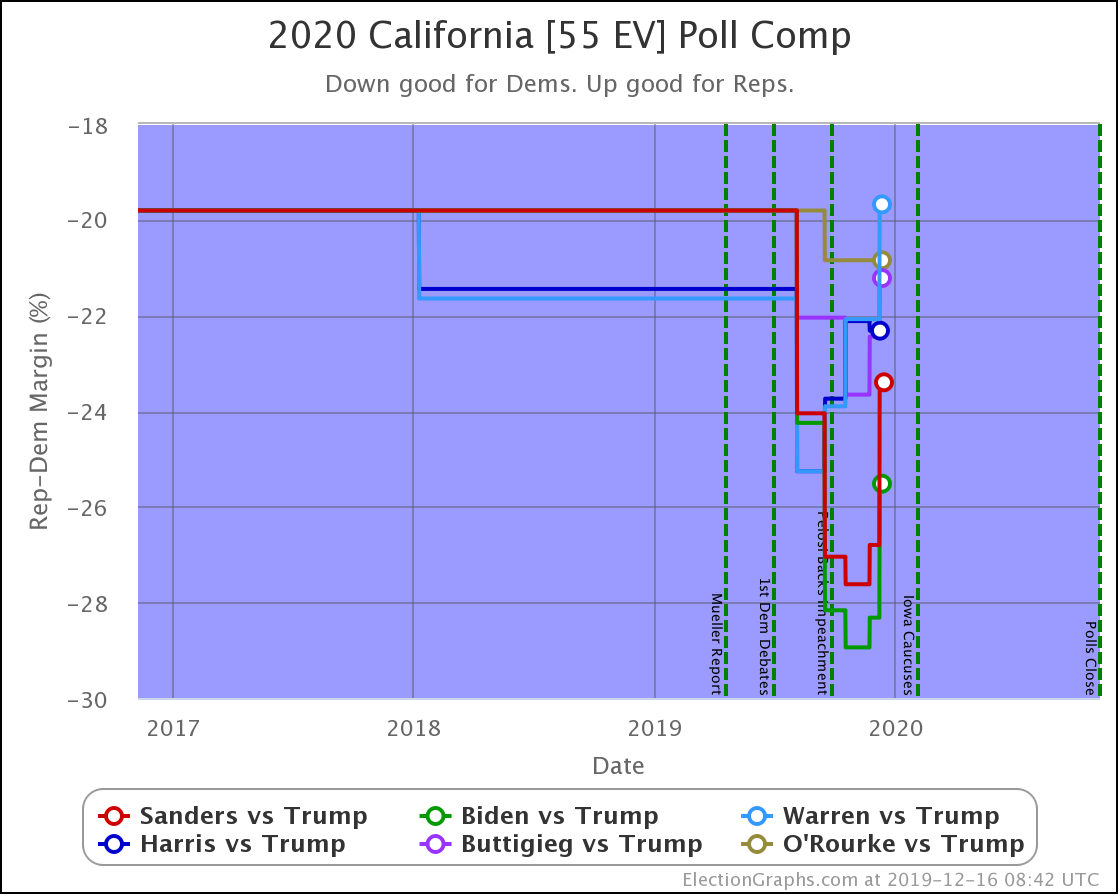
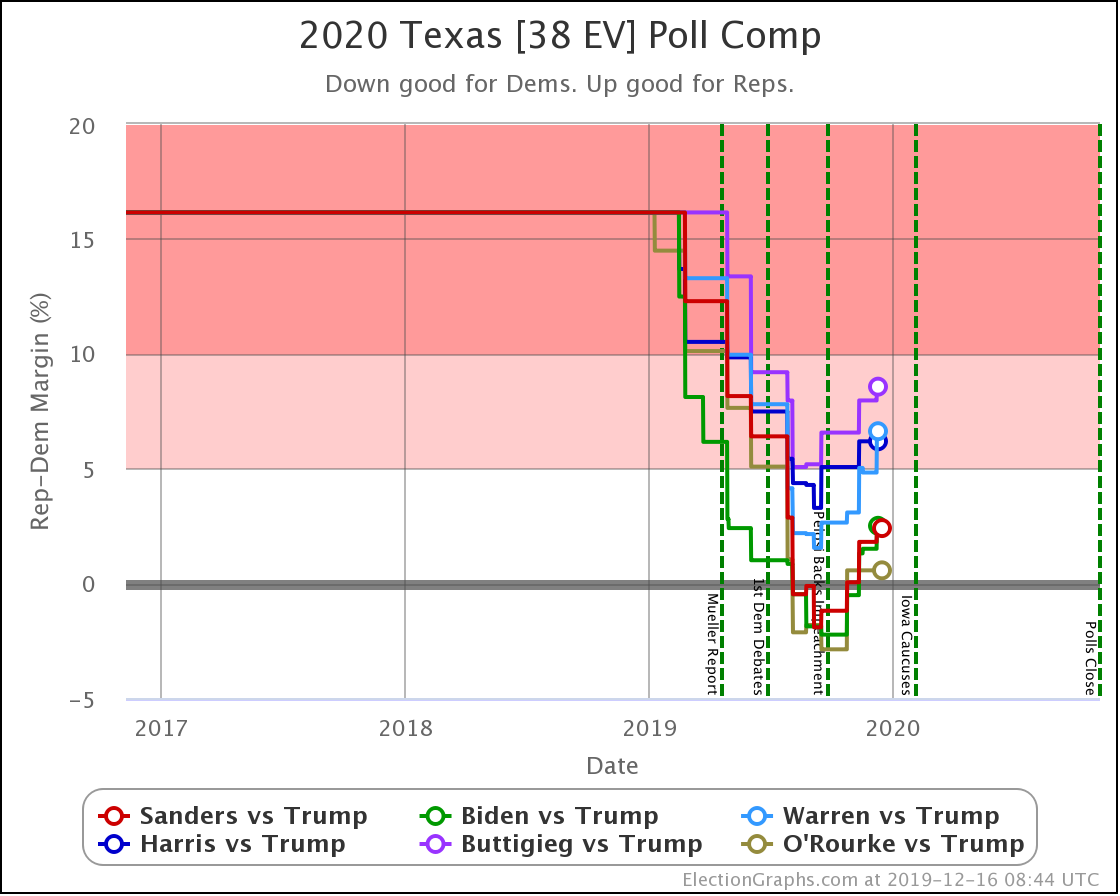
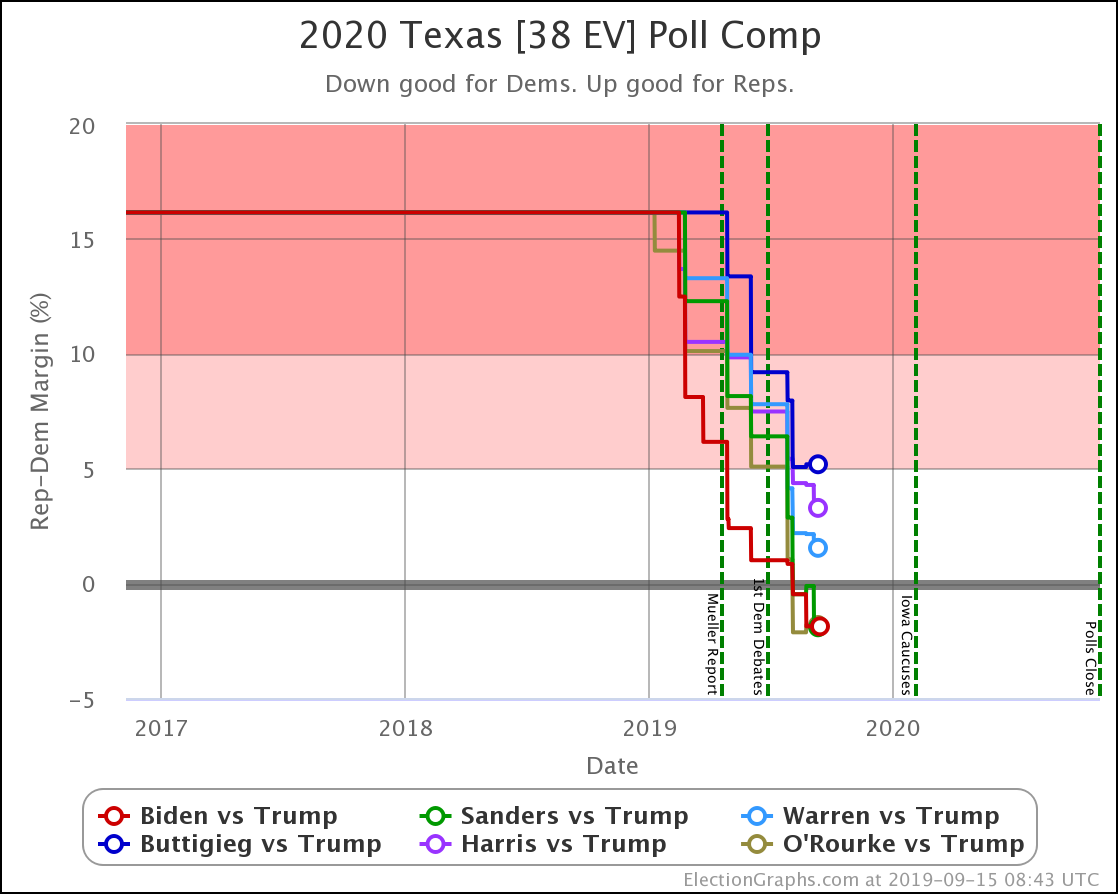
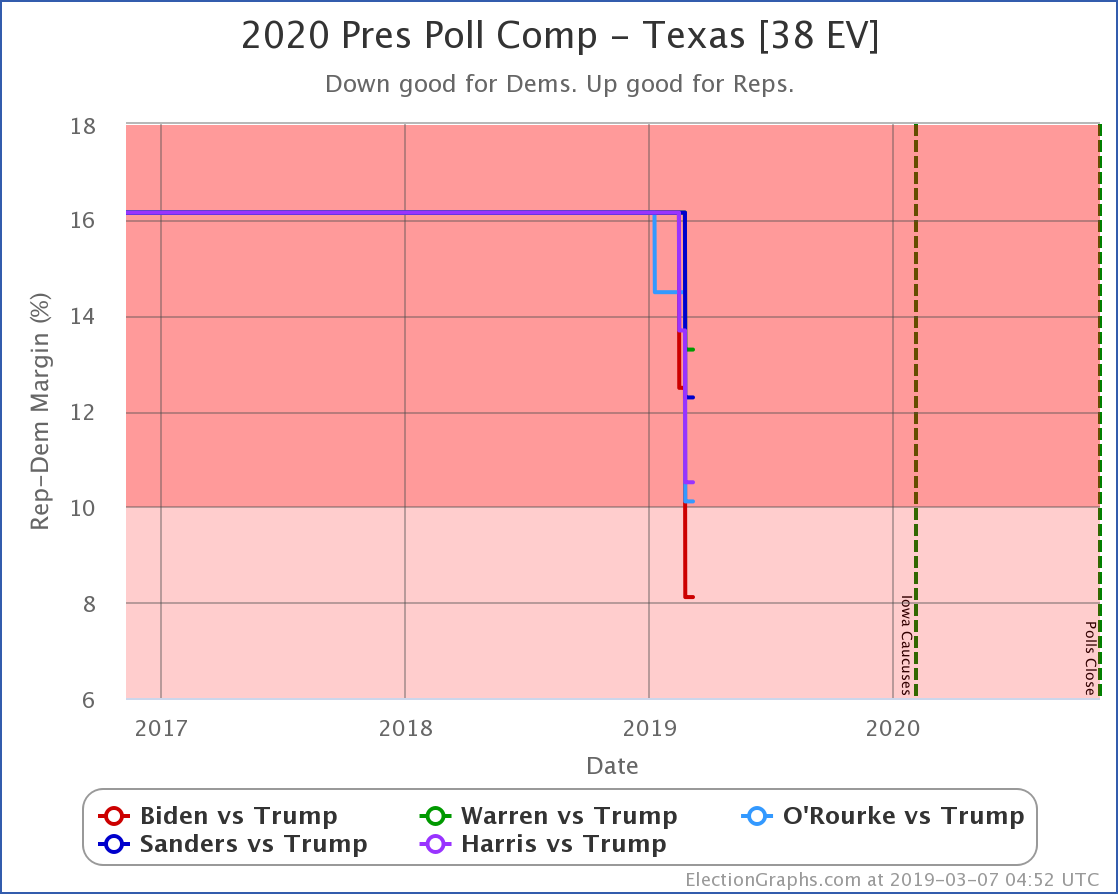
The most striking individual state result is that after peaking in September with three of the top six Democrats leading Trump in the Texas averages, and two more getting close, Texas has been moving back toward Trump.
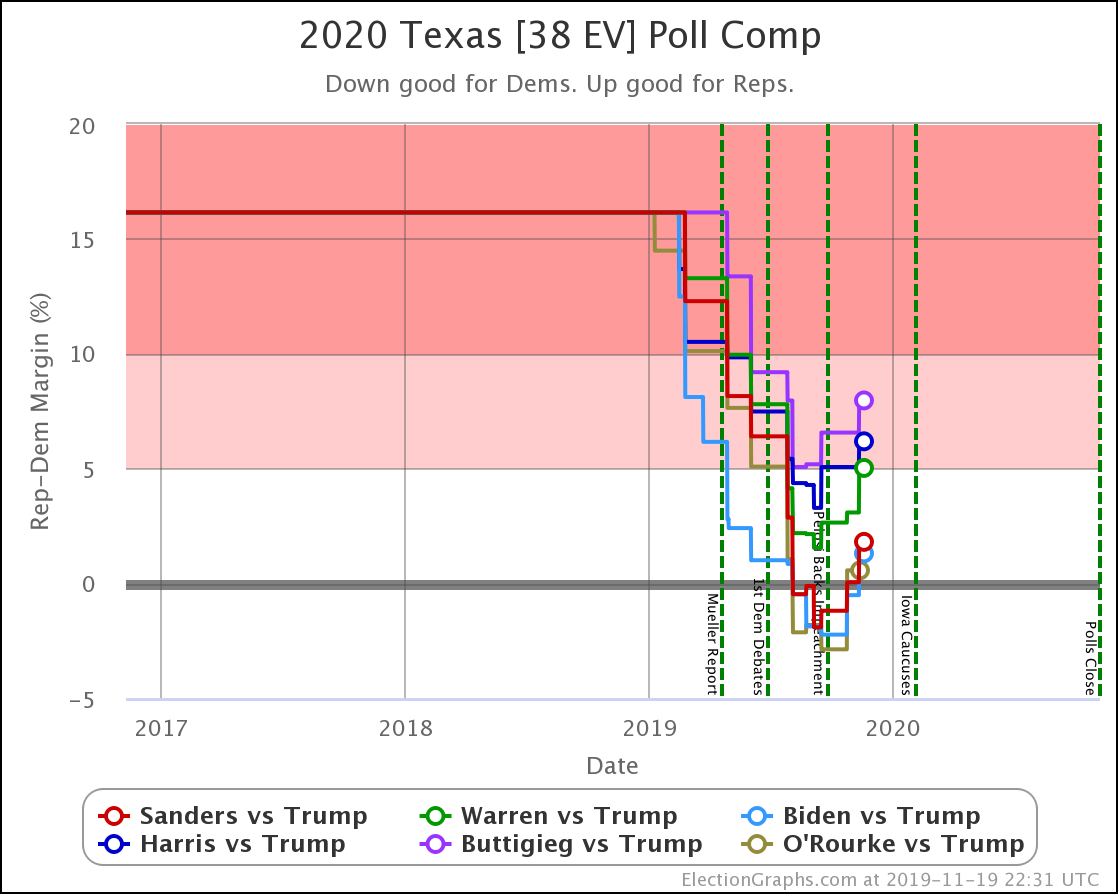
As of now, none of the six most polled Democrats lead in Texas, and only three of those keep Trump's lead to less than 5%. And one of those (O'Rourke) has already dropped out of the race, leaving only Sanders and Biden still making it close.
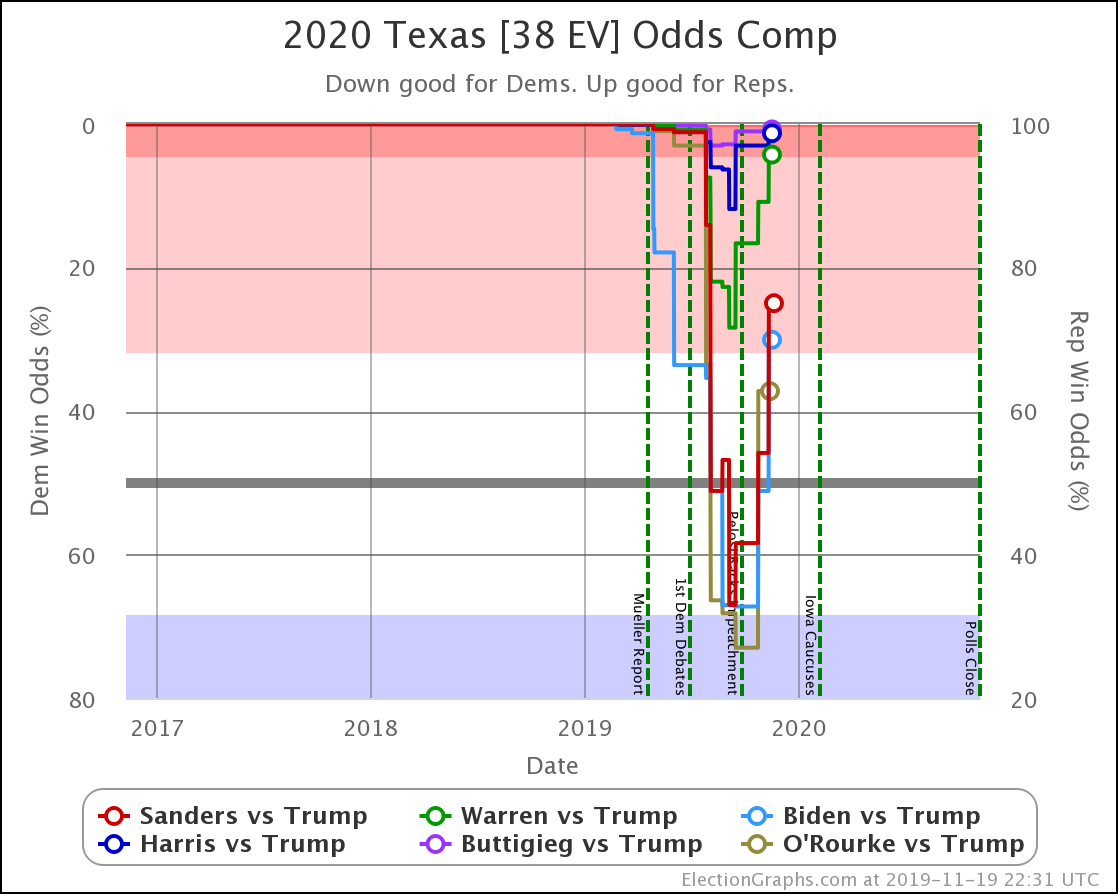
Converting this to win odds, Biden has a 30.1% chance of winning the state (if the election was today), and Sanders has a 25.0% chance of winning.
None of the rest (except O'Rourke, who is out) is above 5%.
So Texas is reverting to form. It may be closer than it has been in previous years, but at least for the moment, the Democratic hopes for a blue Texas seem to be fading.
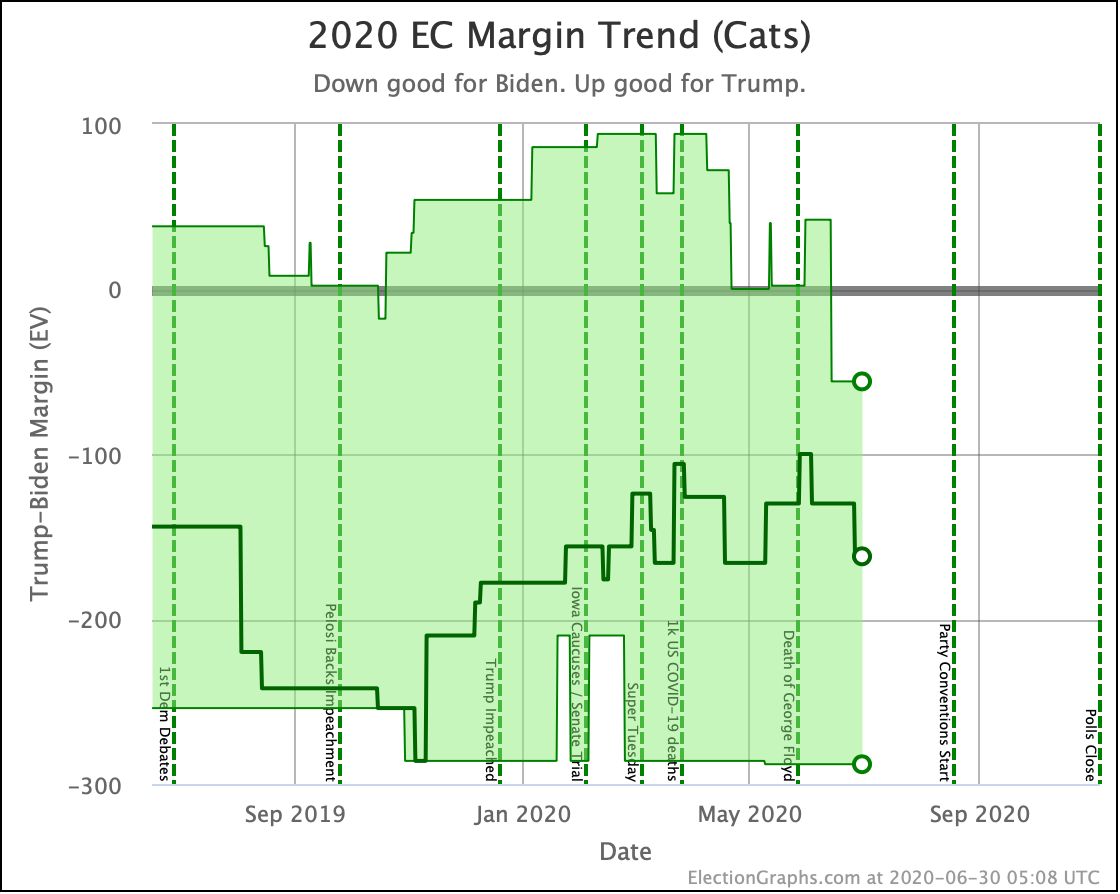
I'll go over other states with new polling at the end of the post, but first, a look at four ways of looking at the changes in the national summary since the last post.
O'Rourke vs. Trump is now in the top six best-polled candidate combinations (replacing Sanders vs. Pence). But since O'Rourke dropped out, we will leave him out and only look at the top five for now.
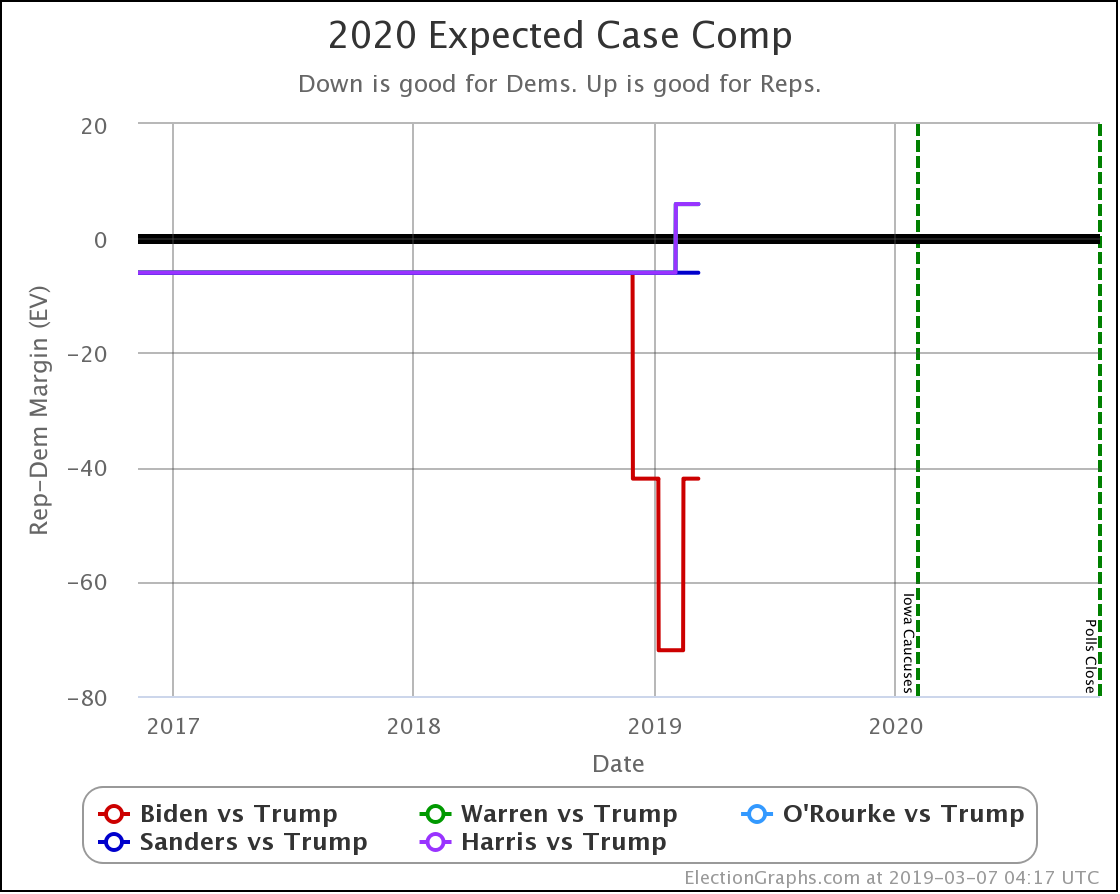
I haven't done posts showing the update-to-update comparisons for the older "categorization method" before, but since that used to be the bread and butter of Election Graphs, let's start there.
| Dem |
1 Nov |
20 Nov |
𝚫 |
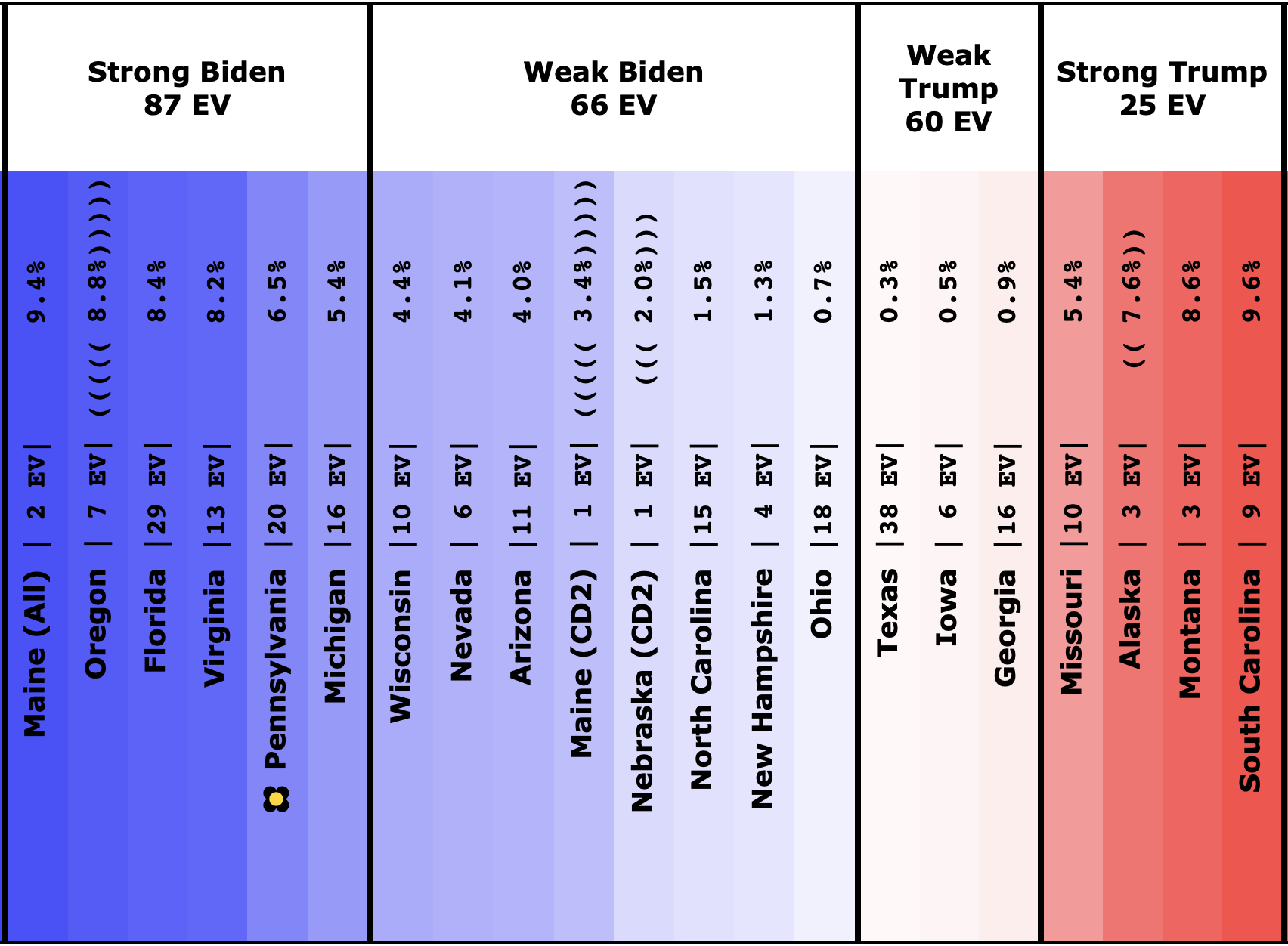
| Biden |
+254 |
+210 |
-44 |
| Sanders |
+190 |
+118 |
-72 |
| Warren |
+38 |
+48 |
+10 |
| Harris |
+20 |
+20 |
Flat |
| Buttigieg |
+6 |
+6 |
Flat |
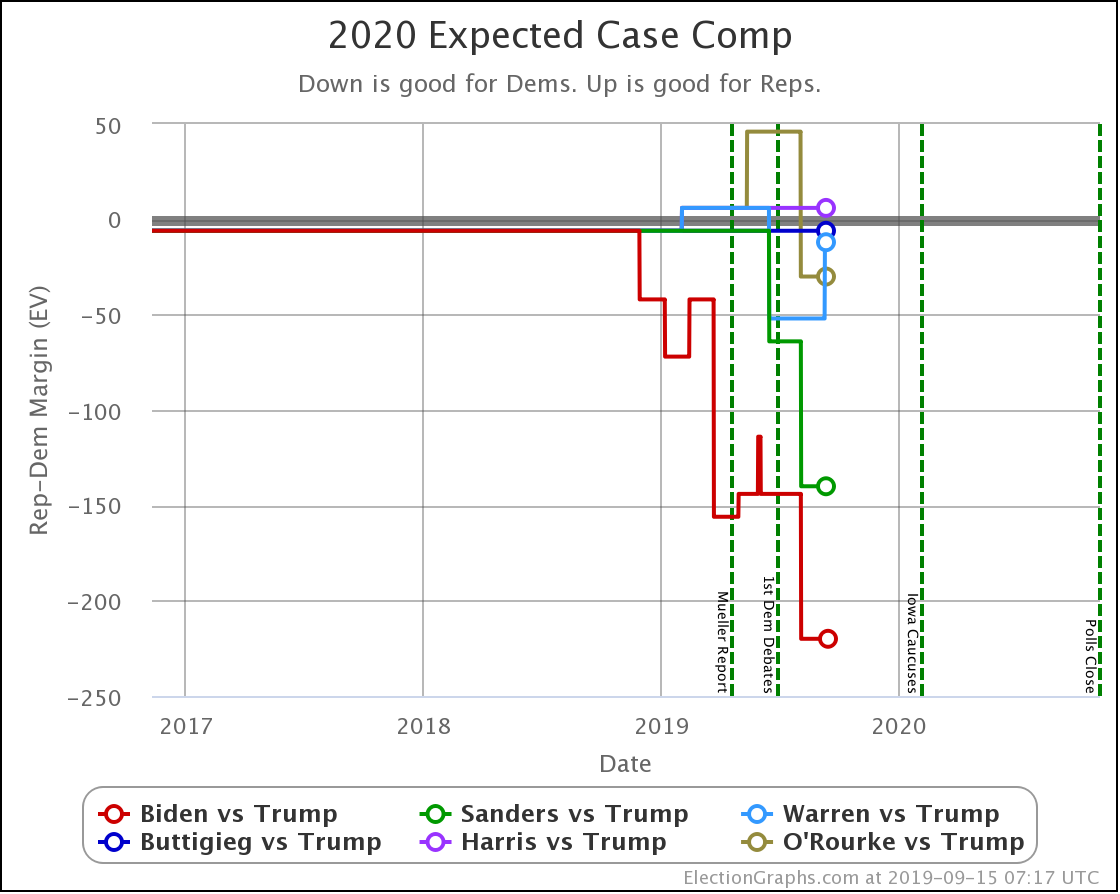
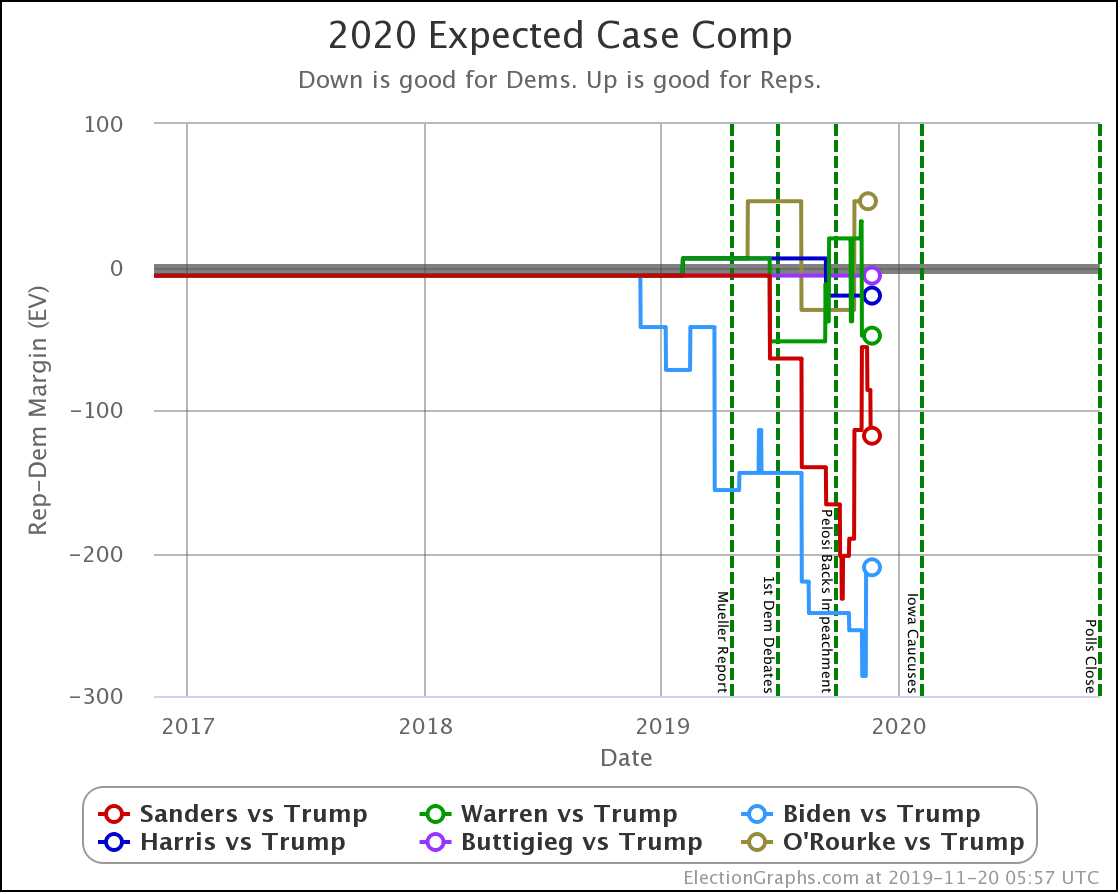
In this "expected case" view, where every candidate wins every state where they lead in the poll average, both Sanders and Biden have lost ground.
Warren improves her position a little.
Harris and Buttigieg are flat.
| Dem |
1 Nov |
20 Nov |
𝚫 |
| Biden |
+5.3% |
+4.4% |
-0.9% |
| Sanders |
+4.7% |
+1.8% |
-2.9% |
| Harris |
+1.4% |
+1.4% |
Flat |
| Warren |
+0.3% |
+0.6% |
+0.3% |
| Buttigieg |
+0.6% |
+0.2% |
-0.4% |
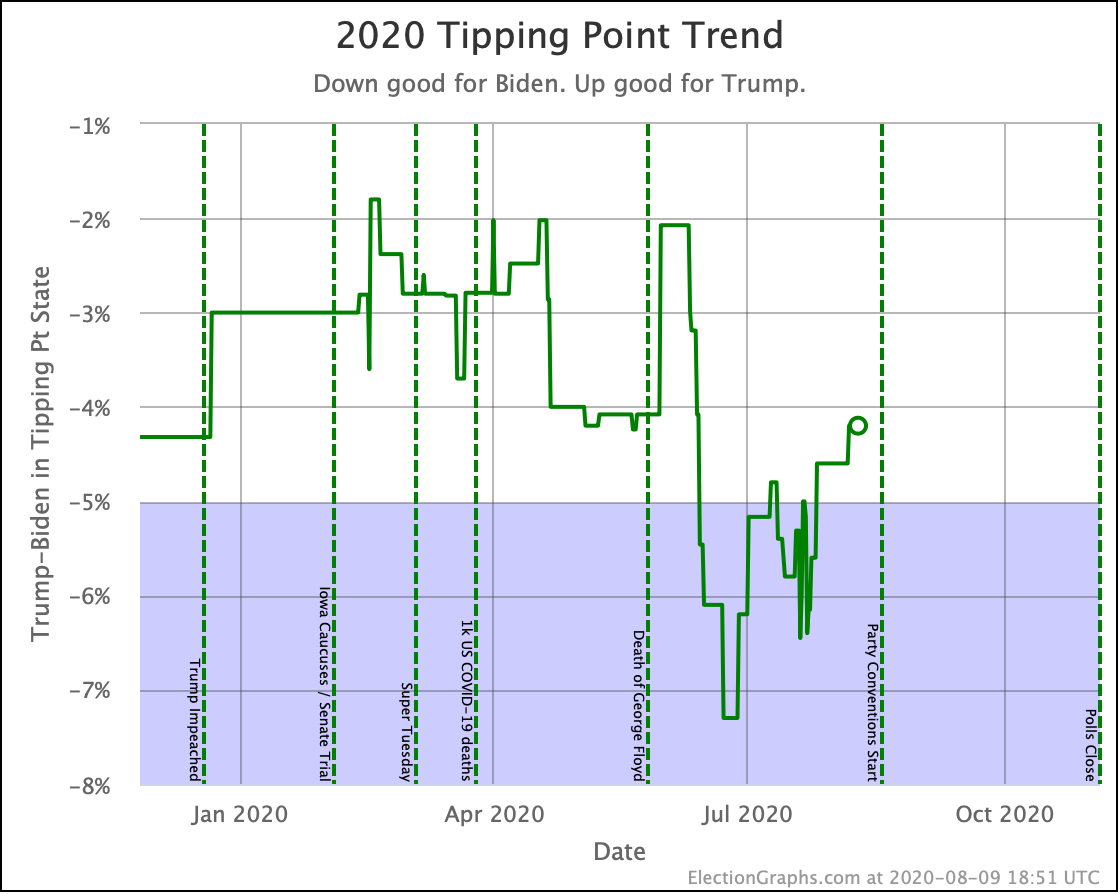
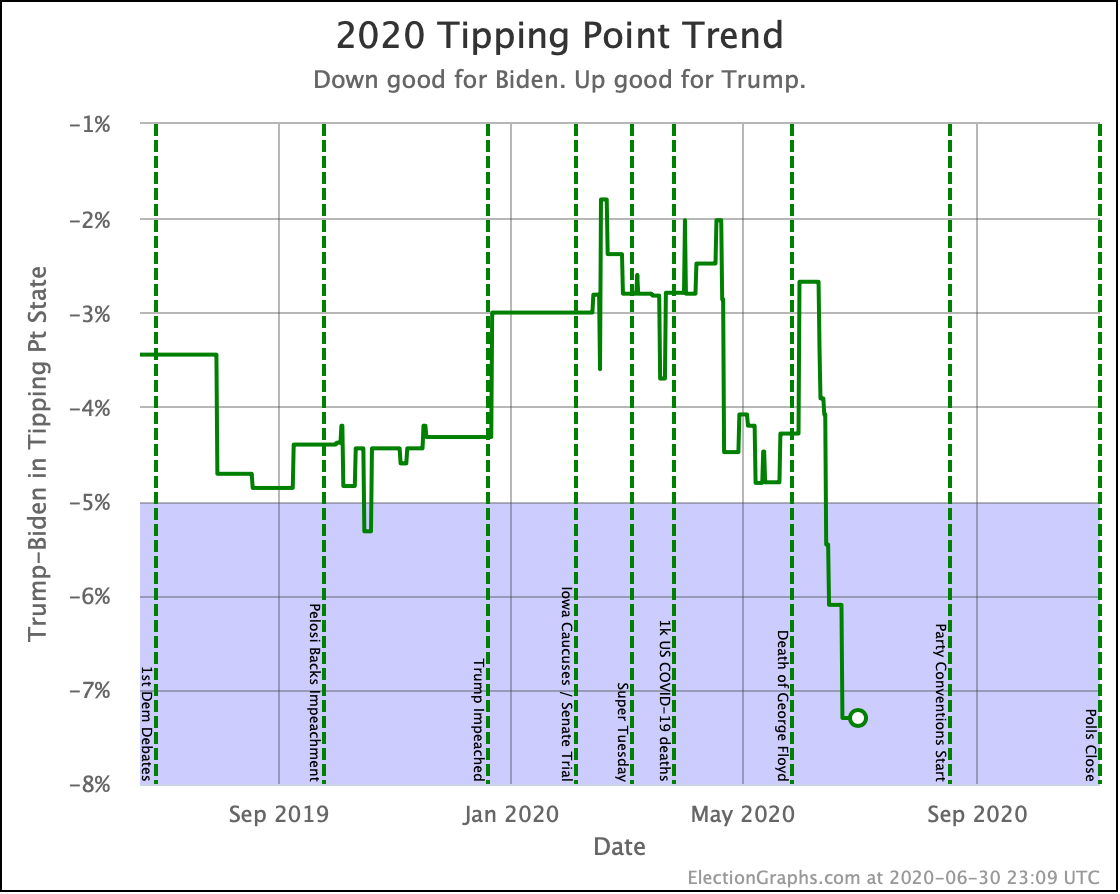
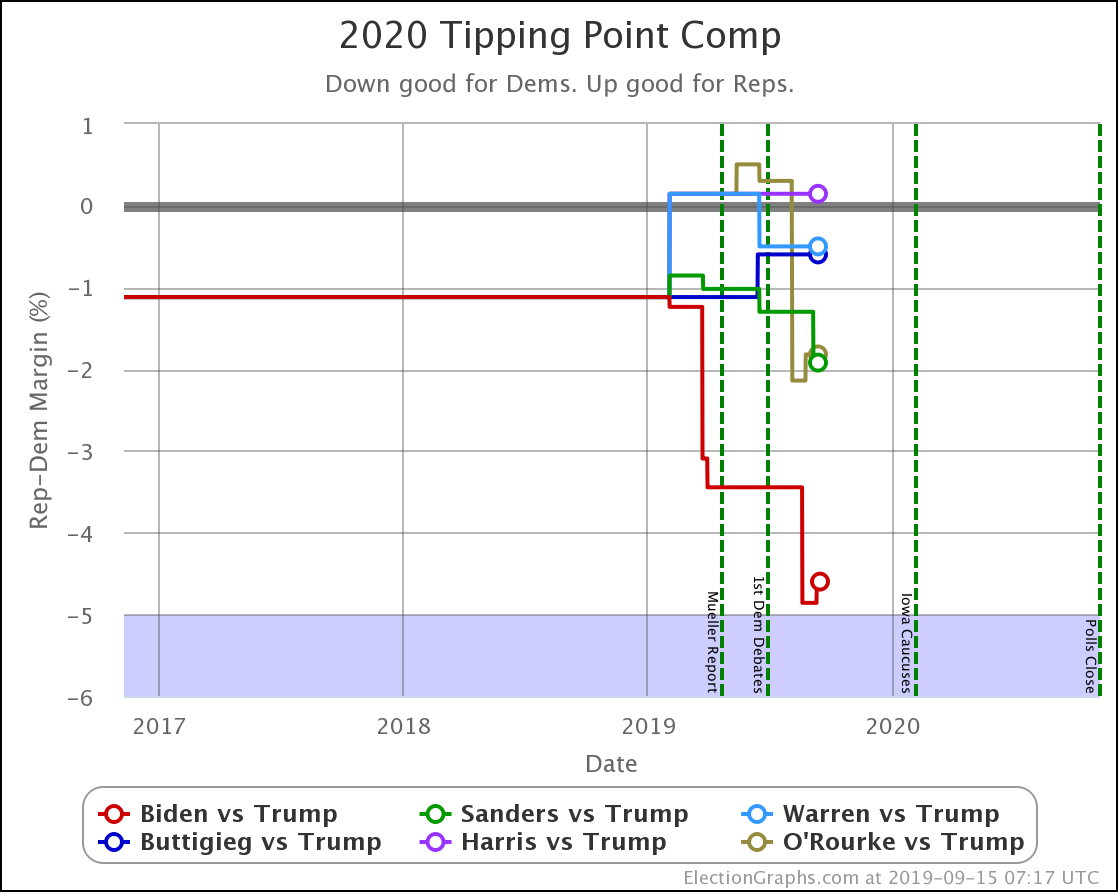
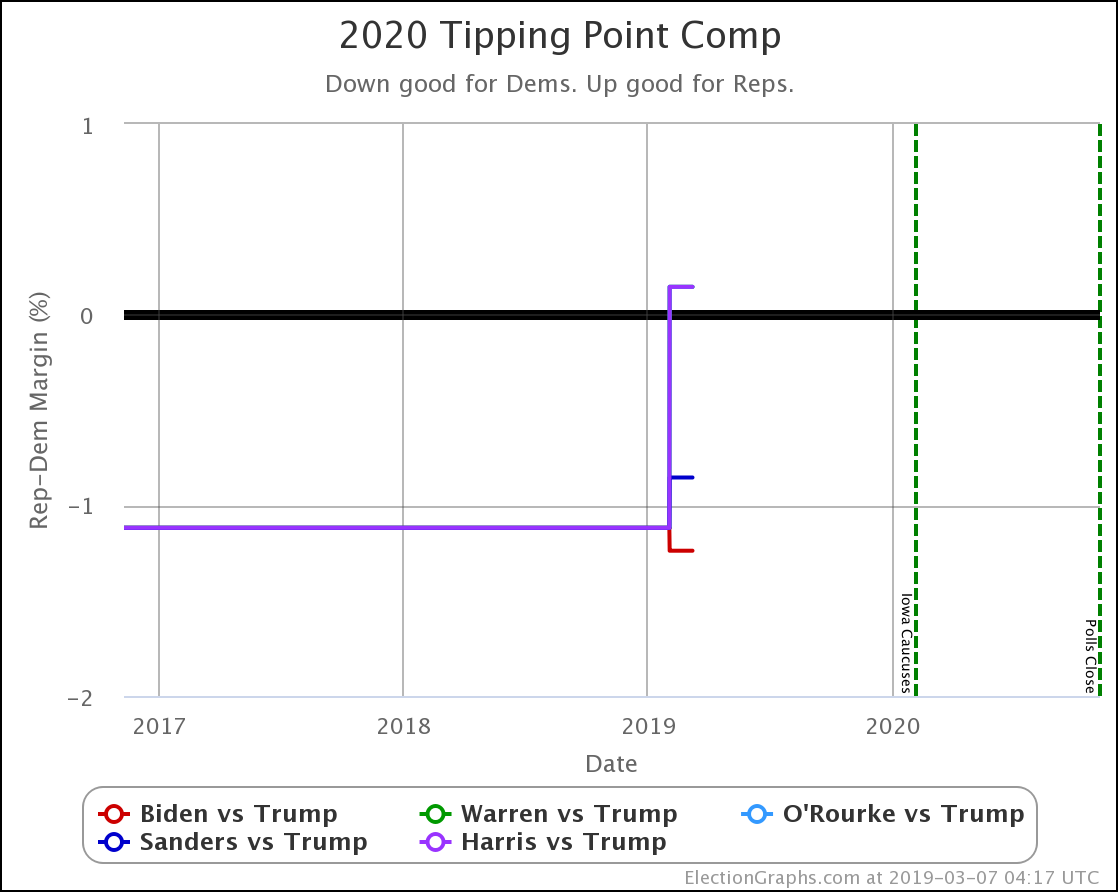
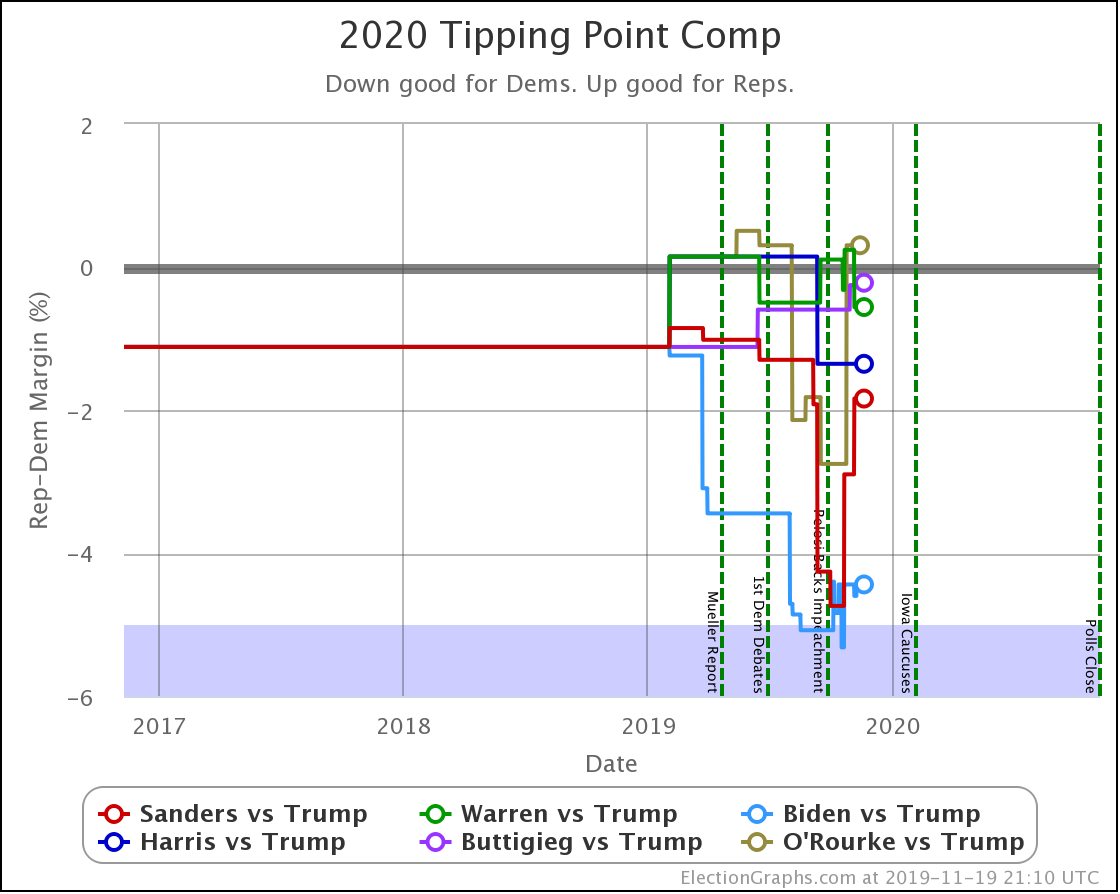
Looking at the tipping points, which is analogous to the popular vote, but adjusted for the structure of the electoral college, once again, Warren is the only Democrat who is improving.
Harris is flat.
Biden, Sanders, and Buttigieg all lose ground to different degrees.
Note that while for a short time, Biden had a tipping point greater than 5%, meaning he could win using only states where he led by more than 5% and didn't even need any swing states. That is no longer true.
Now all five of these Democrats have tipping points indicating that they need to win at least some tight states to win.
Now, moving on to the more elaborate probabilistic model I look at a bit more these days…
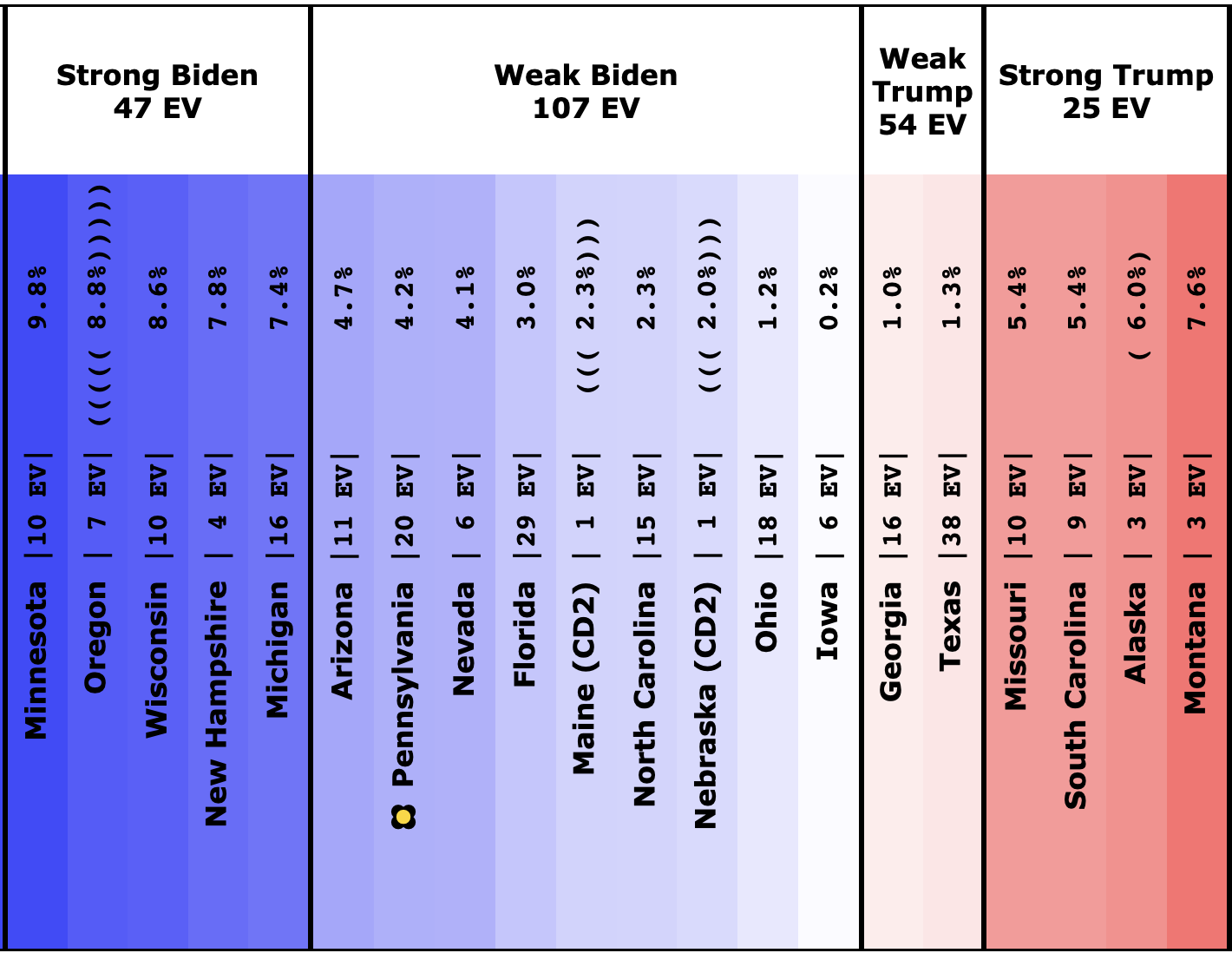
| Dem |
1 Nov |
20 Nov |
𝚫 |
| Biden |
+184 |
+158 |
-26 |
| Sanders |
+124 |
+88 |
-36 |
| Warren |
+36 |
+50 |
+14 |
| Harris |
+8 |
+12 |
+4 |
| Buttigieg |
-4 |
-6 |
-2 |
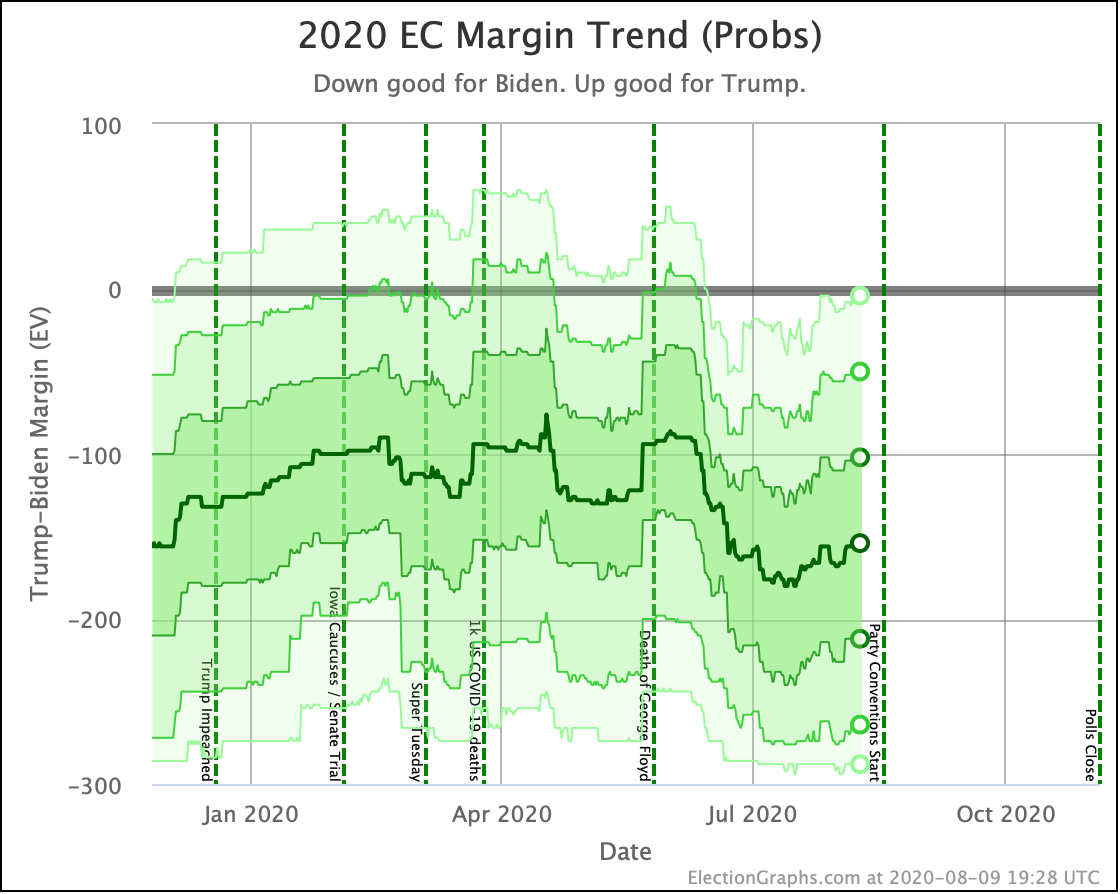
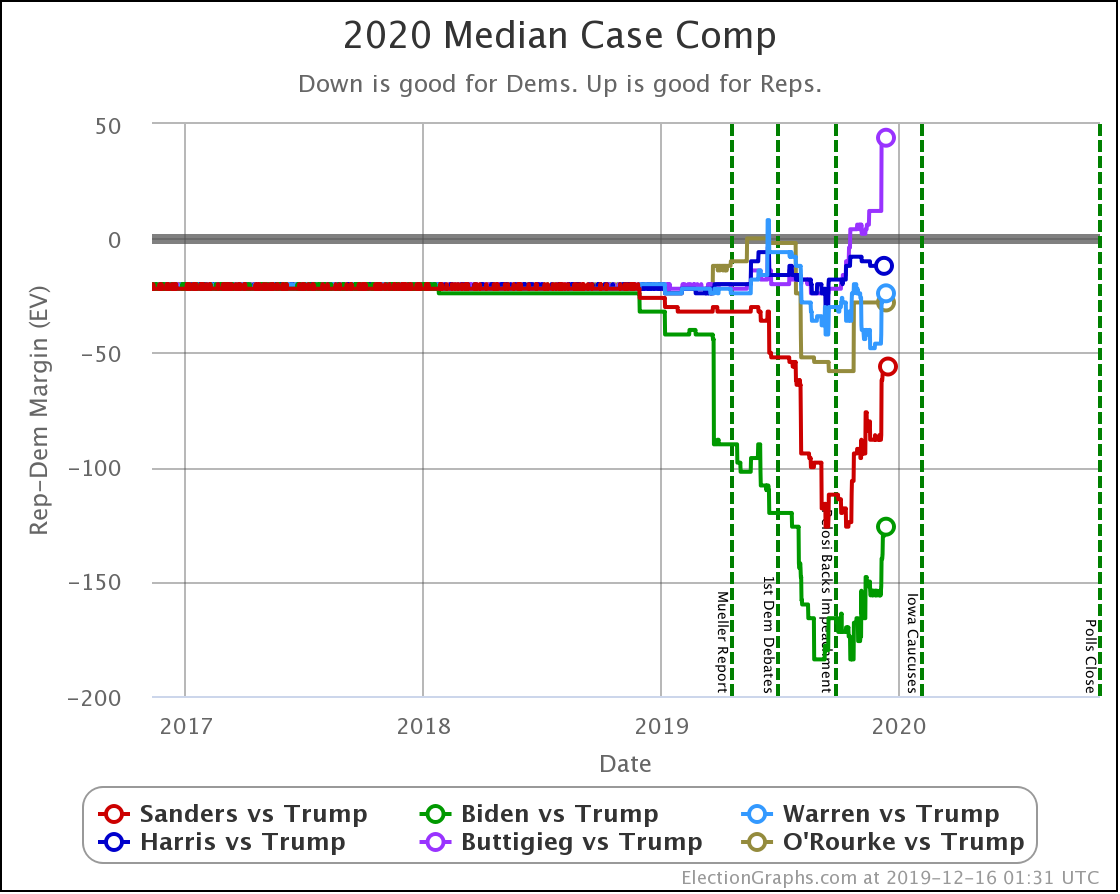
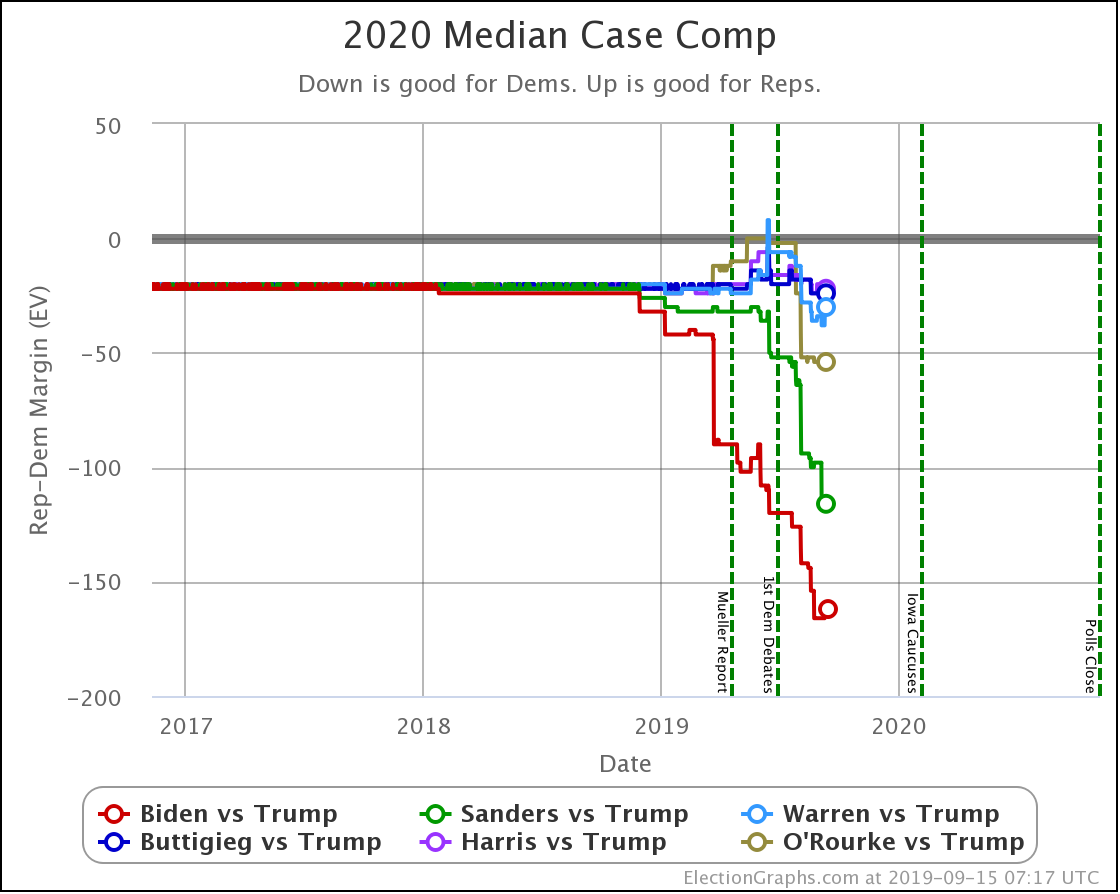
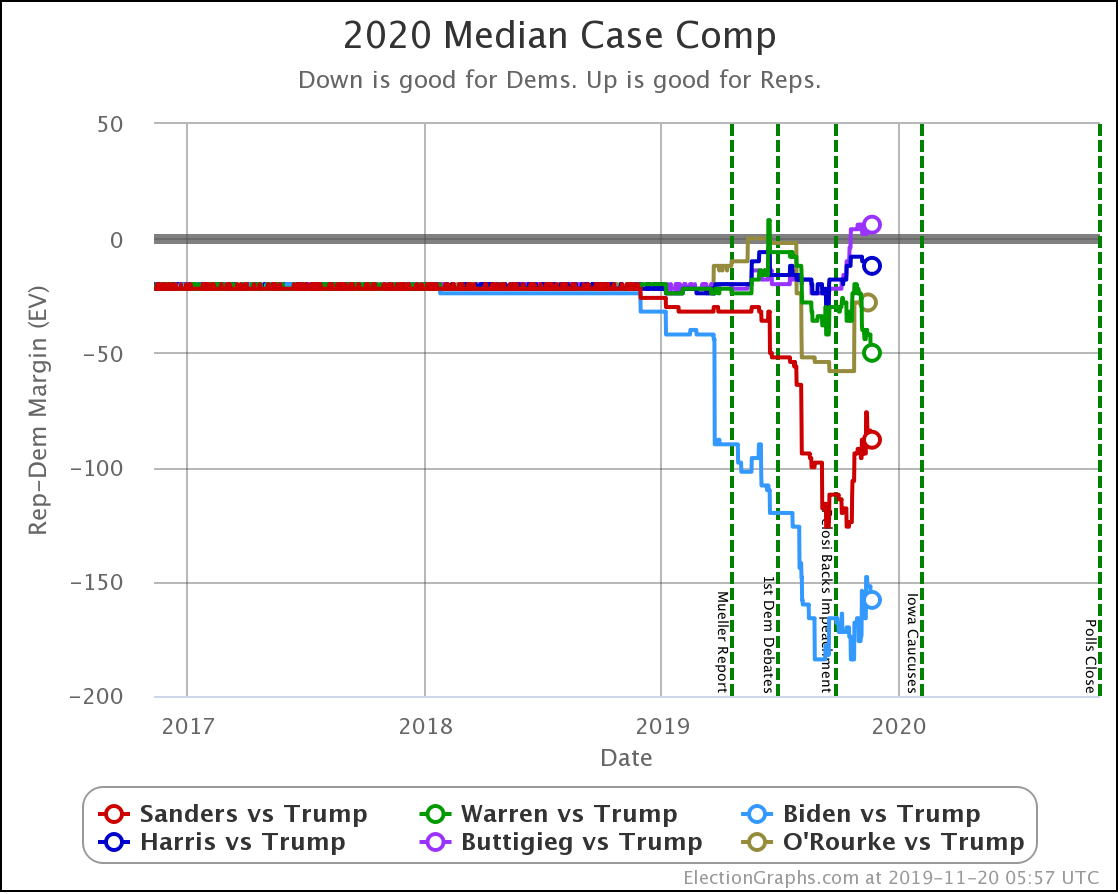
This view shows the "Median Case." The median case is the electoral vote margin in the exact middle of the 1,000,001 simulation runs done for each candidate combination when sorted by the margin. About half the time, the Democrat does better than this. About half the time, they do worse.
Warren and Harris both improve a bit. Biden, Sanders, and Buttigieg all lose ground.
Note that while in the classification view, all five Democrats lead Trump, in the probabilistic view, Buttigieg's median case is actually to lose.
But we need to look at probabilities, not the single "median case" estimate. You should not think that since a candidate is ahead or behind on the median case, that maps to winning and losing.
For instance, Buttigieg's median case is a six electoral vote loss to Trump. But if you look at the 2σ range, that is the range of outcomes that you would expect to occur 95.45% of the time; you get a range from Buttigieg winning by 92 electoral votes to Trump winning by 90 electoral votes.
There is a huge range of possibilities. It isn't just "Trump is ahead in the median case, so he wins."
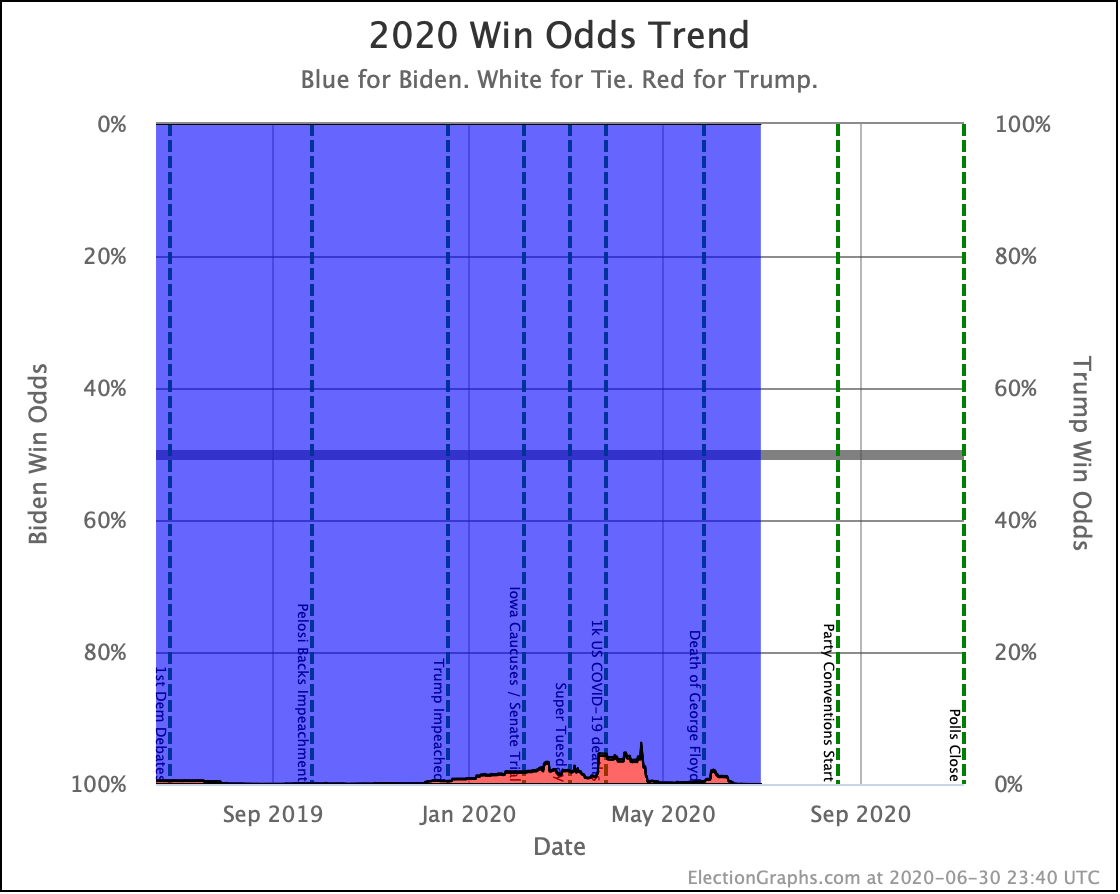
So time to look at the win odds…
| Dem |
1 Nov |
20 Nov |
𝚫 |
| Biden |
100.0% |
99.9% |
-0.1% |
| Sanders |
98.3% |
95.0% |
-3.3% |
| Warren |
73.1% |
81.8% |
+8.7% |
| Harris |
54.6% |
58.2% |
+3.6% |
| Buttigieg |
46.0% |
44.3% |
-1.7% |
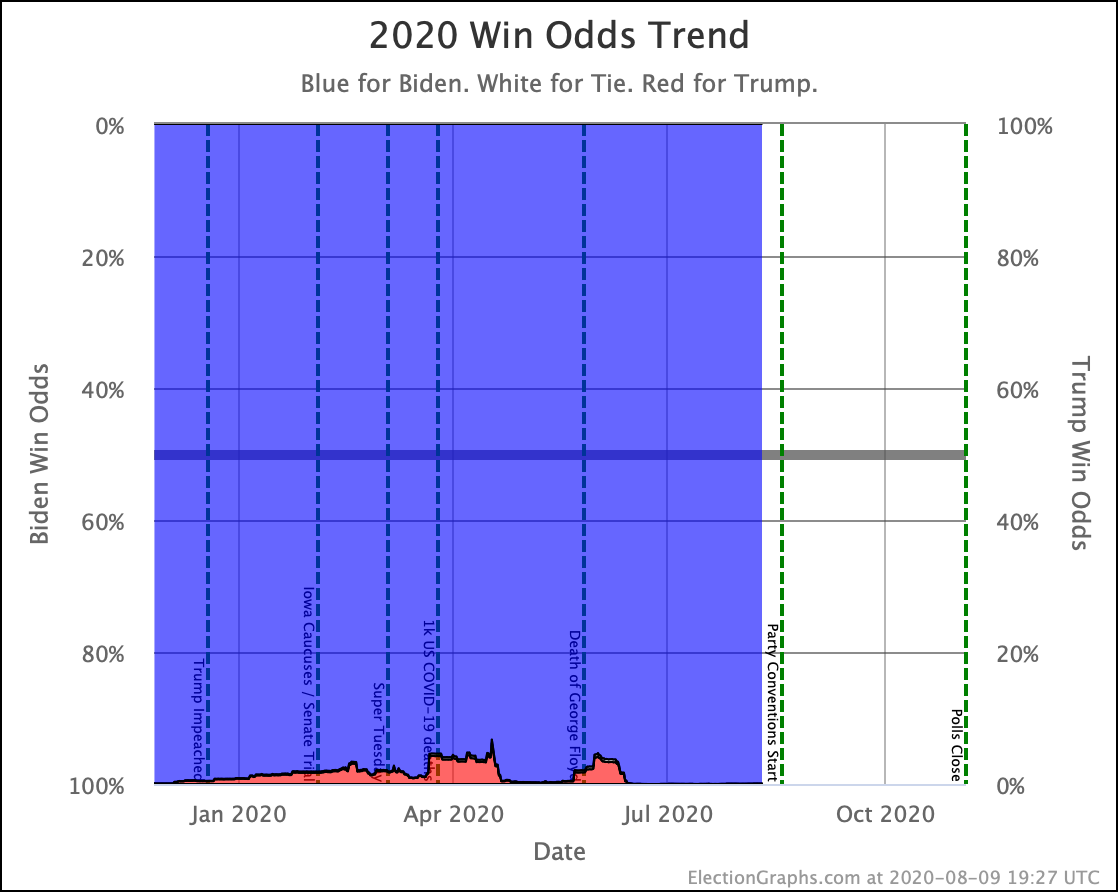
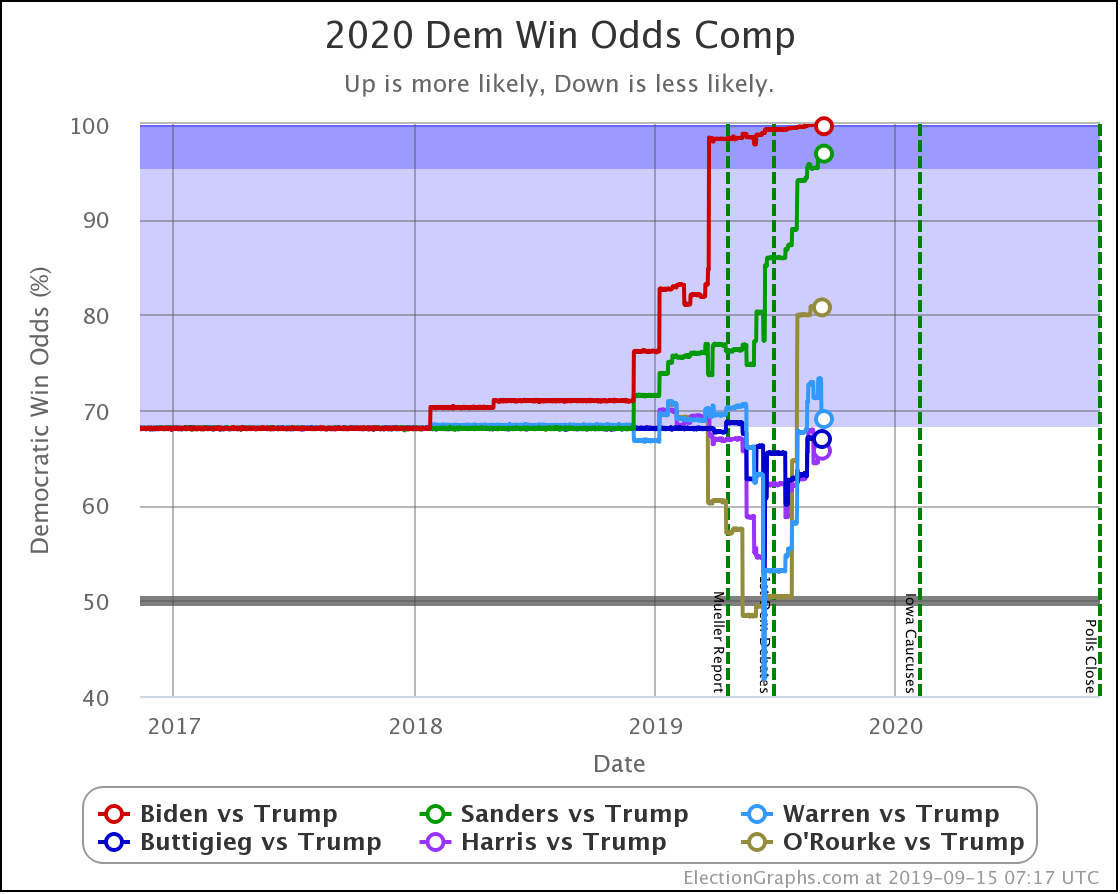
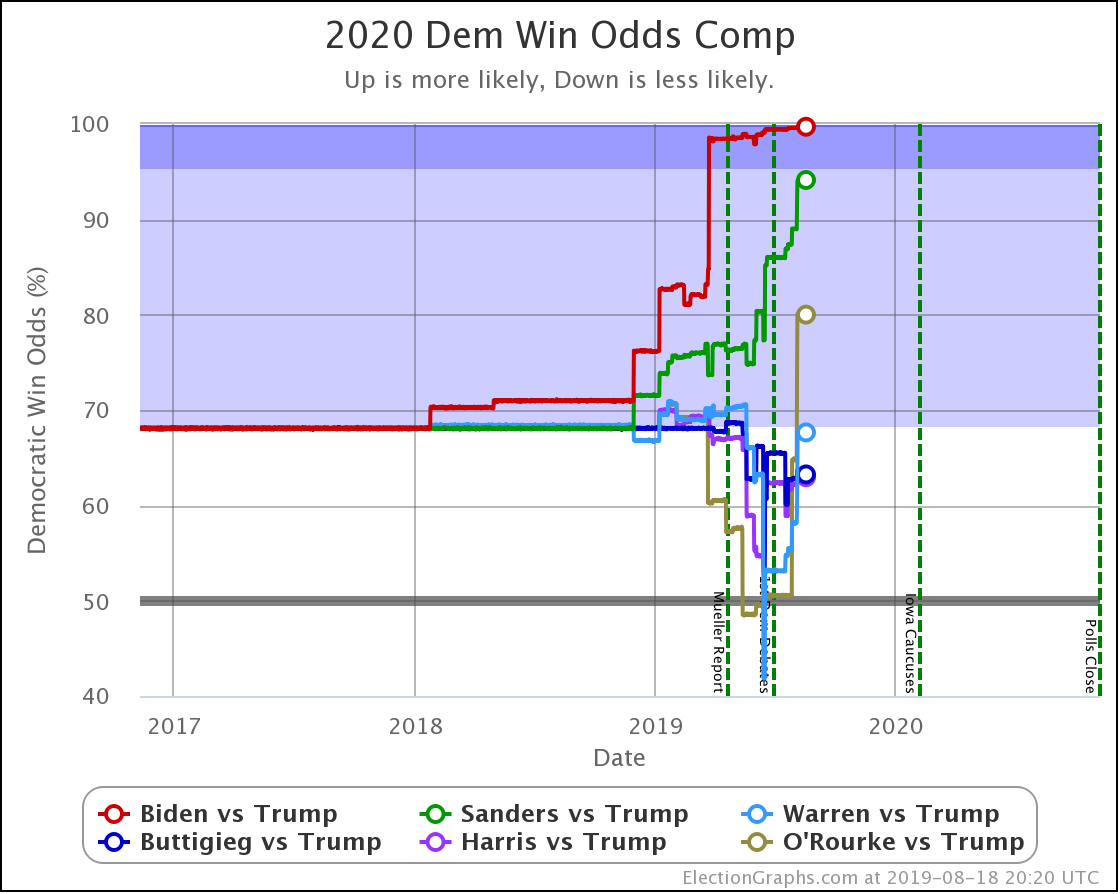
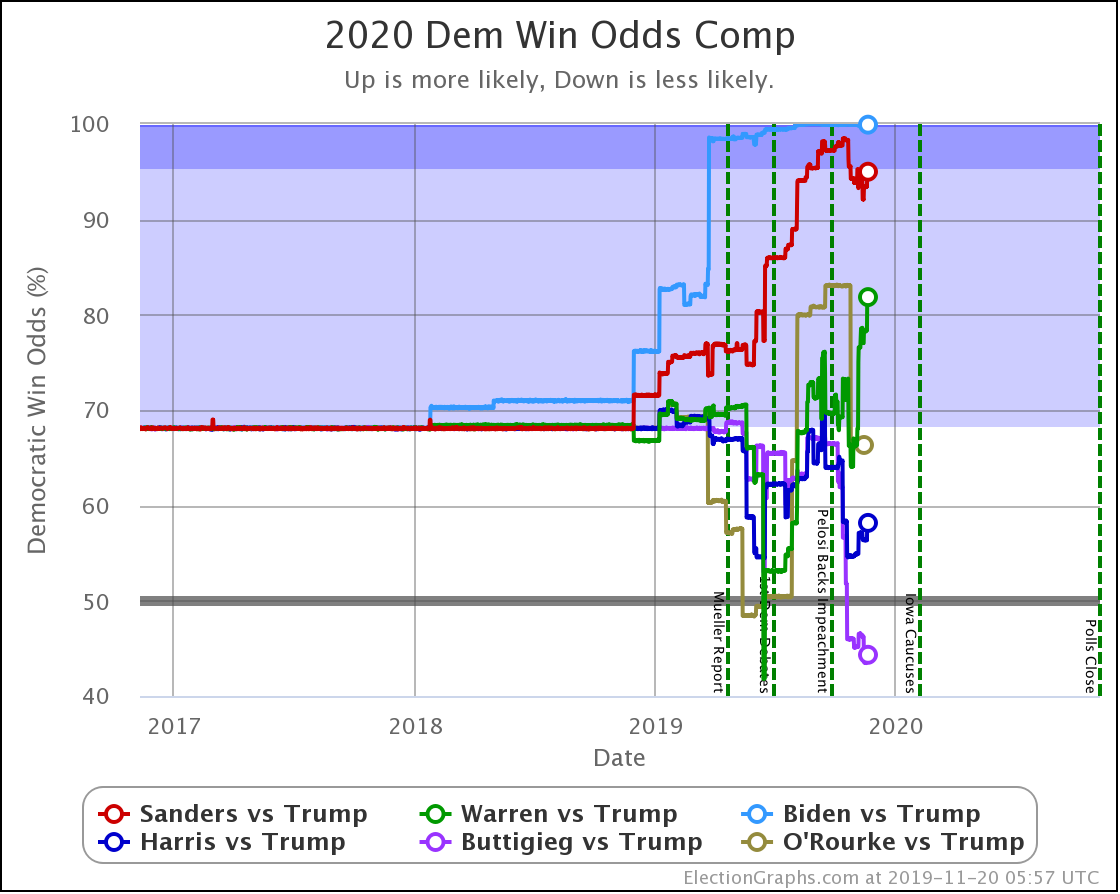
The trends above, which cover just under three weeks, show Warren and Harris improving, while Biden, Sanders, and Buttigieg slip back.
But looking back a bit farther, we can see some overall trends going back to September.
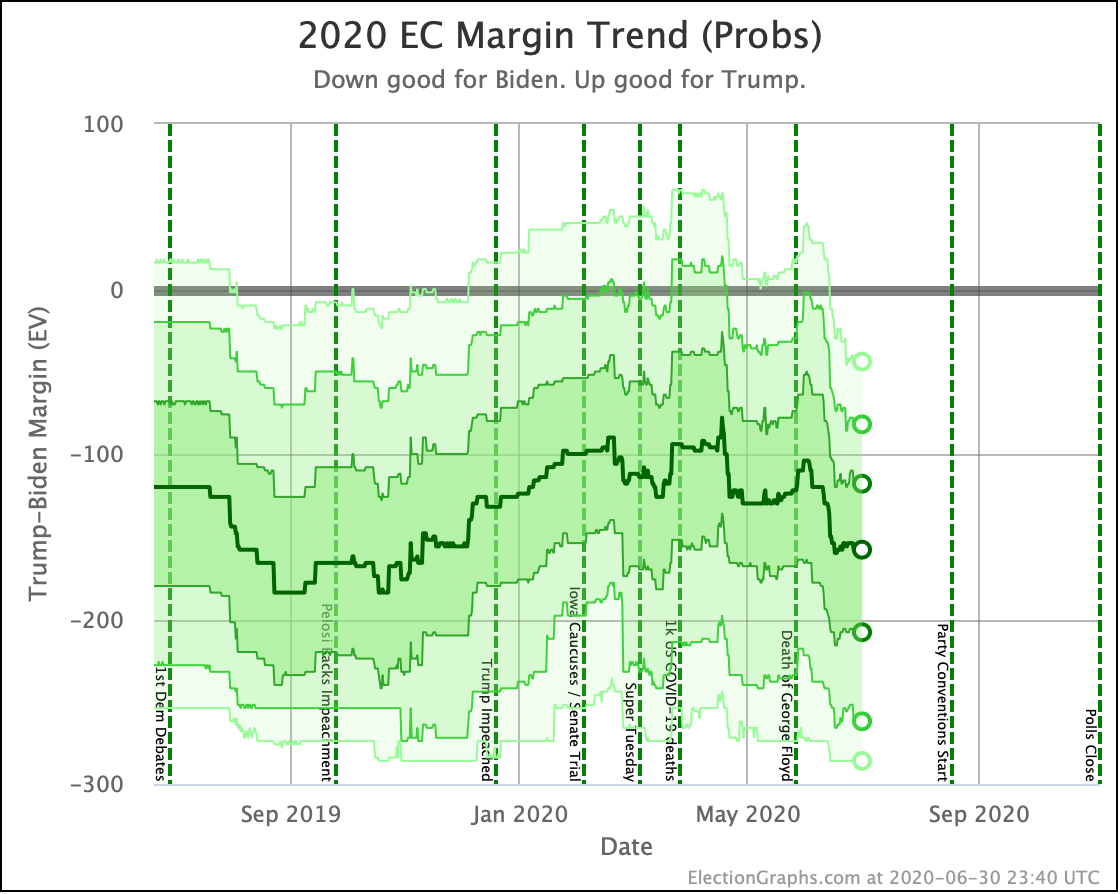
Biden continues to be pegged at a 99%+ chance of winning. His lead in some states has slipped, but his overall margins are high enough that this hasn't yet started to impact his chances of winning.
Sanders never had as big a margin lead as Biden, so as some of those states slipped back toward Trump, you see a more significant impact on his odds of winning.
Harris and Buttigieg have never done all that much better than a coin flip against Trump, peaking at around a 70% chance of winning. But since September, they have both dropped significantly, with Buttigieg now only at a 44.3% chance of winning, and Harris only at 58.2%.
The only candidate consistently improving over the last few months has been Warren. She bottomed out at only a 41.7% shot of winning in June, and while there have been ups and downs, the trend is clearly in Warren's direction.
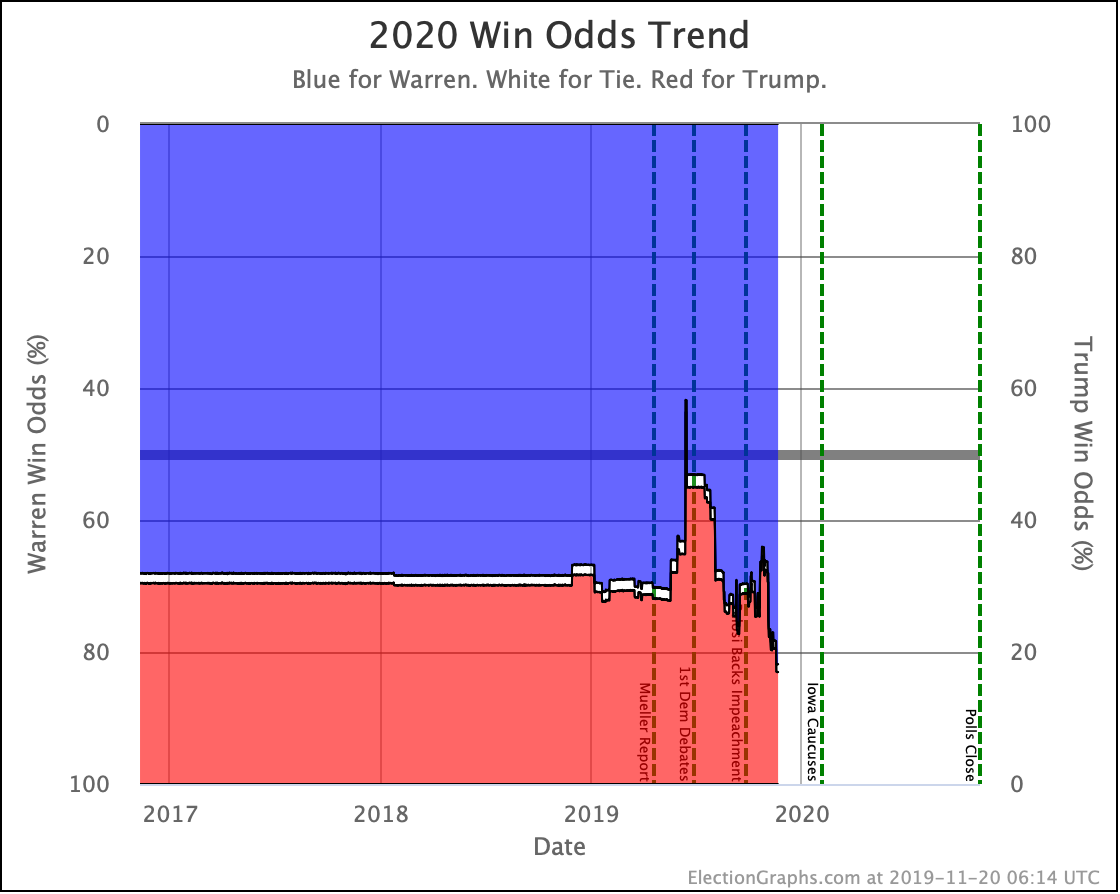
We will, of course, see if that lasts. As can be seen by the spike toward Trump in June, trends can reverse quite quickly.
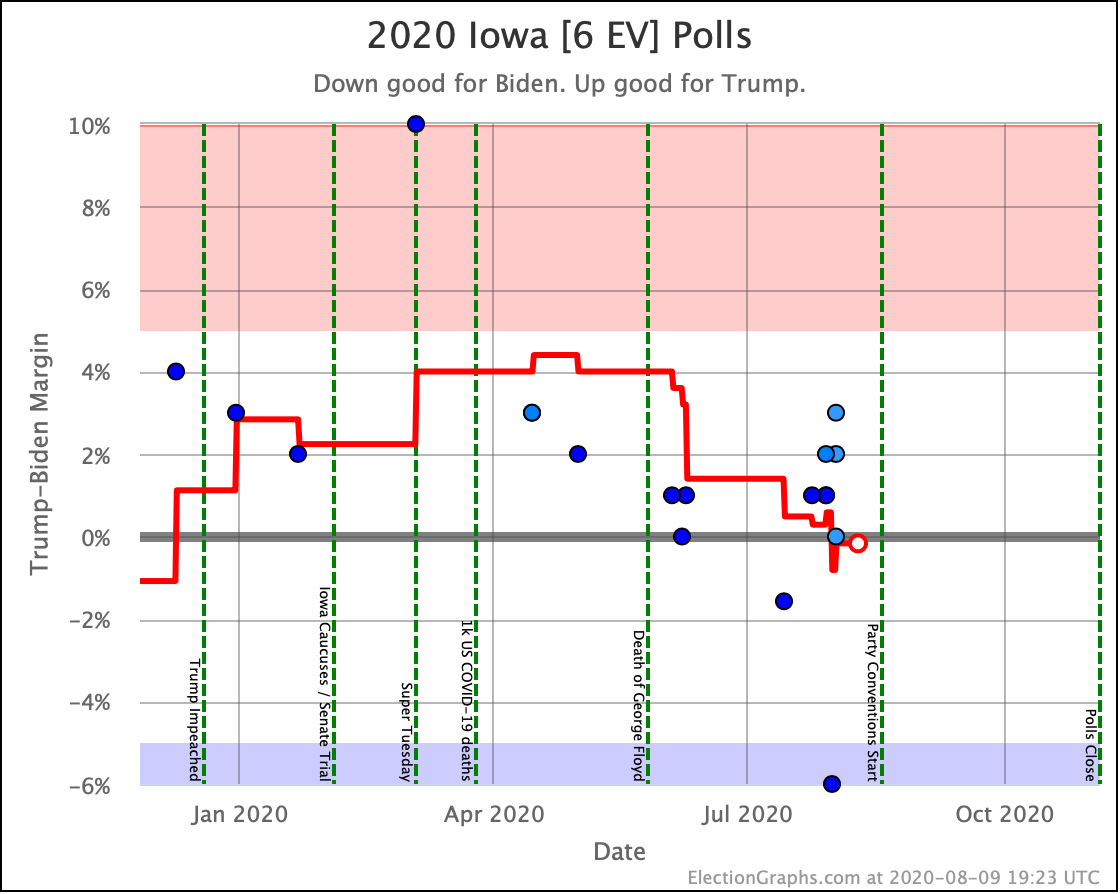
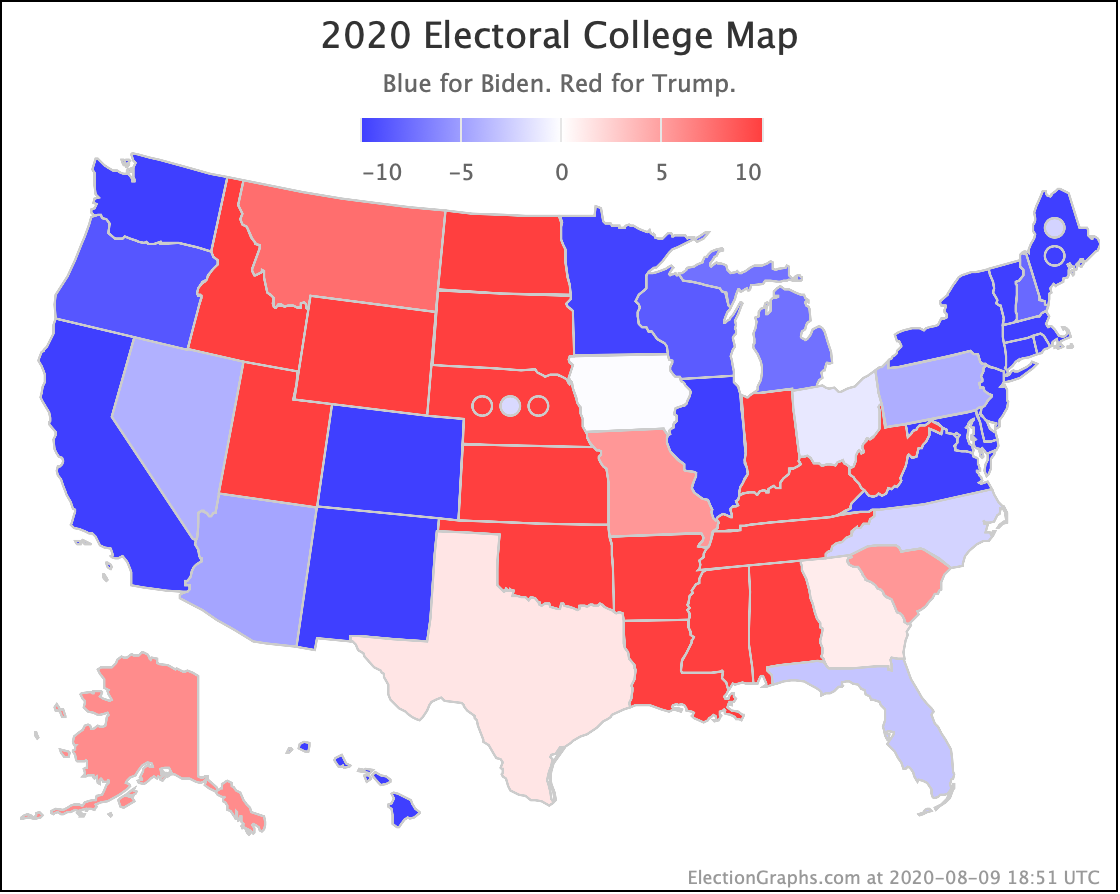
Now, besides Texas, here are a few additional states where there are trends worth noting. (Since so many places had new polls, I'll skip a few where there is less to comment on.)
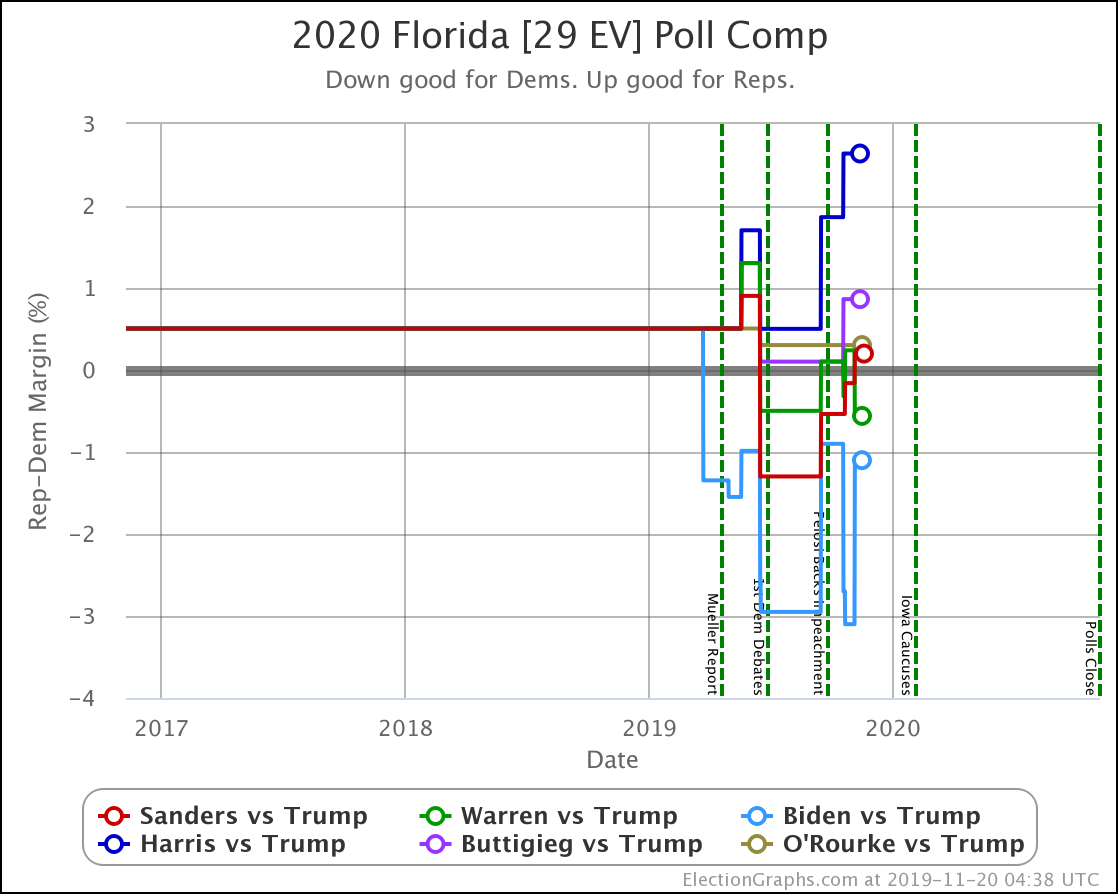
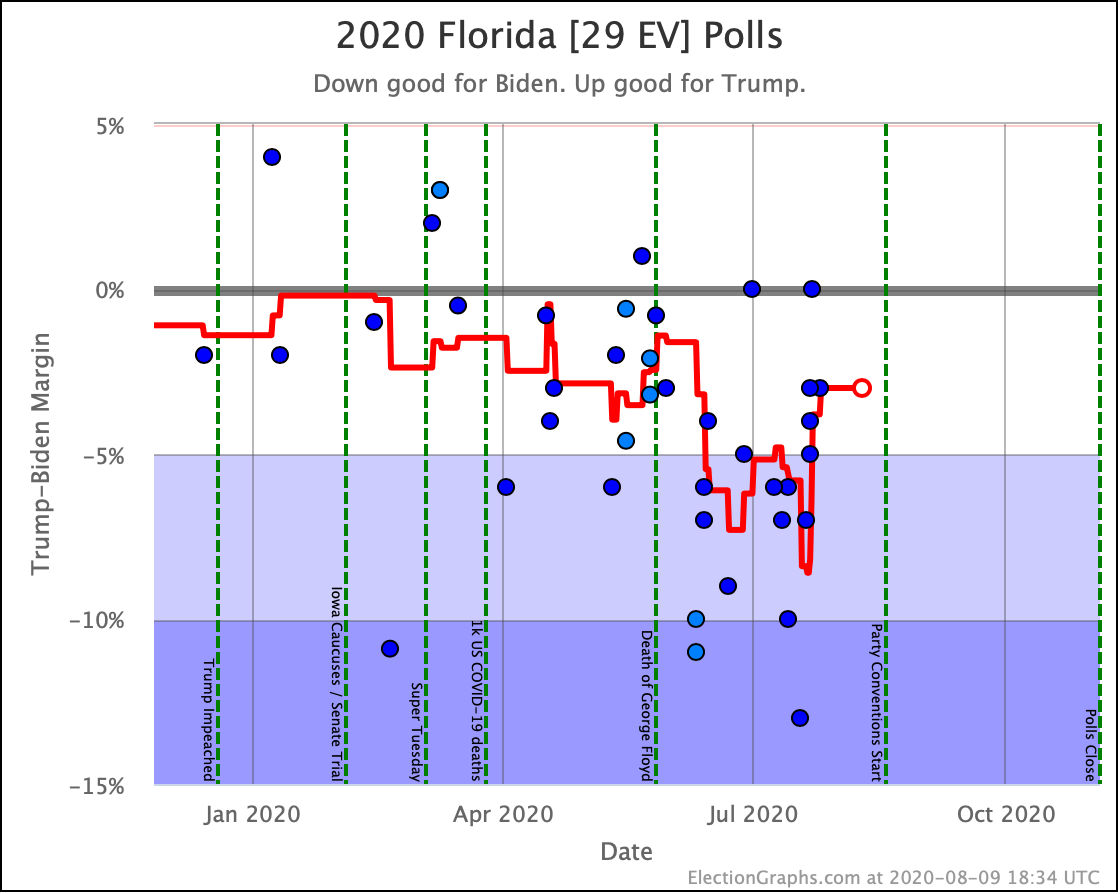
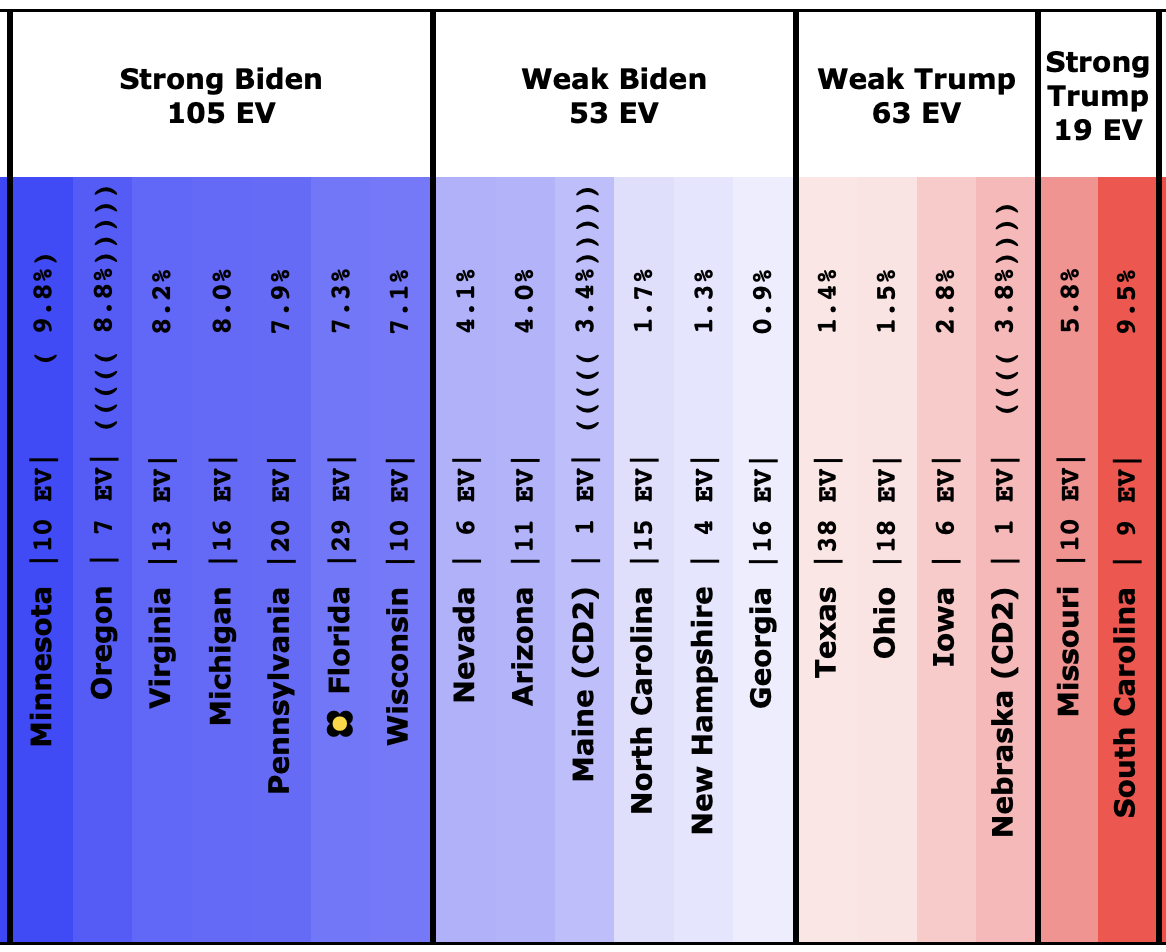
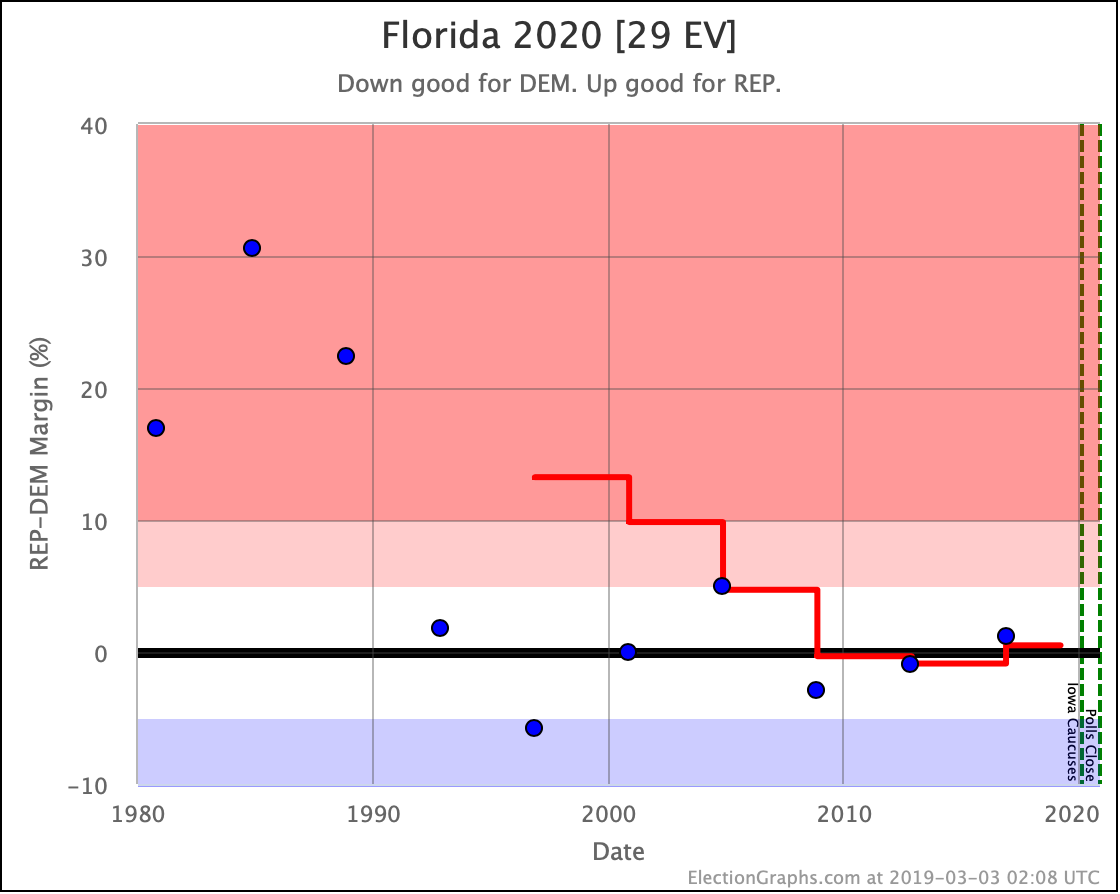
No clear trends in Florida except to note that it is an exceptionally close race no matter which Democrat you match up against Trump. As has been usual for the last few presidential races, Florida is right on the line. And it is big. So it makes a huge difference.
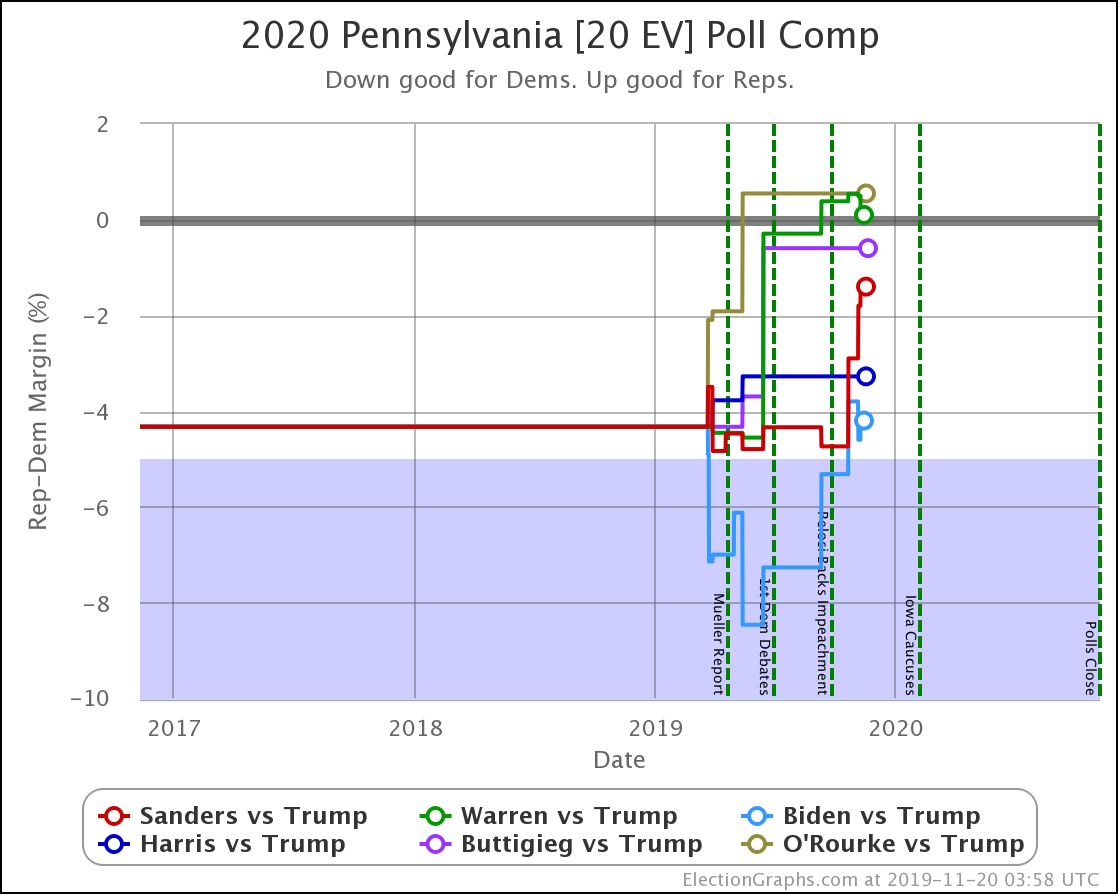
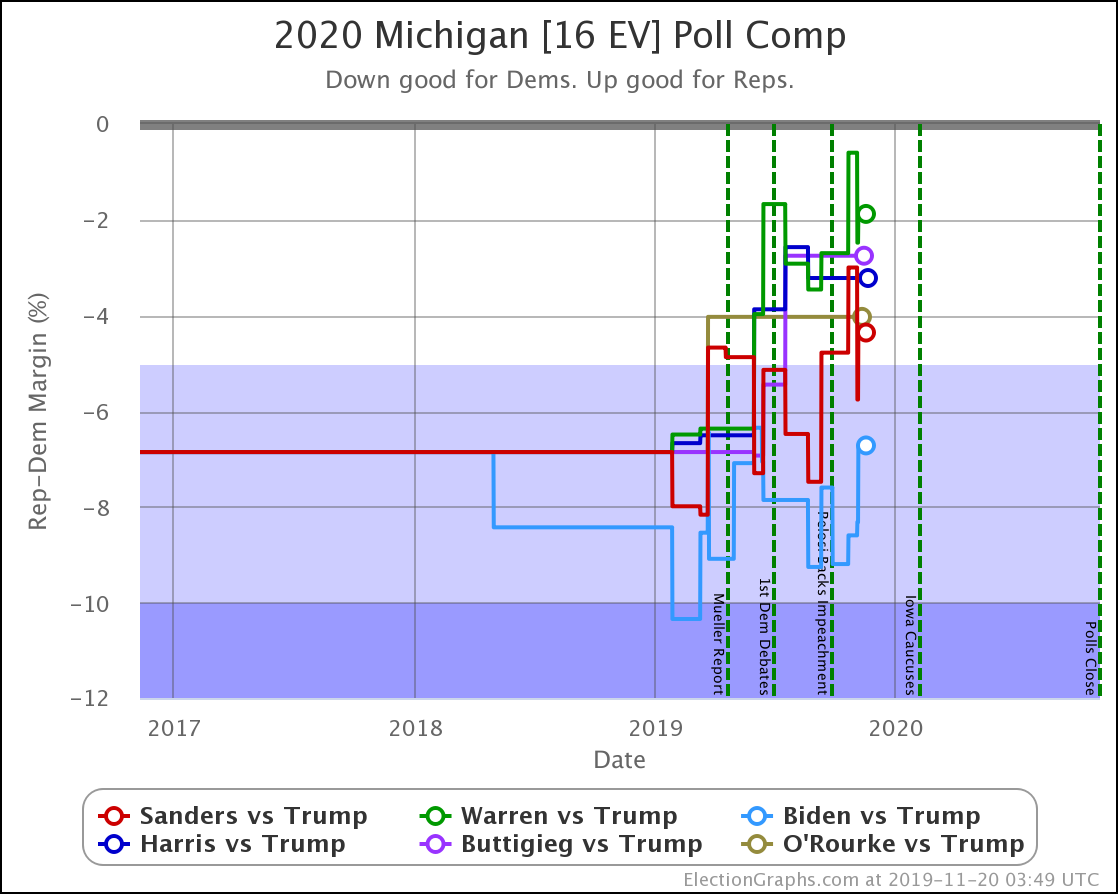
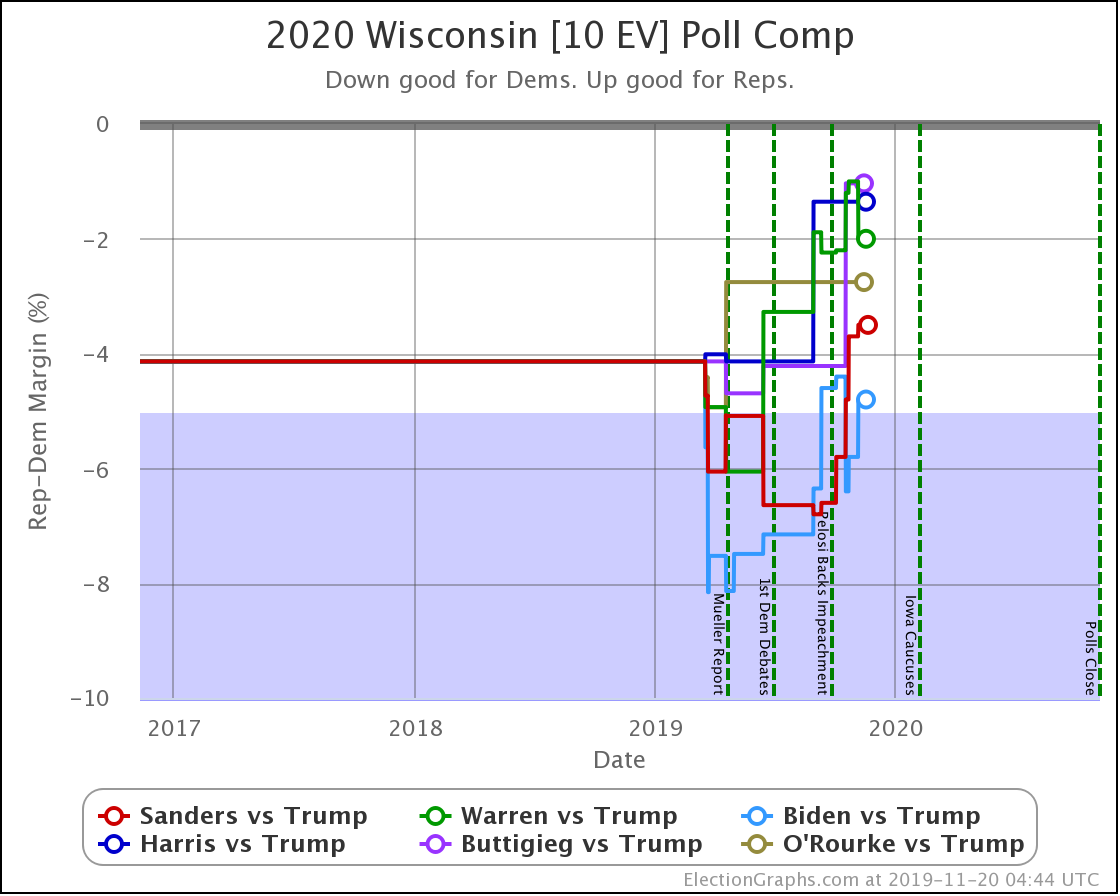
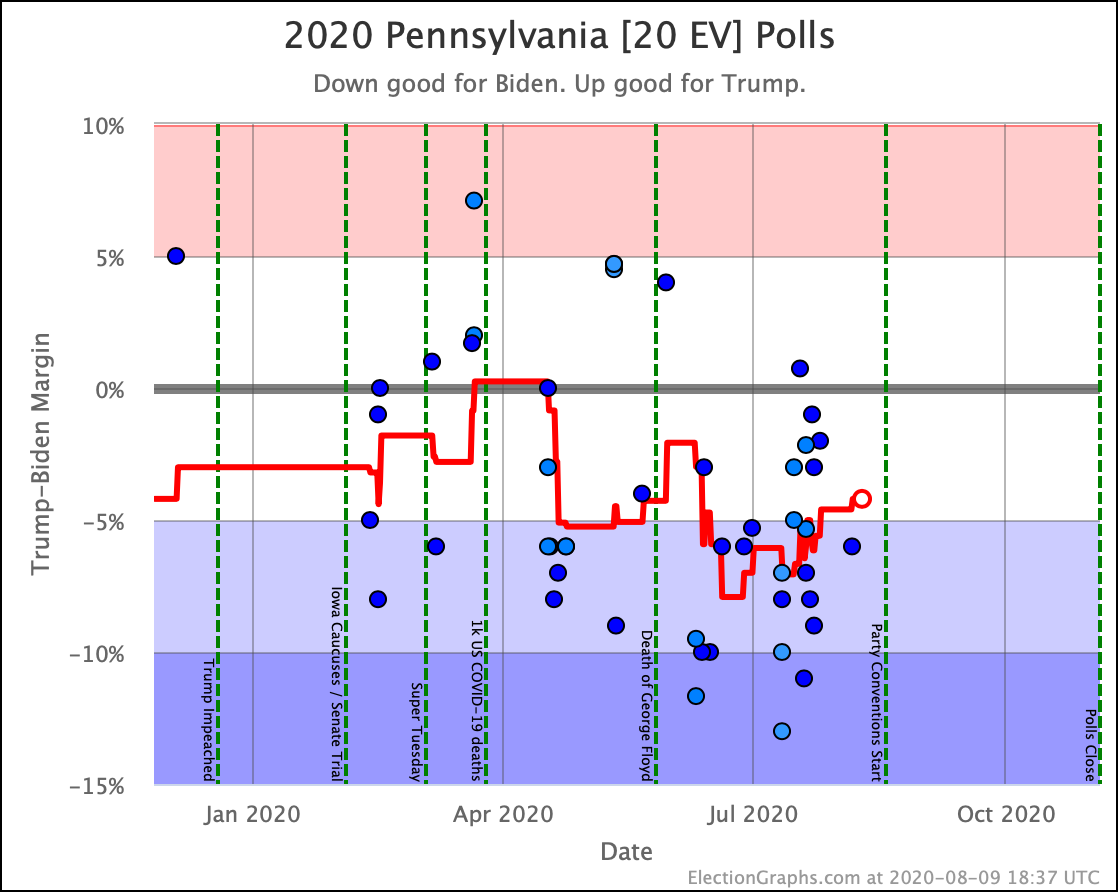
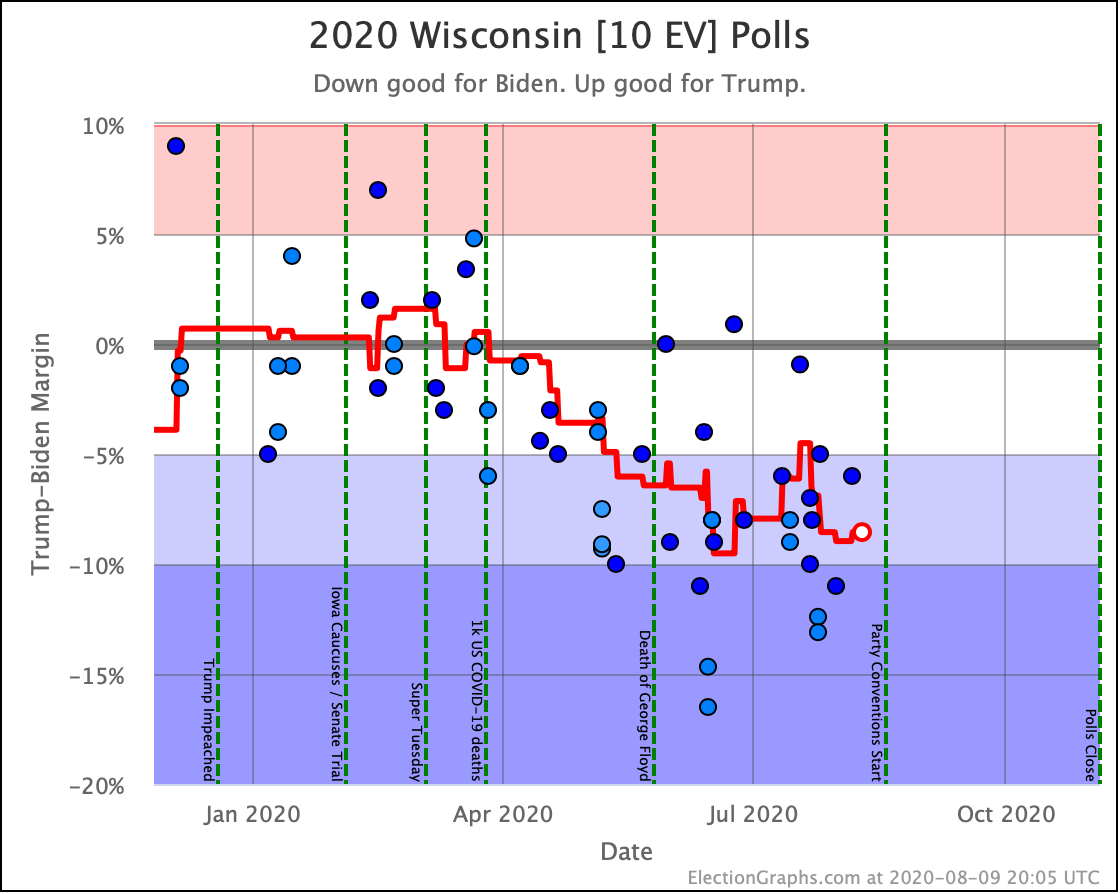
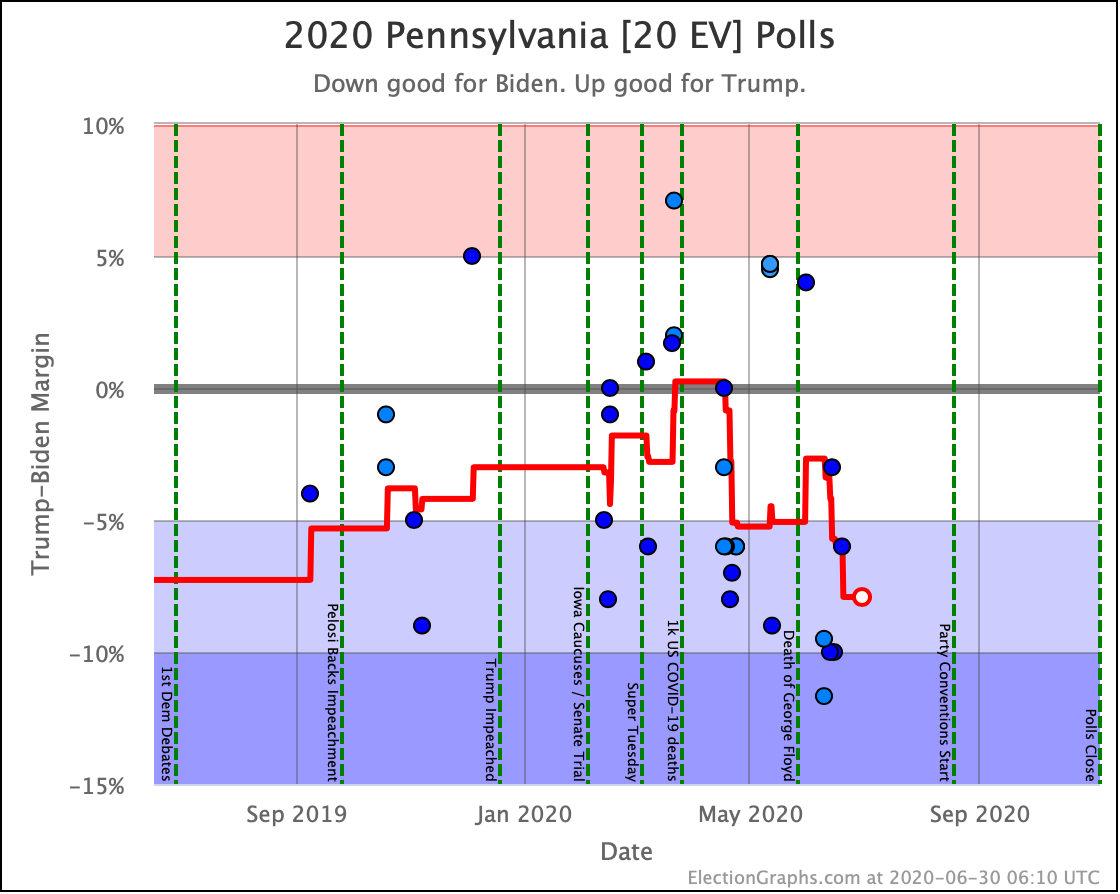
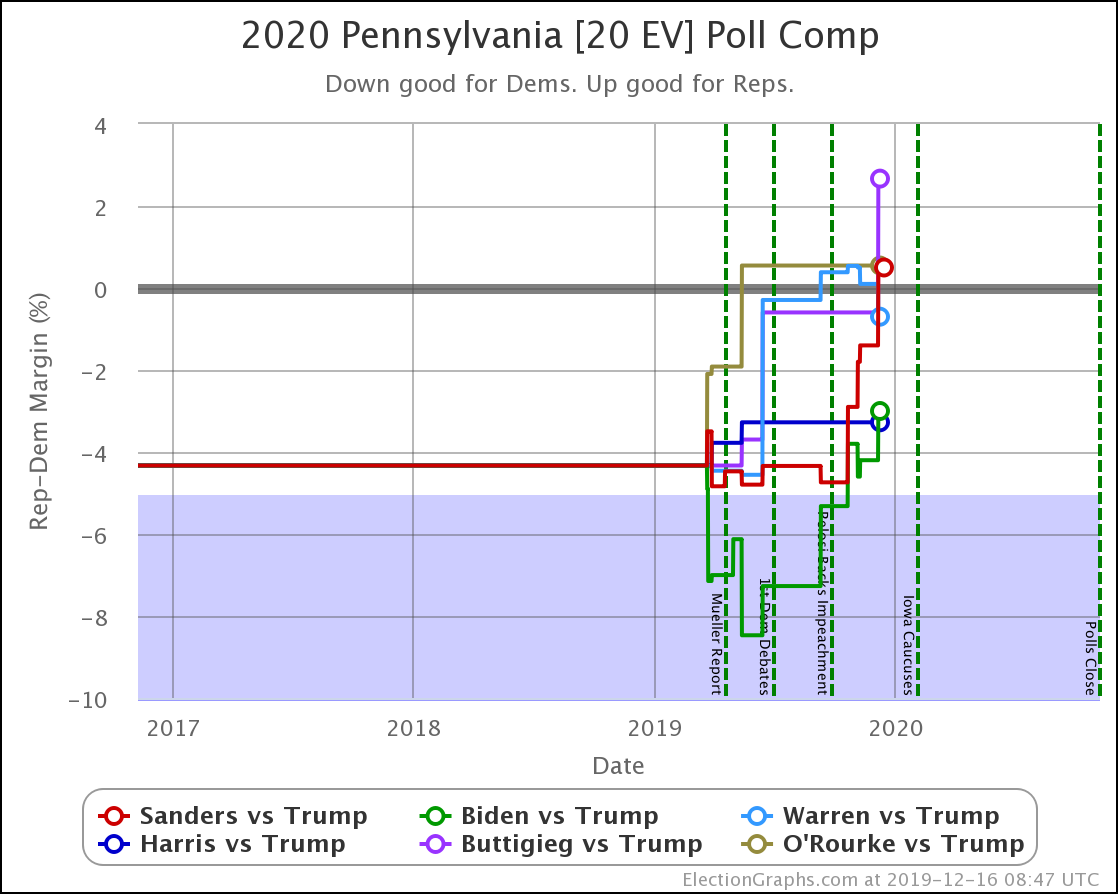
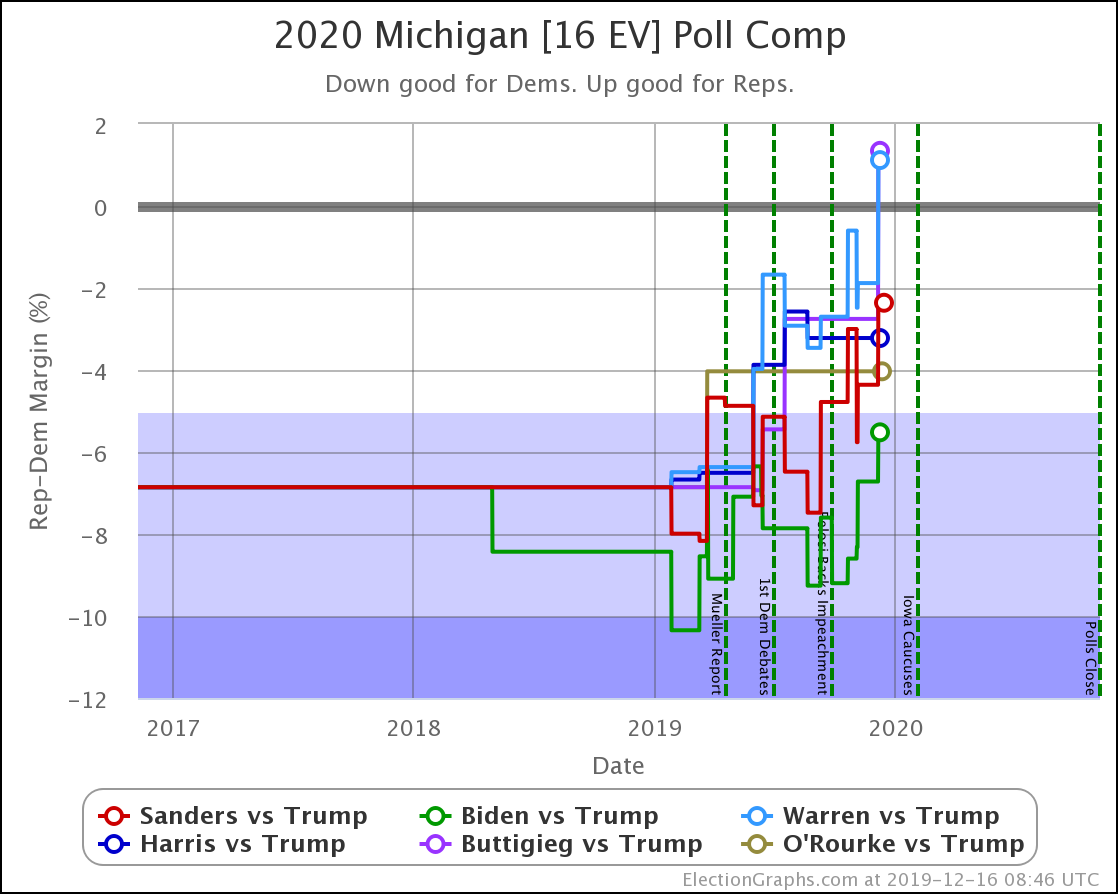
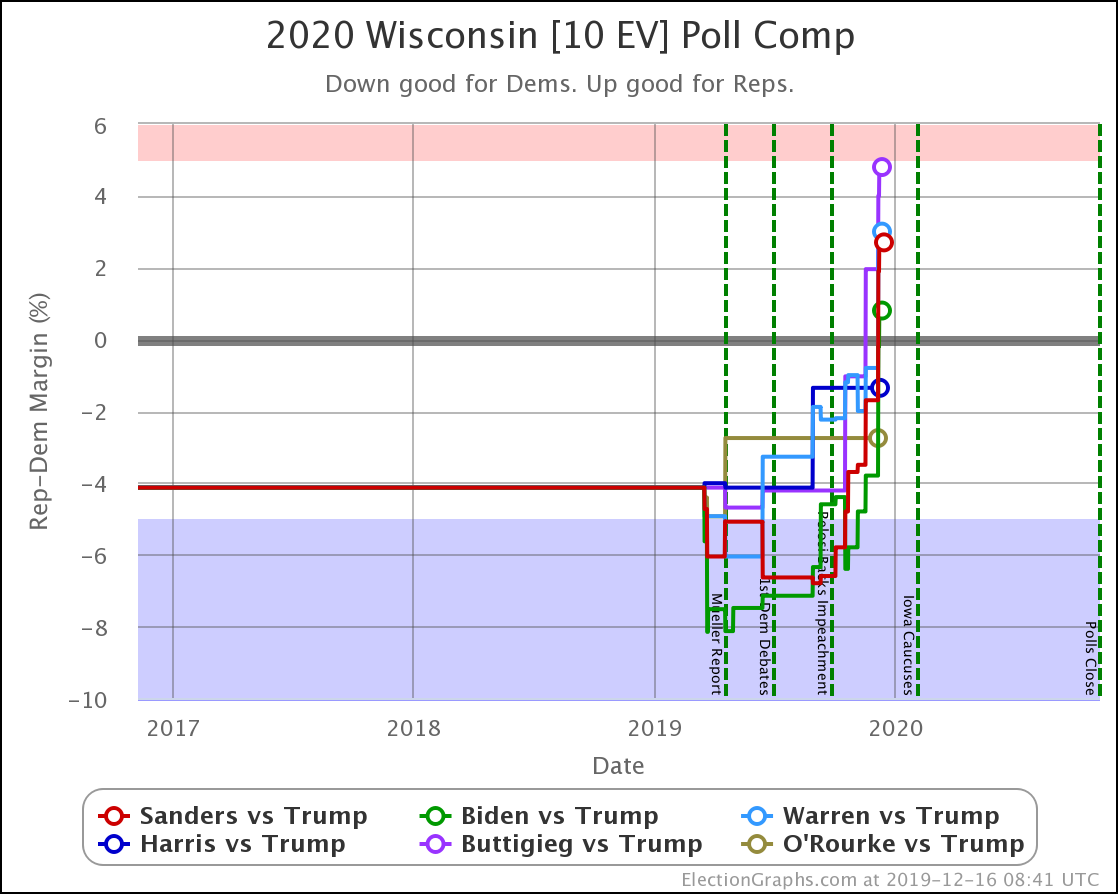
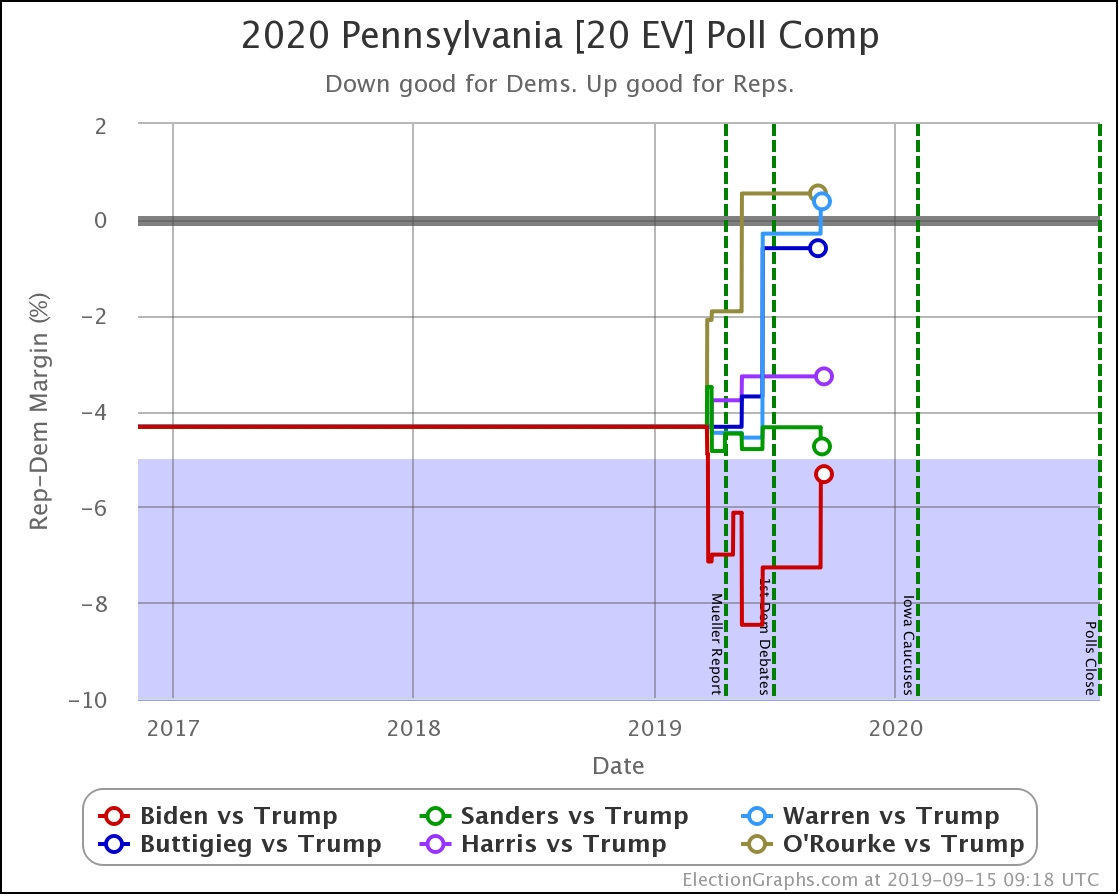
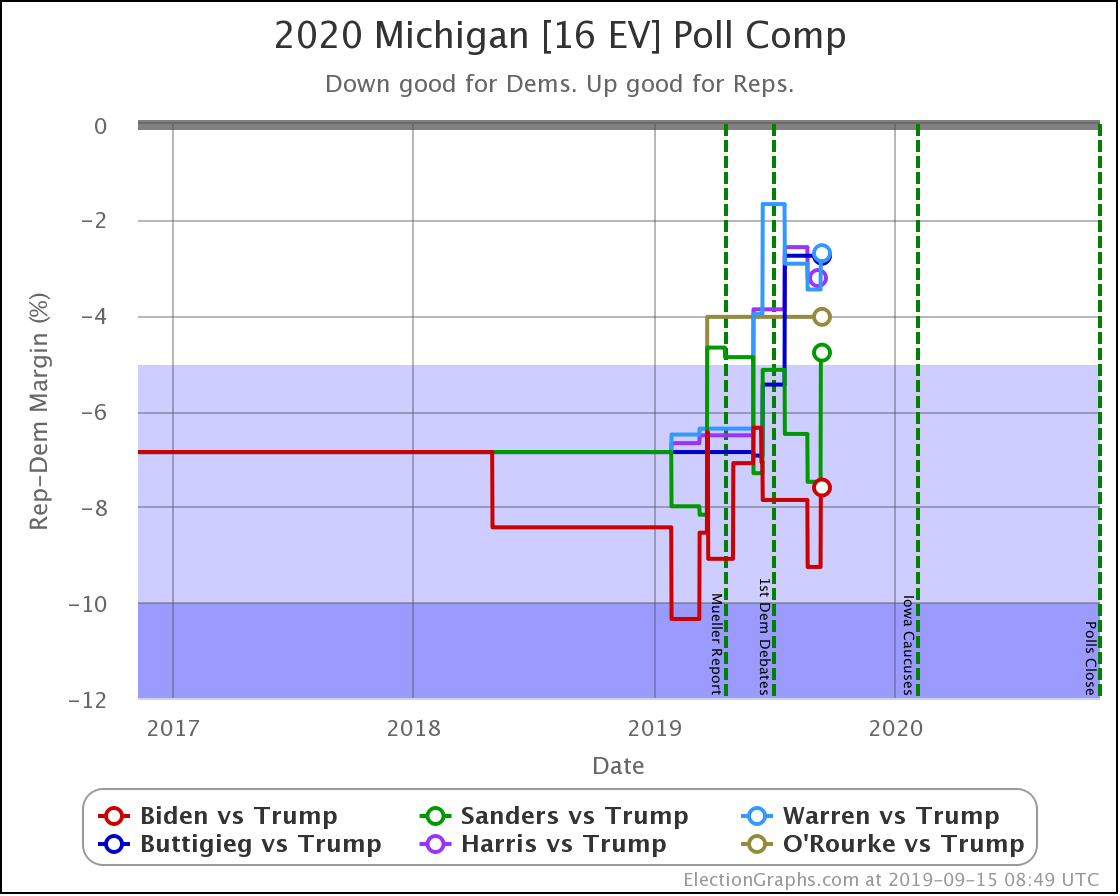
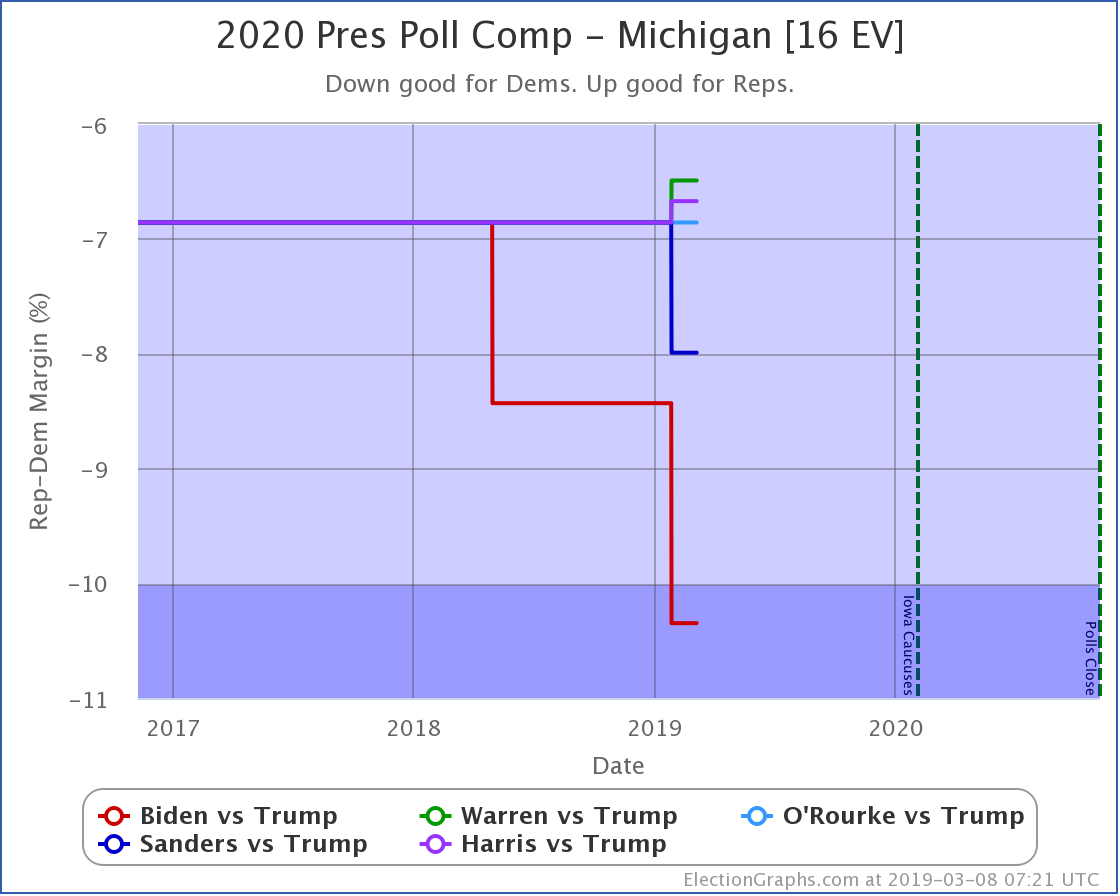
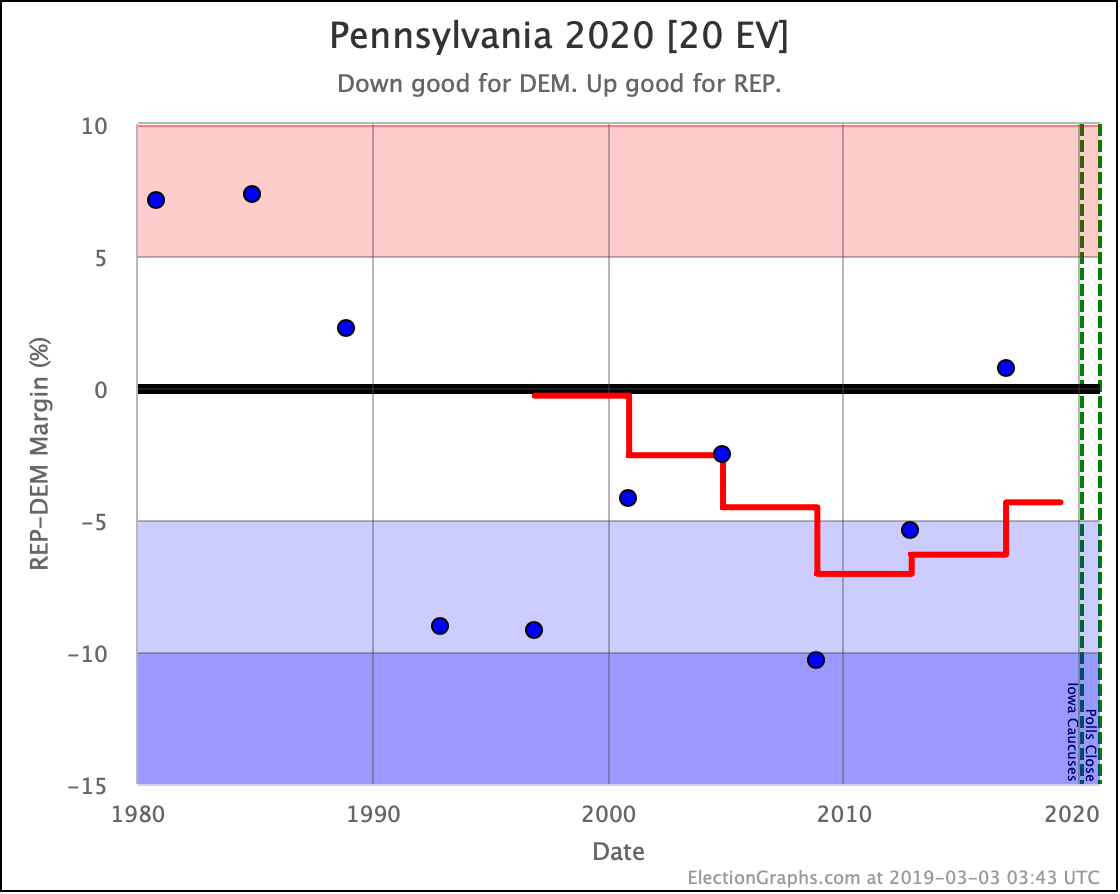
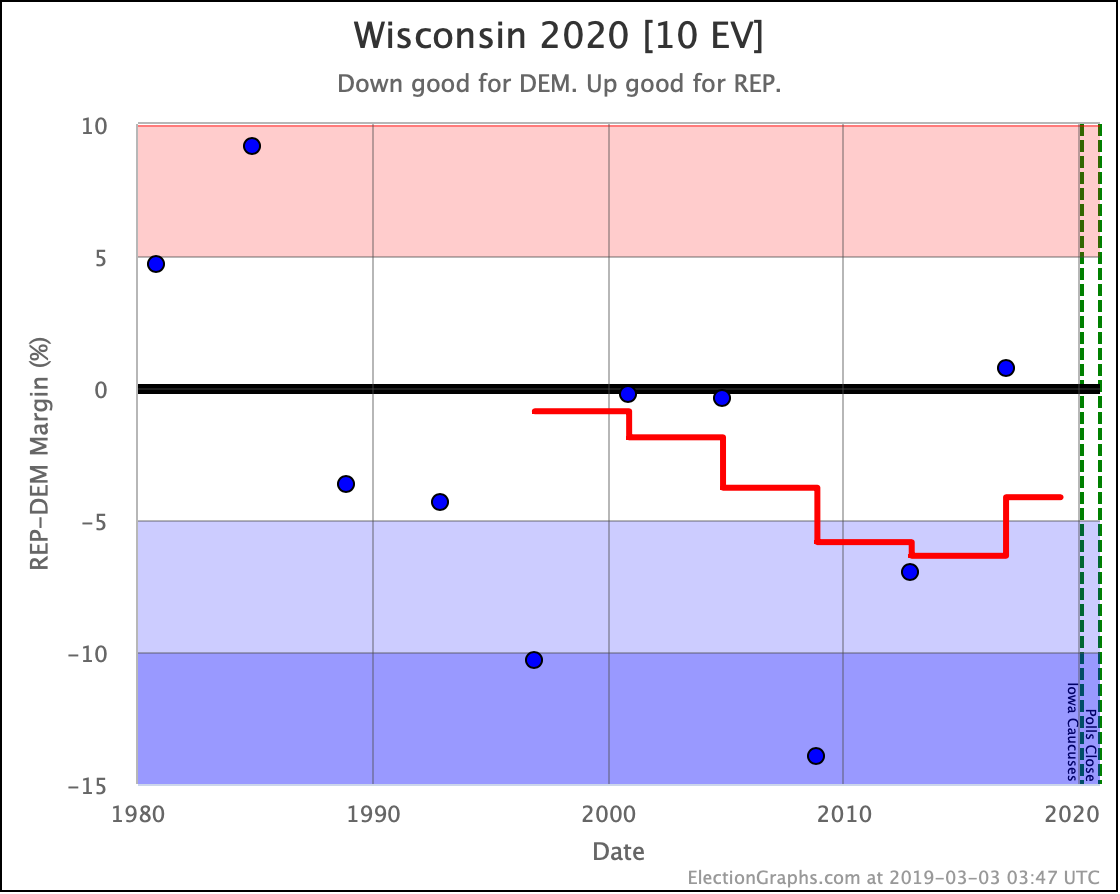
The general trend in Pennsylvania, Michigan, and Wisconsin over the past few months has been for Democratic leads to decrease.
In Pennsylvania, there is no Democrat with more than a 5% lead, and Warren (and O'Rourke) are both slightly behind.
At this point, only Biden has a lead higher than 5% in Michigan.
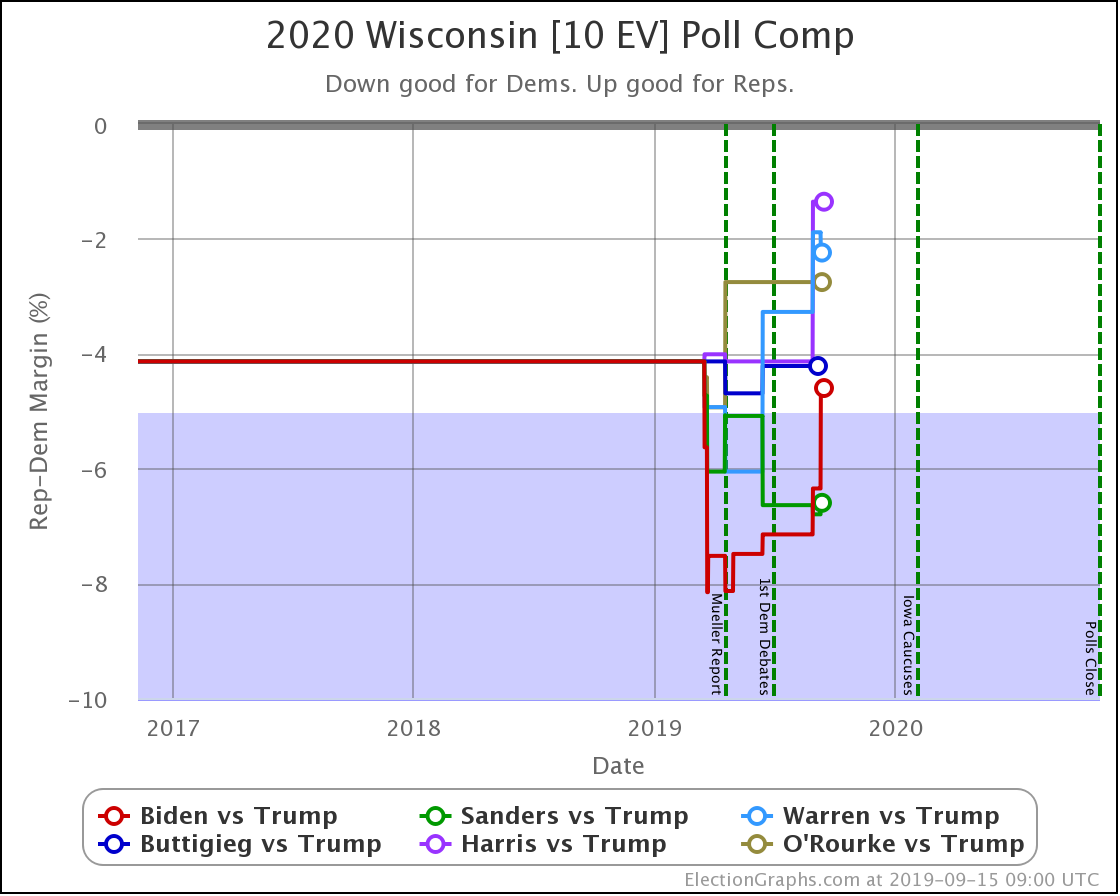
In Wisconsin, all the Democrats still lead, but none by more than 5%.
These are, of course, the three states that gave Trump his victory in 2016. At the moment, they are all looking to be close battlegrounds once again.
The people who say that the Democratic nominee needs to pay close attention to these states are certainly not wrong.
And at the moment, the Democrats seem to be slipping in all three.
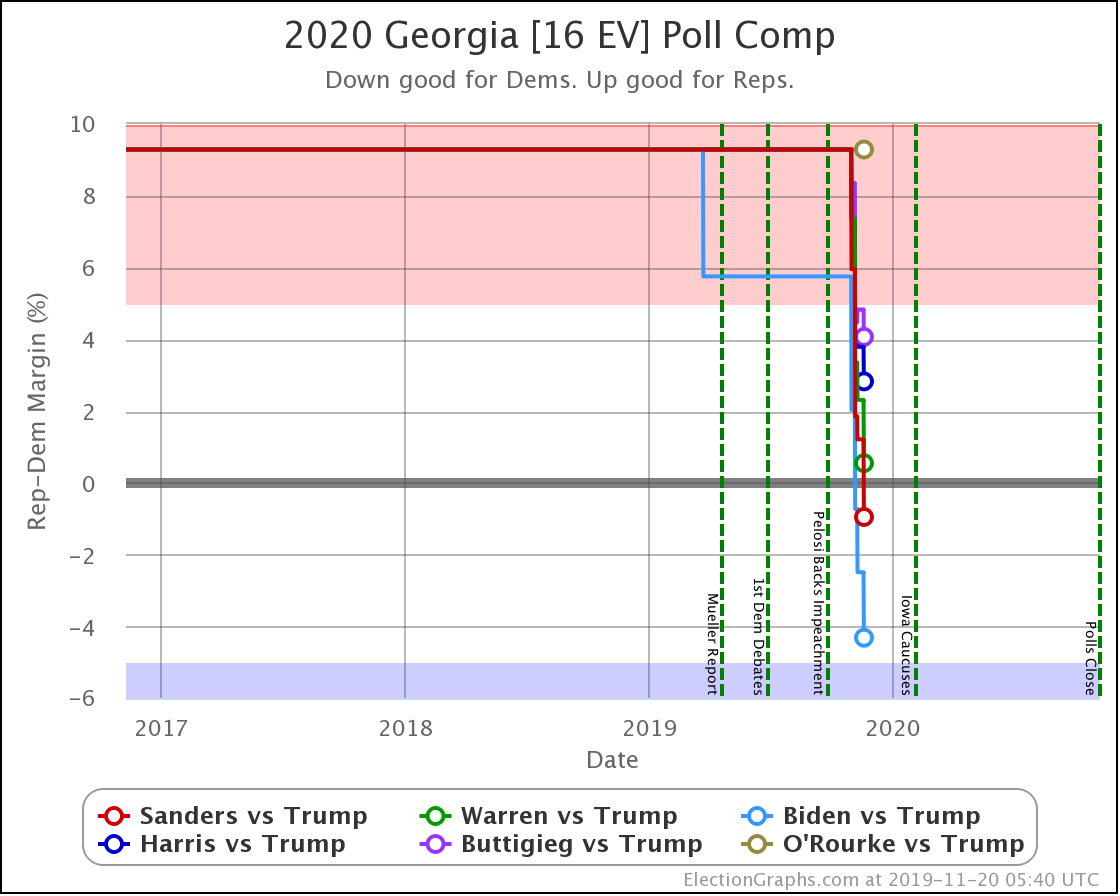
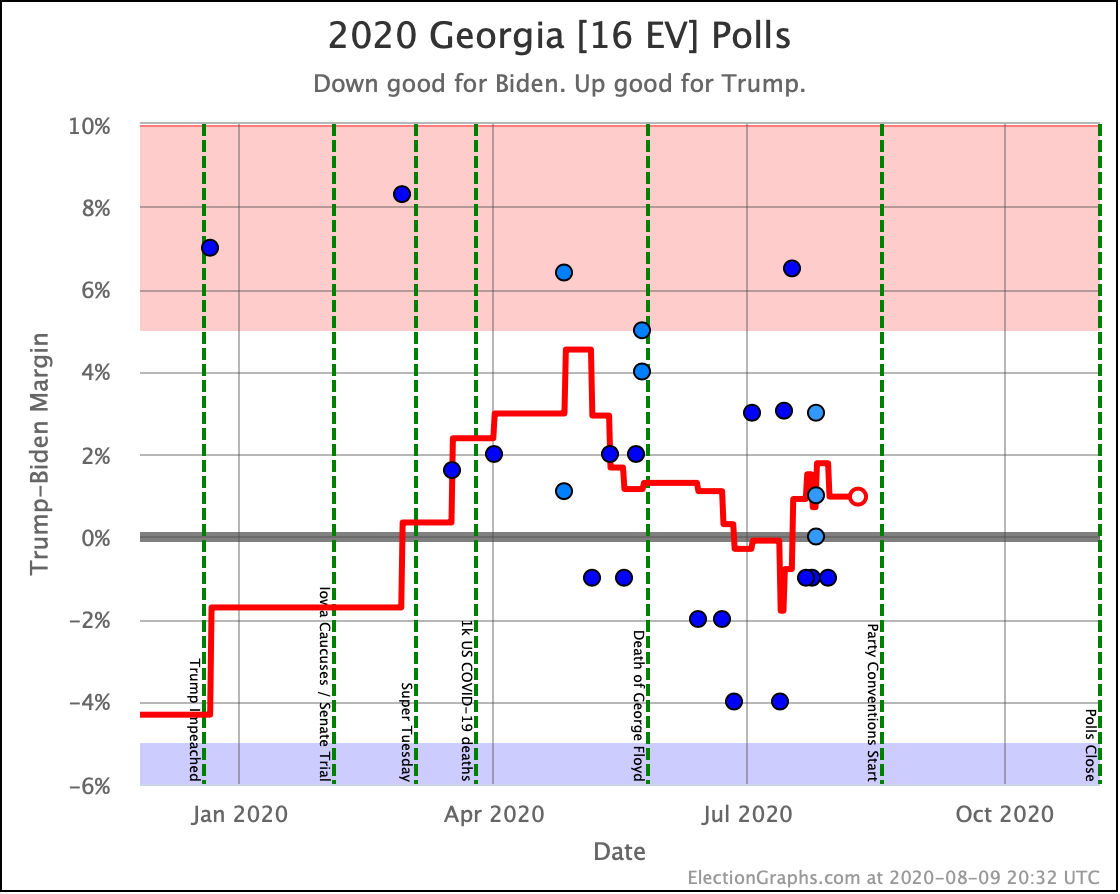
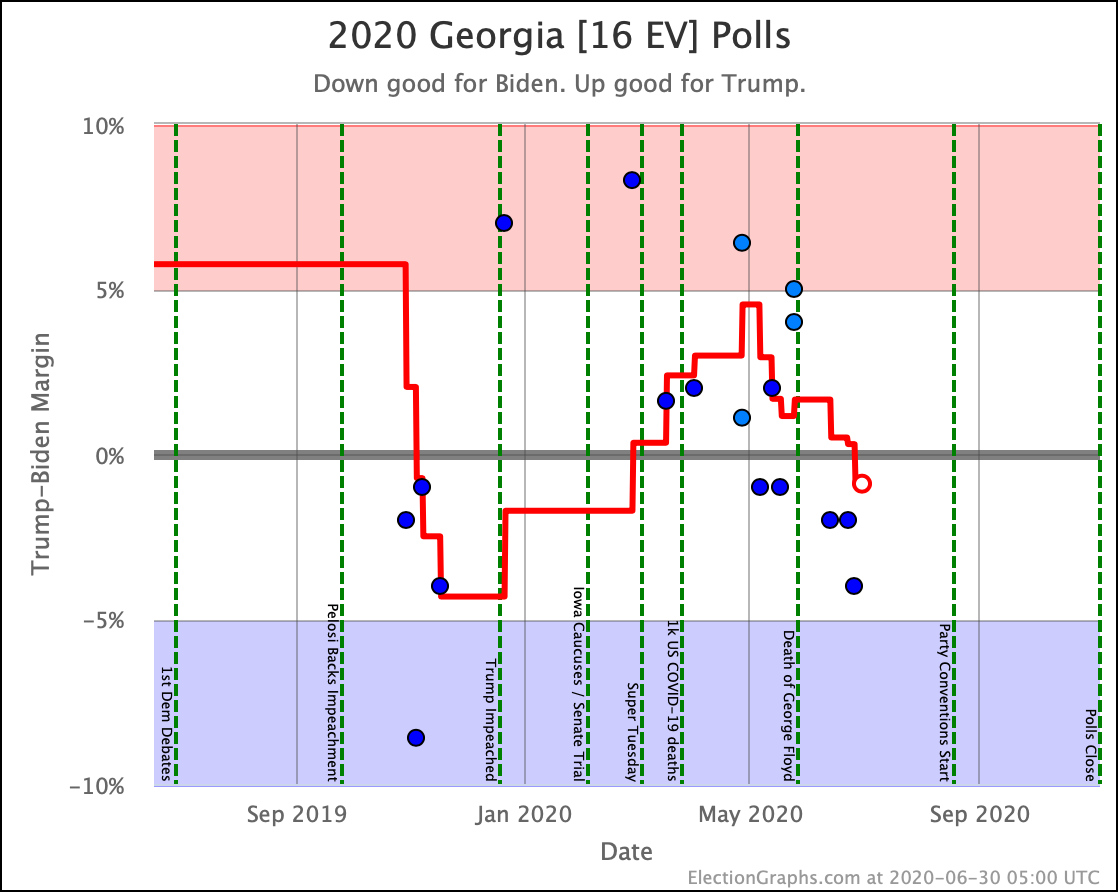
Pollsters have not paid as much attention to Georgia as I would like. But there have been a bunch of polls in the last few weeks and they show a competitive state, which is a significant change from the historical average.
The poll average now shows Biden and Sanders ahead, with Warren, Harris, and Buttigieg all bringing Trump's lead under 5%.
(O'Rourke has never been polled in Georgia, and now that he has dropped out, probably will never be. Sniff.)
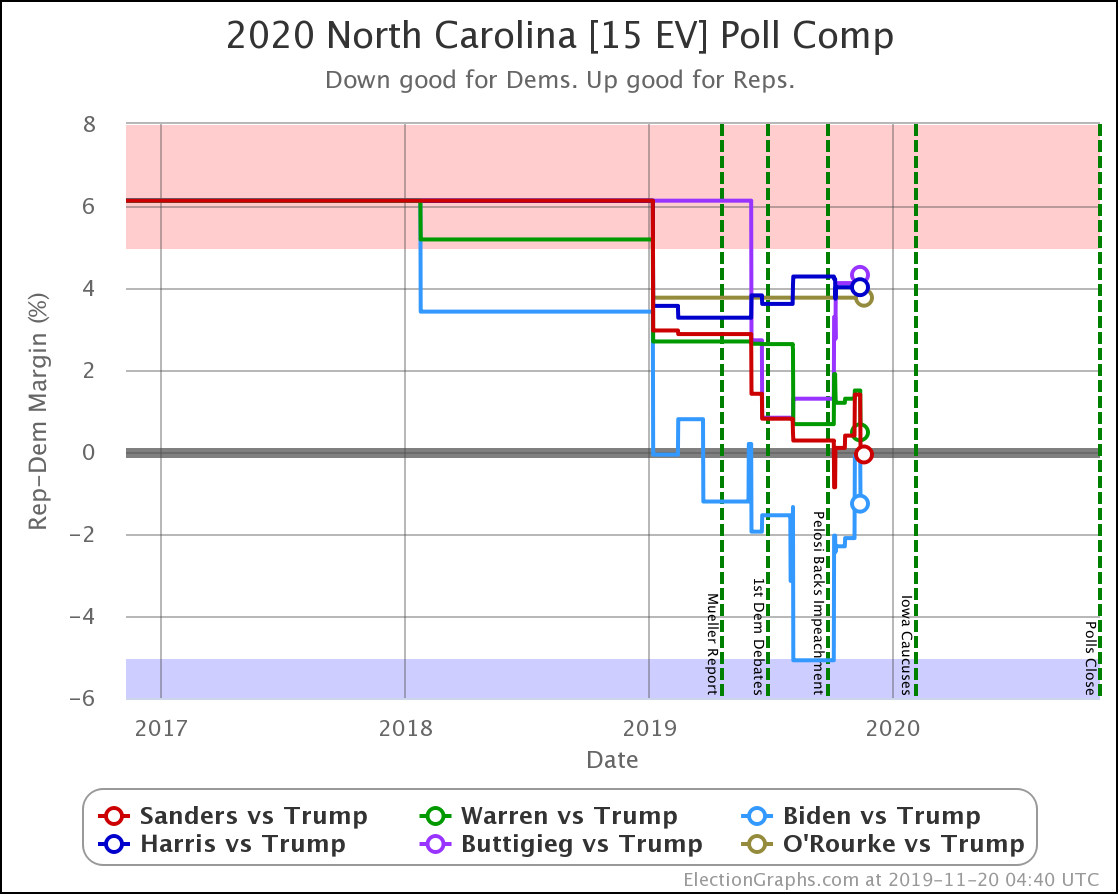
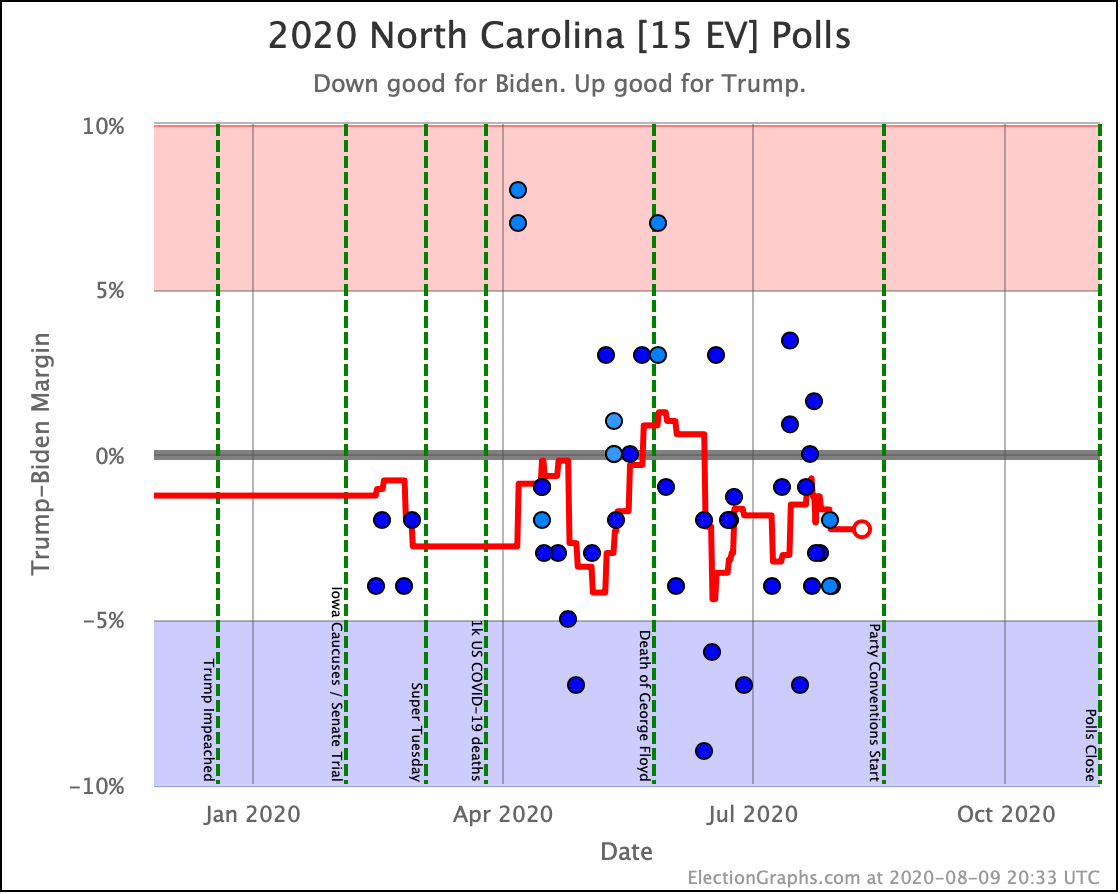
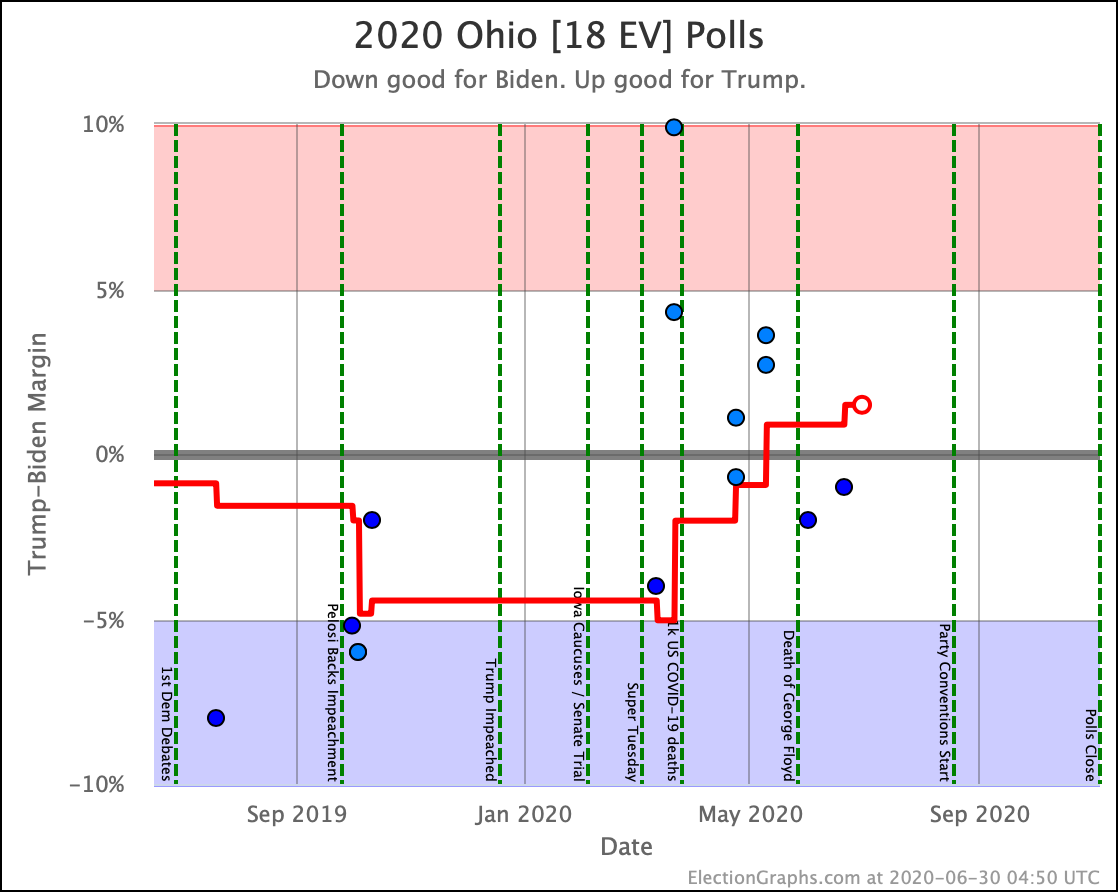
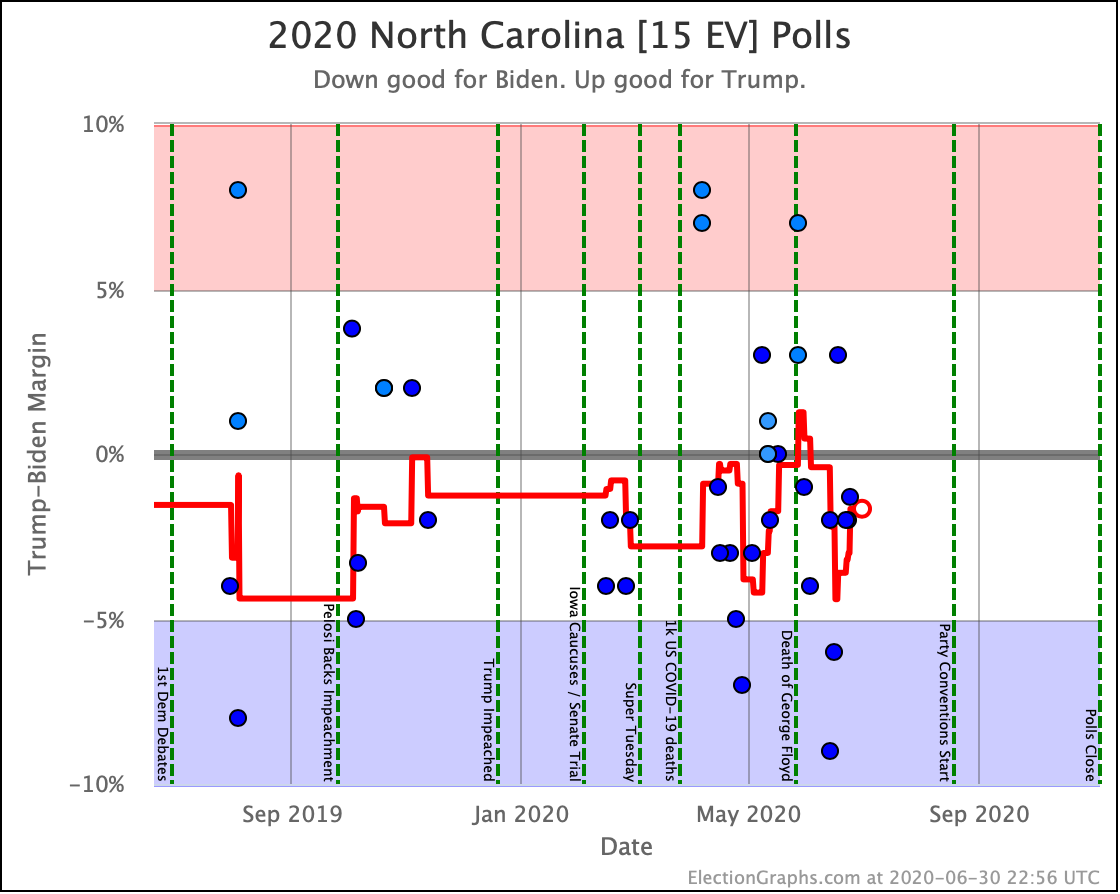
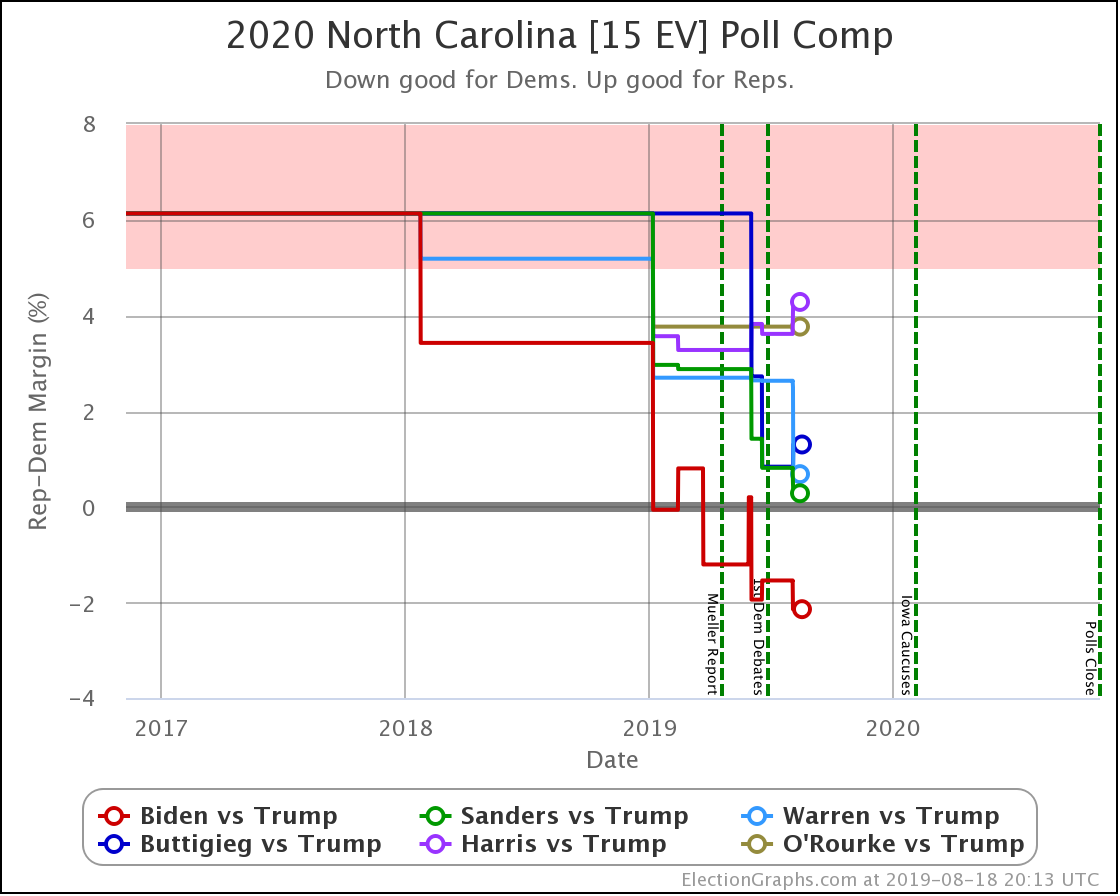
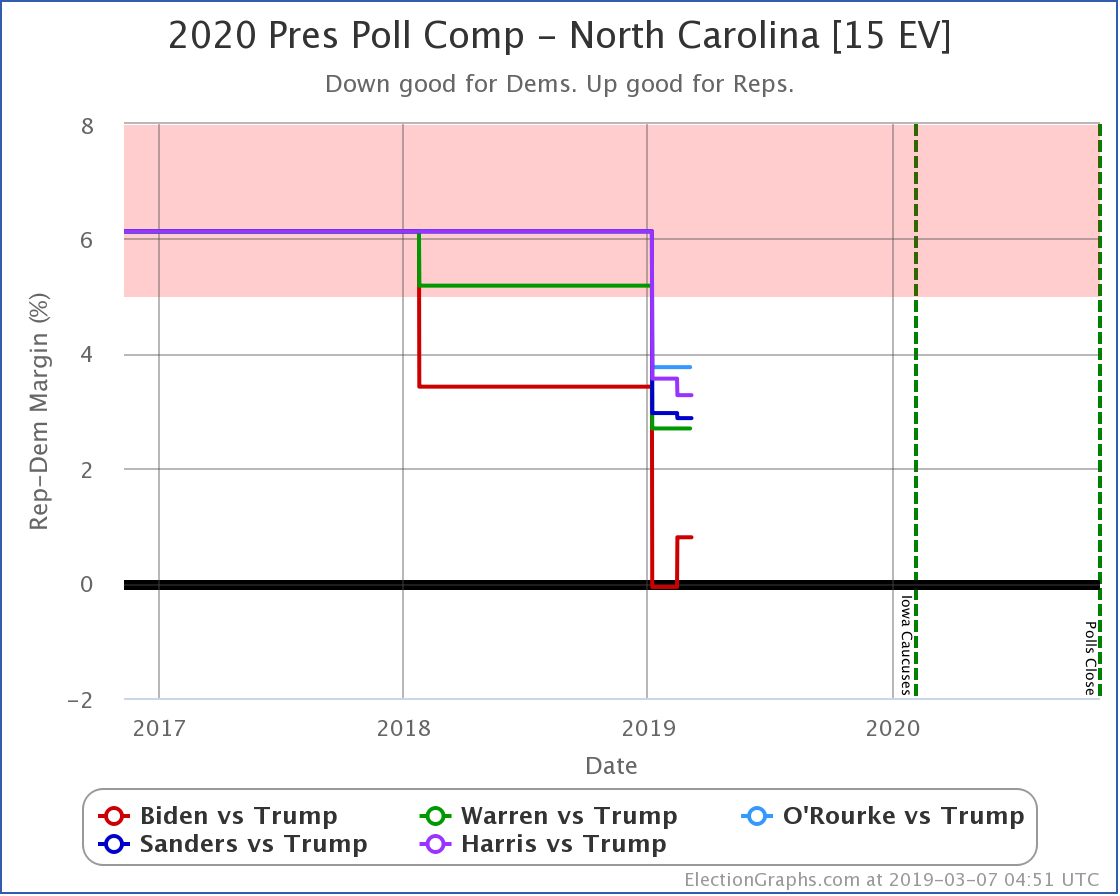
Although Biden has reversed a bit recently, overall Sanders, Warren, and Biden are making North Carolina a narrowly fought battleground.
Harris and Buttigieg, while they are still keeping Trump's lead under 5%, do not seem to be gaining any additional ground lately.
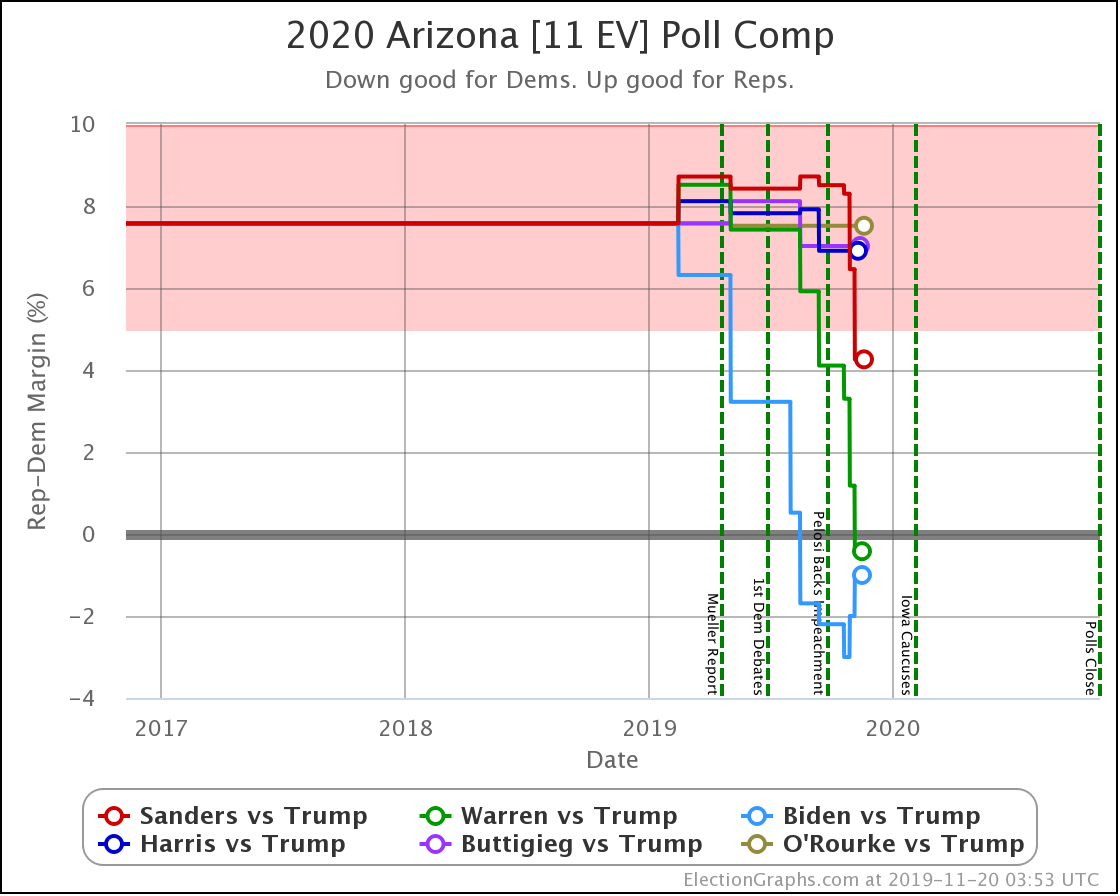
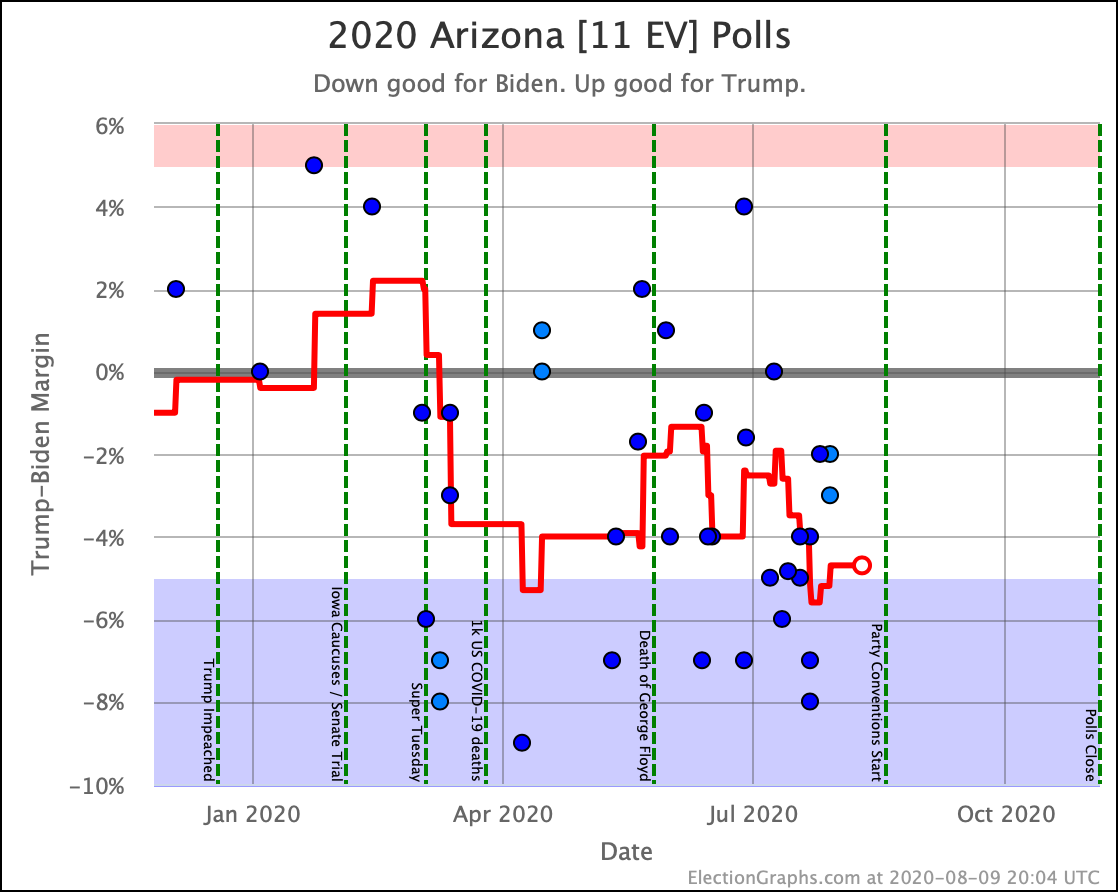
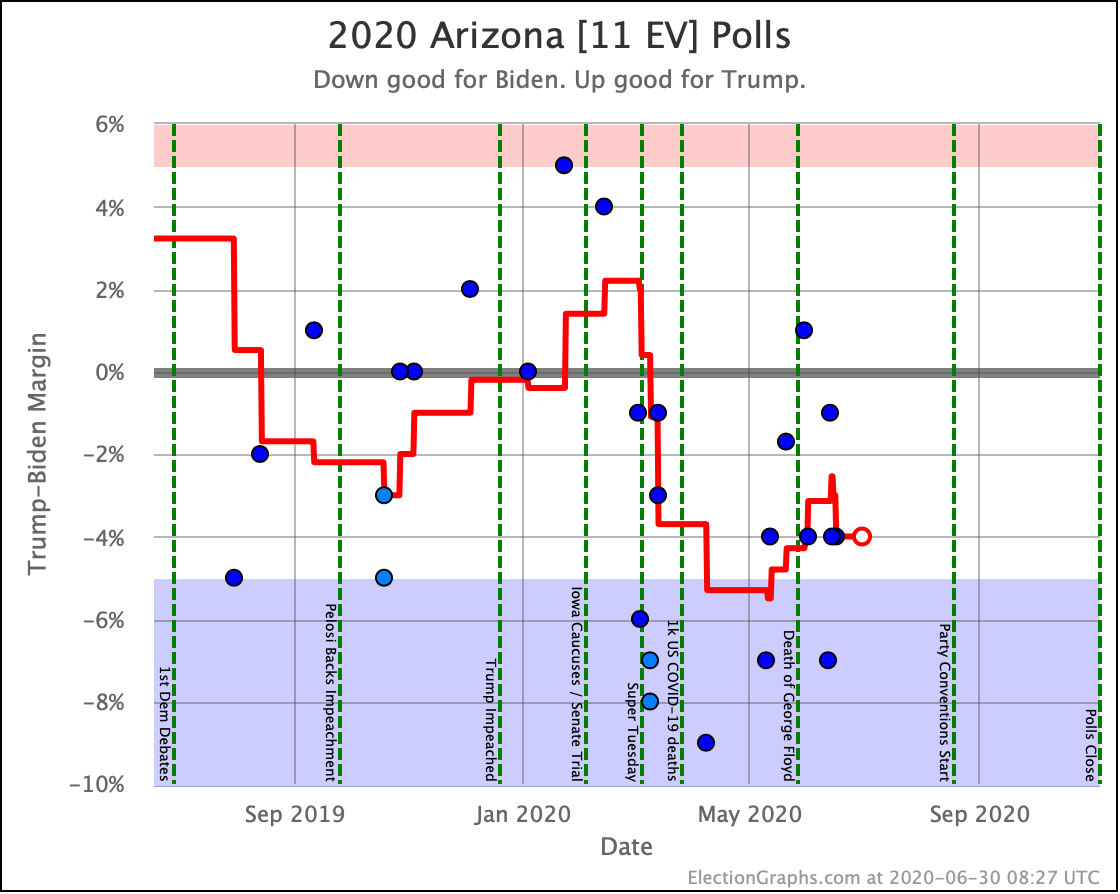
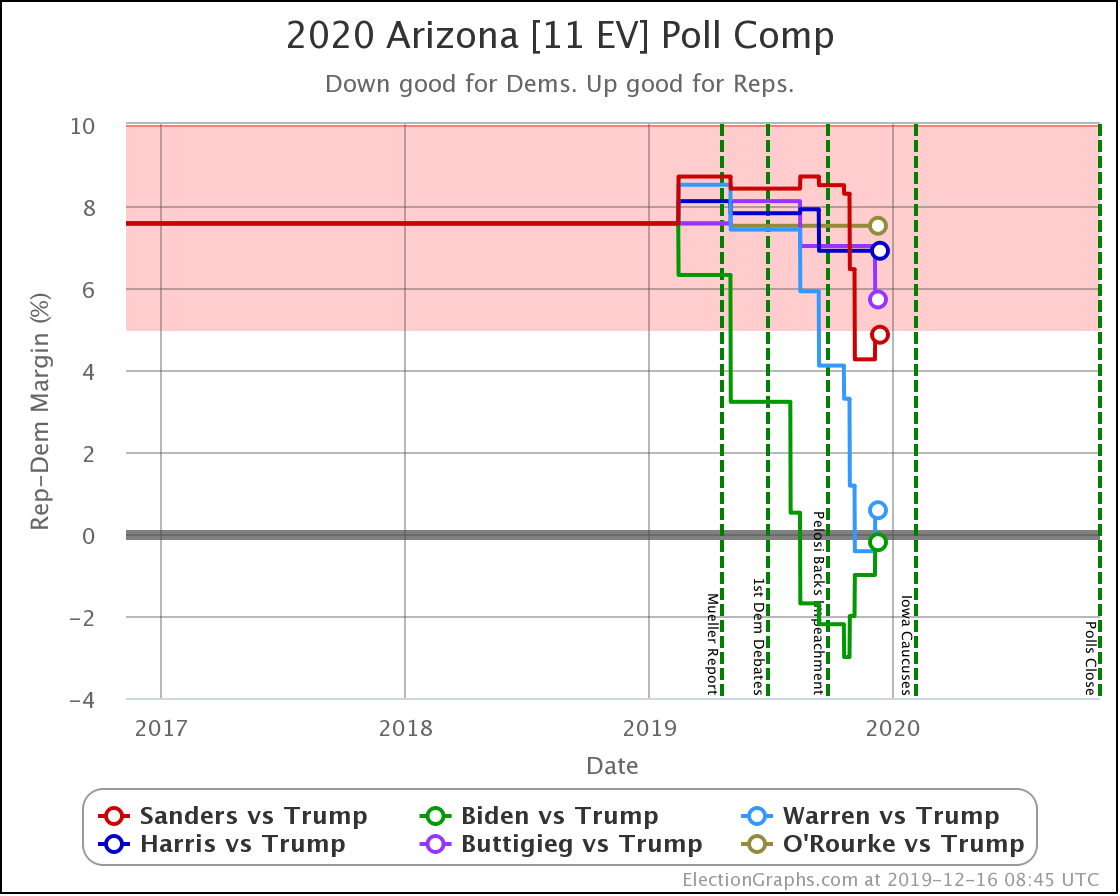
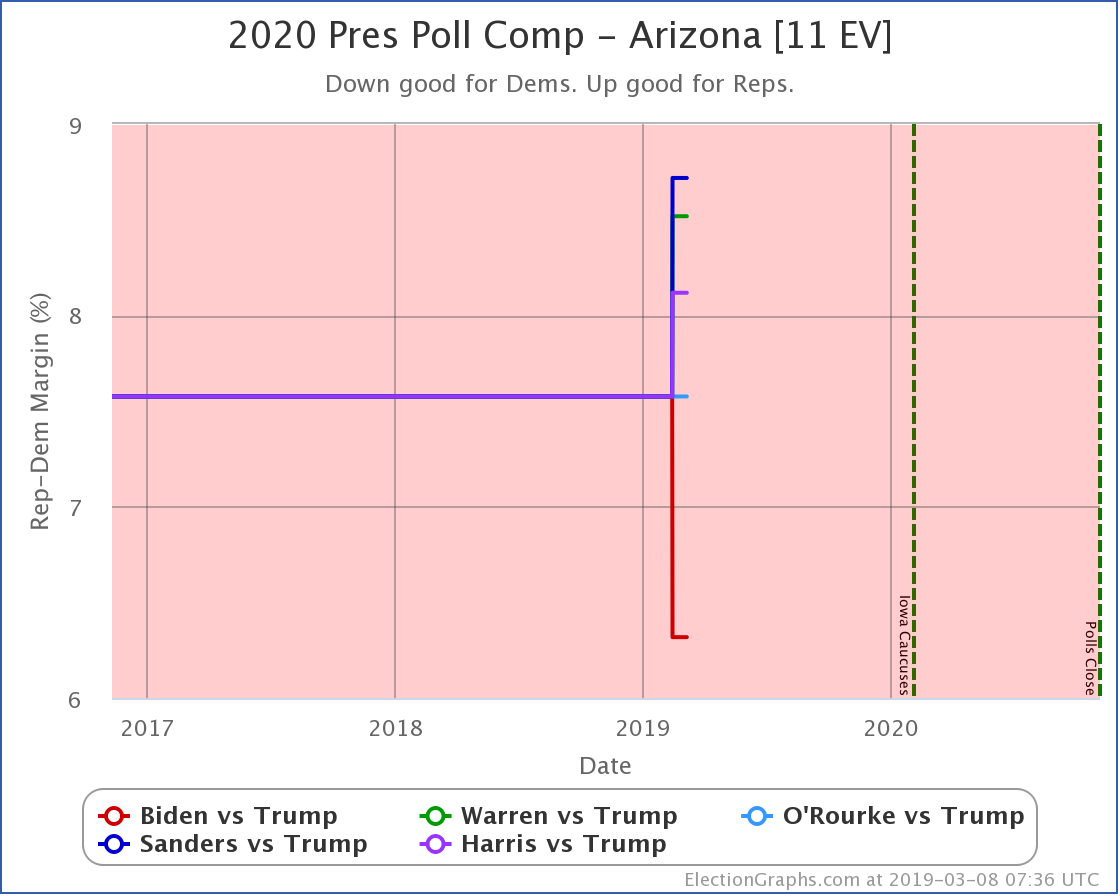
Arizona has also been moving toward the Democrats. At least for Sanders, Warren, and Biden. Warren and Biden actually are slightly leading. Sanders brings Trump's lead under 5%.
Harris and Buttigieg, on the other hand, are not making things much closer than the historical 7.6% average Republican margin in the state. Just as in North Carolina, they lag behind the stronger Democrats.
So Trump is gaining in Texas, Pennsylvania, Michigan, and Wisconsin.
But the Democrats are gaining in Georgia, North Carolina, and Arizona.
As we get closer, things will heat up; there will be lots more polls and more movement.
Are we having fun yet?
349.7 days until polls start to close on election night.
For more information:
This post is an update based on the data on the Election Graphs Electoral College 2020 page. Election Graphs tracks a poll-based estimate of the Electoral College. The charts, graphs, and maps in the post above are all as of the time of this post. Click through on any image to go to a page with the current interactive versions of that chart, along with additional details.
Follow @ElectionGraphs on Twitter or Election Graphs on Facebook to see announcements of updates. For those interested in individual poll updates, follow @ElecCollPolls on Twitter for all the polls as I add them. If you find the information in these posts informative or useful, please consider visiting the donation page.